有些数据,天生就不愿意被"默认实现"管束。顶栏的用户信息、一次性的弹窗数据、需要把包体掐到克的查询......这些场景里,你会更希望自己说了算:字段要精、时机要准、交互要顺。
这篇把思路捋直:从 mask、表格/表单、字段 三类常见场景切入,串起 手写 GraphQL / 平台 API / 继承基类 三种打法。代码沿用原文,不做改动;只把脉络、取舍与价值点摆到台面上,便于你复用、扩展、和团队对齐。
读者画像 & 前置
- 使用 Oinone 前端(Vue + TS)进行二开、组件自定义的同学。
- 了解
@kunlun/dependencies 基本能力与平台默认页面的取数机制。
一套心法:何时选哪种打法?
| 任务 / 诉求 | 更适合的打法 | 关键价值
| 一次性、与业务模型无关、字段极少 (如顶栏用户信息) | 手写 GraphQL | 精准控制字段与包体;生命周期简单;请求可读 | | 同一模型、可复用查询能力 (分页/筛选/字段控制) | 平台 API:customQuery* / queryOne / constructOne | 语义清晰、少坑位;统一方法名约定,方便后端协作 | | 平台已有完整基类能力 (下拉、分页、级联、联动) | 继承基类 | 代码更少、能力更全;维护成本小,升级不焦虑 |
简单记:可一次则写、可复用则 API、可借力就继承。
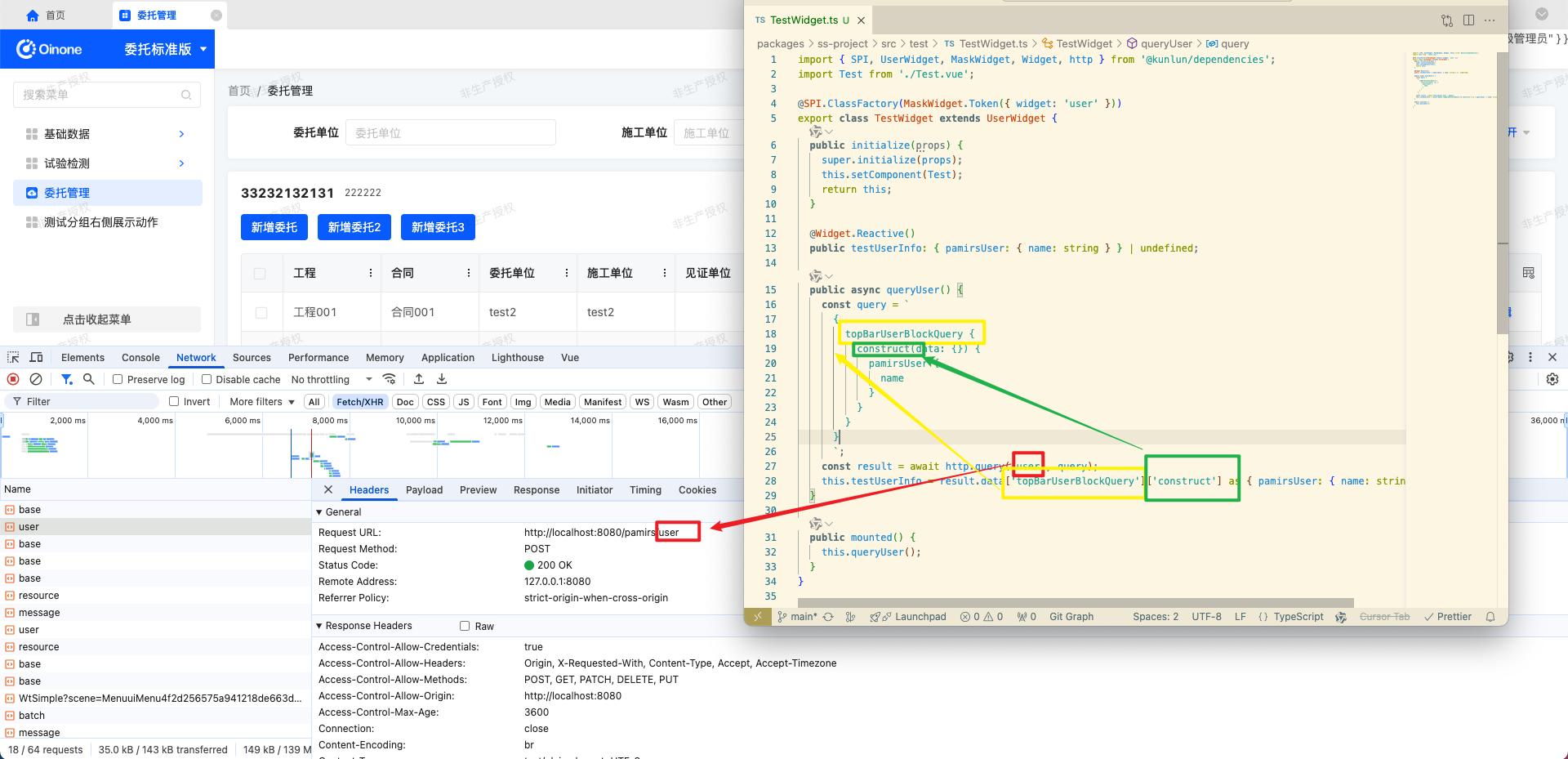
- 自定义 mask:一次请求,轻装上阵
mask 通常跨页展示、与模型解耦、只请求一次。此类场景更像"拿一张名片":字段要准、包体要小。选手写 GraphQL,更直觉也更省事。
操作路径
- 继承平台用户组件(
UserWidget),在 mounted 时发起查询。
- 打开默认页面抓一份等效的 GraphQL,按需精简字段。
http.query('user', gql),拿到 result.data 后写入响应式变量。
价值点
- 字节级瘦身 :只取
name 等必需字段,首屏更轻。
- 生命周期可控 :
mounted 一次拉取,组件级缓存即可。
- 改动半径小:与业务模型零耦合。
示例截图
![]()
![]() 示例代码(TS)
示例代码(TS)
import { SPI, UserWidget, MaskWidget, Widget, http } from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(MaskWidget.Token({ widget: 'user' }))
export class TestWidget extends UserWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
// 添加响应式注解,这样能在 vue 中接受到 ts 中的变量
@Widget.Reactive()
public testUserInfo: { pamirsUser: { name: string } } | undefined;
public async queryUser() {
const query = `
{
topBarUserBlockQuery {
construct(data: {}) {
pamirsUser {
name
}
}
}
}
`;
const result = await http.query('user', query);
this.testUserInfo = result.data['topBarUserBlockQuery']['construct'] as { pamirsUser: { name: string } };
}
public mounted() {
this.queryUser();
}
}
示例代码(VUE)
<template>
<div class="Test">
{{ testUserInfo }}
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'Test',
props: ['testUserInfo']
});
</script>
- 自定义表格 / 表单:两条路,按需拿 =====================
平台的默认实现已经把取数、回填这条路铺好了。你可以"顺着路走",也可以"自己抄近道"。
