【SpringCloud技术专题】「Hystrix」(3)Command运作的原理和源码分析
# [每日一句] > **也许你度过了很糟糕的一天,但这并不代表你会因此度过糟糕的一生。** ### 构建一个Hystrix的Command模式 这里我们需要关注三点: - (模板构造器)**HystrixCommand构造函数当中的super** - (真正的执行者)**HystrixCommand定义的run,run其实就是真正执行命令的地方** - (触发启动)**new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("test").execute()中execute是发起执行的过程** ### 实现Demo ```java public class HelloWorldHystrixCommand extends HystrixCommand { private final String name; public HelloWorldHystrixCommand(String name) { super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup")); this.name = name; } @Override protected String run() throws Exception { //Thread.sleep(100); return "hello"+name; } } public static void main(String[] args){ String result = new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("test").execute(); System.out.println(result); } ``` ### HystrixCommand初始化过程 > **HystrixCommand的类关系图下,这里我们只需要暂时关注HystrixCommand继承自AbstractCommand即可,其他的我也没仔细看**。 #### HystrixCommand类依赖图 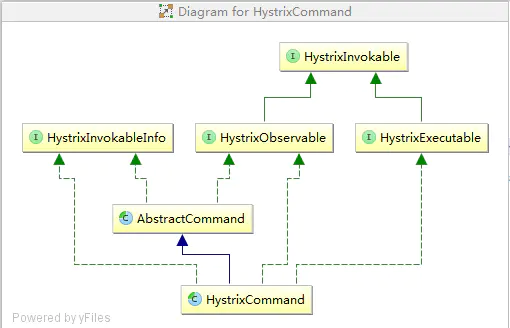 ##### HelloWorldHystrixCommand的构造步骤如下: 1. **具体类HelloWorldHystrixCommand继承自HystrixCommand, 通过super()调用了HystrixCommand的构造函数** 2. **HystrixCommand通过super()命令调用AbstractCommand实现初始化** #### AbstractCommand类当中比较核心的几个对象如下: - metrics:统计指标 - circuitBreaker:熔断器变量 - threadPool:隔离的线程池 - concurrencyStrategy :并发策略 ```java protected HystrixCommand(HystrixCommandGroupKey group) { super(group, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null); } protected AbstractCommand(HystrixCommandGroupKey group, HystrixCommandKey key, HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixCircuitBreaker circuitBreaker, HystrixThreadPool threadPool,HystrixCommandProperties.Setter commandPropertiesDefaults, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter threadPoolPropertiesDefaults, HystrixCommandMetrics metrics, TryableSemaphore fallbackSemaphore, TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore, HystrixPropertiesStrategy propertiesStrategy, HystrixCommandExecutionHook executionHook) { this.commandGroup = initGroupKey(group); this.commandKey = initCommandKey(key, getClass()); this.properties = initCommandProperties(this.commandKey, propertiesStrategy, commandPropertiesDefaults); this.threadPoolKey = initThreadPoolKey(threadPoolKey, this.commandGroup, this.properties.executionIsolationThreadPoolKeyOverride().get()); this.metrics = initMetrics(metrics, this.commandGroup, this.threadPoolKey, this.commandKey, this.properties); this.circuitBreaker = initCircuitBreaker(this.properties.circuitBreakerEnabled().get(), circuitBreaker, this.commandGroup, this.commandKey, this.properties, this.metrics); // 线程池相关配置,通过线程池进行隔离 this.threadPool = initThreadPool(threadPool, this.threadPoolKey, threadPoolPropertiesDefaults); //Strategies from plugins this.eventNotifier = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getEventNotifier(); this.concurrencyStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getConcurrencyStrategy(); HystrixMetricsPublisherFactory.createOrRetrievePublisherForCommand(this.commandKey, this.commandGroup, this.metrics, this.circuitBreaker, this.properties); this.executionHook = initExecutionHook(executionHook); this.requestCache = HystrixRequestCache.getInstance(this.commandKey, this.concurrencyStrategy); this.currentRequestLog = initRequestLog(this.properties.requestLogEnabled().get(), this.concurrencyStrategy); /* fallback semaphore override if applicable */ this.fallbackSemaphoreOverride = fallbackSemaphore; /* execution semaphore override if applicable */ this.executionSemaphoreOverride = executionSemaphore; } ``` ### Hystrix的执行 > **从Hystrix的整个执行的生命周期来看**,**可以分为两个阶段,阶段一主要是Observable的创建,阶段二主要是Observable的执行**。 - **两个过程的实际实现中运用了大量的RxJava的技能包,所以阅读起来有一点绕,我只能按照我粗浅的理解来尽量把整个过程讲解清楚。** - **切入详细的过程当中,大家需要带有两个疑问去看代码,只有找到能解答这两个疑问的代码才算看懂了主流程,两个疑问分别是:(1)如何分配执行线程;(2)如何判定超时。** #### Hystrix的Observable创建过程 Hystrix的创建过程比较复杂,大致核心流程如下: 1. **类HystrixCommand中execute方法开始执行,内部的queue()是实际执行整个过程,get()是获取执行的结果。** 2. **类HystrixCommand中queue方法,delegate = toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture(),toObservable负责创建Observable对象,toFuture负责执行任务(Future)。** 3. **类AbstractCommand中toObservable方法,hystrixObservable = `Observable.defer(applyHystrixSemantics)`负责关联applyHystrixSemantics。** 4. **类AbstractCommand中applyHystrixSemantics方法,executeCommandAndObserve(cmd)负责执行具体的AbstractCommand采用相关的Observable进行关联绑定。** 5. **类AbstractCommand中executeCommandAndObserve方法中,`executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(cmd).lift(new HystrixObservableTimeoutOperator (_cmd))`负责关联执行_cmd并关联超时检测任务。