2-1 表格(Table)
2-1-1 继承即用:自动获取数据
继承 TableWidget,在 vue 侧以 props 接 dataSource 即可。生成的默认页面天然"通电",表格会自动回填。 示例代码(TS)
import { BaseElementWidget, SPI, TABLE_WIDGET, TableWidget, ViewType } from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
BaseElementWidget.Token({
viewType: ViewType.Table,
widget: ['table', TABLE_WIDGET]
})
)
export class TestWidget extends TableWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
}
示例代码(VUE)
<template>
<div class="Test">
{{ dataSource }}
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'Test',
props: ['dataSource']
});
</script>
价值点:最省心。默认分页、查询条件、回填全打包好了。
效果图: ![]()
2-1-2 重写 fetchData:自定义请求
当你要改查询逻辑/拼装条件/收敛返回字段 ,重写 fetchData 更合适。用 customQueryPage,把分页、条件、请求/返回字段一次说清楚。
this.generatorPagination()、this.generatorCondition() 提供现成分页与条件拼装。this.rootRuntimeContext.getRequestFields() 精准控制字段,性能更稳。
示例代码(TS)
import {
ActiveRecord,
BaseElementWidget,
Condition,
customQueryPage,
SPI,
TABLE_WIDGET,
TableWidget,
ViewType
} from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
BaseElementWidget.Token({
viewType: ViewType.Table,
widget: ['table', TABLE_WIDGET]
})
)
export class TestWidget extends TableWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
/**
* 获取数据
*/
public async fetchData(condition?: Condition): Promise<ActiveRecord[]> {
// load 方法会激活 spin 转圈组件
return await this.load(async () => {
const pagination = this.generatorPagination();
// 生成表格的查询条件,会把搜索里的条件拼上
// const finalCondition = this.generatorCondition(condition);
// 这里也可以手拼,模糊匹配名称带 'a' 的记录
const finalCondition = new Condition('name').like('a');
/**
* this.model.model 是模型的编码
* 'queryPage' 是模型中定义的查询方法名,可以和后端约定,甚至配置。这里使用默认的 queryPage
* 第三个参数是查询条件,可以携带分页参数等信息
* 第四个参数是请求字段,可以配置请求字段,默认是所有字段,可以配置成需要的字段,可以减少请求字段,提高性能
* 第五个参数是返回字段,默认是所有字段
* */
const result = await customQueryPage(
this.model.model,
'queryPage',
{
pageSize: pagination.pageSize,
currentPage: pagination.current,