** 6. **类AbstractCommand中executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation是执行的具体的命令,【HystrixObservableTimeoutOperator是超时检测任务】。** 7. **类AbstractCommand中executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation方法中,getUserExecutionObservable负责执行具体任务,同时通过`subscribeOn(threadPool.getScheduler(new Func0 ()))`关联threadPool隔离执行任务,关键的隔离任务的位置。** 8. **类HystrixCommand中getUserExecutionObservable方法中,`Observable.just(run())`负责执行任务,这个run方法就是HelloWorldHystrixCommand的run方法,也就是这里终于回调回了真正的run函数。** #### execute执行方法 ```java public R execute() { try { return queue().get(); } catch (Exception e) { throw Exceptions.sneakyThrow(decomposeException(e)); } } ``` #### 获取Observable获取相关的Future ```java public Future queue() { //todo ((Observable )that).single().subscribe(new Subscriber () //todo BlockingOperatorToFuture.toFuture里面真正执行任务 //todo toObservable内部是通过RxJava构建 final Future delegate = toObservable().toBlocking().toFuture(); final Future f = new Future () { @Override public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { if (delegate.isCancelled()) { return false; } if (HystrixCommand.this.getProperties().executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnFutureCancel().get()) { interruptOnFutureCancel.compareAndSet(false, mayInterruptIfRunning); } final boolean res = delegate.cancel(interruptOnFutureCancel.get()); if (!isExecutionComplete() && interruptOnFutureCancel.get()) { final Thread t = executionThread.get(); if (t != null && !t.equals(Thread.currentThread())) { t.interrupt(); } } return res; } @Override public boolean isCancelled() { return delegate.isCancelled(); } @Override public boolean isDone() { return delegate.isDone(); } @Override public R get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { return delegate.get(); } @Override public R get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { return delegate.get(timeout, unit); } }; if (f.isDone()) { try { f.get(); return f; } catch (Exception e) { Throwable t = decomposeException(e); if (t instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) { return f; } else if (t instanceof HystrixRuntimeException) { HystrixRuntimeException hre = (HystrixRuntimeException) t; switch (hre.getFailureType()) { case COMMAND_EXCEPTION: case TIMEOUT: return f; default: throw hre; } } else { throw Exceptions.sneakyThrow(t); } } } return f; } public Observable toObservable() { final AbstractCommand _cmd = this; final Action0 terminateCommandCleanup = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.TERMINAL)) { handleCommandEnd(false); //user code never ran } else if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED, CommandState.TERMINAL)) { handleCommandEnd(true); //user code did run } } }; final Action0 unsubscribeCommandCleanup = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { circuitBreaker.markNonSuccess(); if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) { if (!_cmd.executionResult.containsTerminalEvent()) { _cmd.eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.CANCELLED, _cmd.commandKey); try { executionHook.onUnsubscribe(_cmd); } catch (Throwable hookEx) { logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onUnsubscribe", hookEx); } _cmd.executionResultAtTimeOfCancellation = _cmd.executionResult .addEvent((int) (System.currentTimeMillis() - _cmd.commandStartTimestamp), HystrixEventType.CANCELLED); } handleCommandEnd(false); //user code never ran } else if (_cmd.commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED, CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) { if (!_cmd.executionResult.containsTerminalEvent()) { _cmd.eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.CANCELLED, _cmd.commandKey); try { executionHook.onUnsubscribe(_cmd); } catch (Throwable hookEx) { logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onUnsubscribe", hookEx); } _cmd.executionResultAtTimeOfCancellation = _cmd.executionResult .addEvent((int) (System.currentTimeMillis() - _cmd.commandStartTimestamp), HystrixEventType.CANCELLED); } handleCommandEnd(true); //user code did run } } }; final Func0 > applyHystrixSemantics = new Func0 >() { @Override public Observable call() { if (commandState.get().equals(CommandState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) { return Observable.never(); } return applyHystrixSemantics(_cmd); } }; final Func1 wrapWithAllOnNextHooks = new Func1 () { @Override public R call(R r) { R afterFirstApplication = r; try { afterFirstApplication = executionHook.onComplete(_cmd, r); } catch (Throwable hookEx) { logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onComplete", hookEx); } try { return executionHook.onEmit(_cmd, afterFirstApplication); } catch (Throwable hookEx) { logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onEmit", hookEx); return afterFirstApplication; } } }; final Action0 fireOnCompletedHook = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { try { executionHook.onSuccess(_cmd); } catch (Throwable hookEx) { logger.warn("Error calling HystrixCommandExecutionHook.onSuccess", hookEx); } } }; //defer在subscribe的时候会真正执行 return Observable.defer(new Func0 >() { @Override public Observable call() { /* this is a stateful object so can only be used once */ if (!commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.NOT_STARTED, CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED)) { IllegalStateException ex = new IllegalStateException(""); //TODO make a new error type for this throw new HystrixRuntimeException(FailureType.BAD_REQUEST_EXCEPTION, _cmd.getClass(), getLogMessagePrefix() + " ", ex, null); } commandStartTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (properties.requestLogEnabled().get()) { if (currentRequestLog != null) { currentRequestLog.addExecutedCommand(_cmd); } } final boolean requestCacheEnabled = isRequestCachingEnabled(); final String cacheKey = getCacheKey(); /* try from cache first */ if (requestCacheEnabled) { HystrixCommandResponseFromCache fromCache = (HystrixCommandResponseFromCache ) requestCache.get(cacheKey); if (fromCache != null) { isResponseFromCache = true; return handleRequestCacheHitAndEmitValues(fromCache, _cmd); } } // todo 这里应该在会去执行applyHystrixSemantics方法 Observable hystrixObservable = Observable.defer(applyHystrixSemantics) .map(wrapWithAllOnNextHooks); Observable afterCache; // put in cache if (requestCacheEnabled && cacheKey != null) { // wrap it for caching HystrixCachedObservable toCache = HystrixCachedObservable.from(hystrixObservable, _cmd); HystrixCommandResponseFromCache fromCache = (HystrixCommandResponseFromCache ) requestCache.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, toCache); if (fromCache != null) { // another thread beat us so we'll use the cached value instead toCache.unsubscribe(); isResponseFromCache = true; return handleRequestCacheHitAndEmitValues(fromCache, _cmd); } else { // we just created an ObservableCommand so we cast and return it afterCache = toCache.toObservable(); } } else { afterCache = hystrixObservable; } //todo 关联逻辑 return afterCache .doOnTerminate(terminateCommandCleanup) .doOnUnsubscribe(unsubscribeCommandCleanup) .doOnCompleted(fireOnCompletedHook); } }); } // TODO: 2018/7/9 真正执行代码的地方在这里 private Observable applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand _cmd) { executionHook.onStart(_cmd); if (circuitBreaker.attemptExecution()) { final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore(); final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false); final Action0 singleSemaphoreRelease = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (semaphoreHasBeenReleased.compareAndSet(false, true)) { executionSemaphore.release(); } } }; final Action1 markExceptionThrown = new Action1 () { @Override public void call(Throwable t) { eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.EXCEPTION_THROWN, commandKey); } }; if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire()) { try { executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); // TODO: 2018/7/9 executeCommandAndObserve执行任务的地方 return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd) .doOnError(markExceptionThrown) .doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease) .doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease); } catch (RuntimeException e) { return Observable.error(e); } } else { return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback(); } } else { return handleShortCircuitViaFallback(); } } private Observable executeCommandAndObserve(final AbstractCommand _cmd) { final HystrixRequestContext currentRequestContext = HystrixRequestContext.getContextForCurrentThread(); final Action1 markEmits = new Action1 () { @Override public void call(R r) { if (shouldOutputOnNextEvents()) { executionResult = executionResult.addEvent(HystrixEventType.EMIT); eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.EMIT, commandKey); } if (commandIsScalar()) { long latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - executionResult.getStartTimestamp(); eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.SUCCESS, commandKey); executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, HystrixEventType.SUCCESS); eventNotifier.markCommandExecution(getCommandKey(), properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get(), (int) latency, executionResult.getOrderedList()); circuitBreaker.markSuccess(); } } }; final Action0 markOnCompleted = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (!commandIsScalar()) { long latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - executionResult.getStartTimestamp(); eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.SUCCESS, commandKey); executionResult = executionResult.addEvent((int) latency, HystrixEventType.SUCCESS); eventNotifier.markCommandExecution(getCommandKey(), properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get(), (int) latency, executionResult.getOrderedList()); circuitBreaker.markSuccess(); } } }; final Func1 > handleFallback = new Func1 >() { @Override public Observable call(Throwable t) { circuitBreaker.markNonSuccess(); Exception e = getExceptionFromThrowable(t); executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionException(e); if (e instanceof RejectedExecutionException) { return handleThreadPoolRejectionViaFallback(e); } else if (t instanceof HystrixTimeoutException) { return handleTimeoutViaFallback(); } else if (t instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) { return handleBadRequestByEmittingError(e); } else { /* * Treat HystrixBadRequestException from ExecutionHook like a plain HystrixBadRequestException. */ if (e instanceof HystrixBadRequestException) { eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.BAD_REQUEST, commandKey); return Observable.error(e); } return handleFailureViaFallback(e); } } }; final Action1 > setRequestContext = new Action1 >() { @Override public void call(Notification rNotification) { setRequestContextIfNeeded(currentRequestContext); } }; //todo 这里是否执行超时动作,executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation这个函数非常重要 Observable execution; if (properties.executionTimeoutEnabled().get()) { execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd) .lift(new HystrixObservableTimeoutOperator (_cmd)); //todo HystrixObservableTimeoutOperator负责执行超时动作 } else { execution = executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(_cmd); } return execution.doOnNext(markEmits) .doOnCompleted(markOnCompleted) .onErrorResumeNext(handleFallback) .doOnEach(setRequestContext); } private Observable executeCommandWithSpecifiedIsolation(final AbstractCommand _cmd) { if (properties.executionIsolationStrategy().get() == ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD) { return Observable.defer(new Func0 >() { @Override public Observable call() { executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionOccurred(); if (!commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED)) { return Observable.error(new IllegalStateException( "execution attempted while in state : " + commandState.get().name())); } metrics.markCommandStart(commandKey, threadPoolKey, ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD); if (isCommandTimedOut.get() == TimedOutStatus.TIMED_OUT) { // the command timed out in the wrapping thread so we will return immediately // and not increment any of the counters below or other such logic return Observable.error(new RuntimeException("timed out before executing run()")); } if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.STARTED)) { //we have not been unsubscribed, so should proceed HystrixCounters.incrementGlobalConcurrentThreads(); threadPool.markThreadExecution(); // store the command that is being run endCurrentThreadExecutingCommand = Hystrix.startCurrentThreadExecutingCommand(getCommandKey()); executionResult = executionResult.setExecutedInThread(); try { //todo 估计是前置依赖吧 executionHook.onThreadStart(_cmd); executionHook.onRunStart(_cmd); executionHook.onExecutionStart(_cmd); //todo 真正执行的地方 return getUserExecutionObservable(_cmd); } catch (Throwable ex) { return Observable.error(ex); } } else { //command has already been unsubscribed, so return immediately return Observable.empty(); } } }).doOnTerminate(new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.STARTED, ThreadState.TERMINAL)) { handleThreadEnd(_cmd); } if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.TERMINAL)) { } } }).doOnUnsubscribe(new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.STARTED, ThreadState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) { handleThreadEnd(_cmd); } if (threadState.compareAndSet(ThreadState.NOT_USING_THREAD, ThreadState.UNSUBSCRIBED)) { //if it was never started and was cancelled, then no need to clean up } //if it was terminal, then other cleanup handled it } }).subscribeOn(threadPool.getScheduler(new Func0 () { //todo subscribeOn 据说获取线程的地方???? @Override public Boolean call() { return properties.executionIsolationThreadInterruptOnTimeout().get() && _cmd.isCommandTimedOut.get() == TimedOutStatus.TIMED_OUT; } })); } else { return Observable.defer(new Func0 >() { @Override public Observable call() { executionResult = executionResult.setExecutionOccurred(); if (!commandState.compareAndSet(CommandState.OBSERVABLE_CHAIN_CREATED, CommandState.USER_CODE_EXECUTED)) { return Observable.error(new IllegalStateException( "execution attempted while in state : " + commandState.get().name())); } metrics.markCommandStart(commandKey, threadPoolKey, ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE); // semaphore isolated // store the command that is being run endCurrentThreadExecutingCommand = Hystrix.startCurrentThreadExecutingCommand(getCommandKey()); try { executionHook.onRunStart(_cmd); executionHook.onExecutionStart(_cmd); return getUserExecutionObservable(_cmd); } catch (Throwable ex) { return Observable.error(ex); } } }); } } private Observable getUserExecutionObservable(final AbstractCommand _cmd) { Observable userObservable; try { userObservable = getExecutionObservable(); } catch (Throwable ex) { // the run() method is a user provided implementation so can throw instead of using Observable.onError // so we catch it here and turn it into Observable.error userObservable = Observable.error(ex); } return userObservable .lift(new ExecutionHookApplication(_cmd)) .lift(new DeprecatedOnRunHookApplication(_cmd)); } // 真正执行run的位置 final protected Observable getExecutionObservable() { return Observable.defer(new Func0 >() { @Override public Observable call() { try { return Observable.just(run()); } catch (Throwable ex) { return Observable.error(ex); } } }).doOnSubscribe(new Action0() { @Override public void call() { // Save thread on which we get subscribed so that we can interrupt it later if needed executionThread.set(Thread.currentThread()); } }); } ``` ### Hystrix的执行过程 > toFuture过程中真正触发构建的Observable的的代码在((Observable )that).single().subscribe()当中,关注几个方法: onCompleted负责设置完成标记。 onNext负责设置结果。 ```java public static Future toFuture(Observable that) { final CountDownLatch finished = new CountDownLatch(1); final AtomicReference value = new AtomicReference (); final AtomicReference error = new AtomicReference (); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final Subscription s = ((Observable )that).single().subscribe(new Subscriber (){ @Override public void onCompleted() { finished.countDown(); } @Override public void onError(Throwable e) { error.compareAndSet(null, e); finished.countDown(); } @Override public void onNext(T v) { // "single" guarantees there is only one "onNext" value.set(v); } }); return new Future () { private volatile boolean cancelled; @Override public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { if (finished.getCount() > 0) { cancelled = true; s.unsubscribe(); // release the latch (a race condition may have already released it by now) finished.countDown(); return true; } else { // can't cancel return false; } } @Override public boolean isCancelled() { return cancelled; } @Override public boolean isDone() { return finished.getCount() == 0; } @Override public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { finished.await(); return getValue(); } @Override public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { if (finished.await(timeout, unit)) { return getValue(); } else { throw new TimeoutException("Timed out after " + unit.toMillis(timeout) + "ms waiting for underlying Observable."); } } private T getValue() throws ExecutionException { final Throwable throwable = error.get(); if (throwable != null) { throw new ExecutionException("Observable onError", throwable); } else if (cancelled) { // Contract of Future.get() requires us to throw this: throw new CancellationException("Subscription unsubscribed"); } else { return value.get(); } } }; } ```