condition: finalCondition
},
// 拿到当时视图中的字段
this.rootRuntimeContext.getRequestFields(),
this.rootRuntimeContext.getRequestFields()
);
pagination.total = result.totalElements;
pagination.totalPageSize = result.totalPages;
// 这里 return 出去的值会赋给 dataSource,同2-1-1,在 vue 的 props 里接一下就能使用
return result.content;
});
}
}
2-2 表单(Form)
2-2-1 继承即用:自动获取数据
继承 FormWidget,在 vue 以 props 接 formData。 示例代码(TS & VUE)
import { BaseElementWidget, SPI, FORM_WIDGET, FormWidget, ViewType } from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
BaseElementWidget.Token({
viewType: ViewType.Form,
widget: ['form', FORM_WIDGET]
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
}
<template>
<div class="Test">
{{ formData }}
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'Test',
props: ['formData']
});
</script>
效果图: ![]()
2-2-2 重写 fetchData:单条数据的拿法
表单页常见两种状态:根据 URL id 查询 ,或无 id 直接构造一条空记录。两者都能优雅覆盖:
queryOne(model, { id }, fields):读详情。constructOne({...}):初始化一条可写记录。- 如需自定义方法名,可切到
customQuery。
示例代码(TS)
import {
BaseElementWidget,
SPI,
FORM_WIDGET,
FormWidget,
ViewType,
ActiveRecord,
Condition,
queryOne,
constructOne,
IModel,
customQuery
} from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
BaseElementWidget.Token({
viewType: ViewType.Form,
widget: ['form', FORM_WIDGET]
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
/**
* 获取数据
* 这里只考虑单条数据,非内联表单页的情况
*/
public async fetchData(condition?: Condition): Promise<ActiveRecord> {
return await this.load(async () => {
let result;
// 拿到当前视图的字段
const requestFields = this.rootRuntimeContext.getRequestFields();
// 获取 url 中的 id
const id = this.urlParameters.id;
// 有 id 根据 id 查数据
if (id) {
/**
* 可以调封装好的 queryOne 方法
* 传入模型编码,请求参数,请求字段
* */
result = await queryOne(this.model.model, { id }, requestFields);
// 如果不调 queryOne,也可以自定义传入方法名
// result = await customQuery(this.model.model, 'xxxMethodName', { id }, requestFields, requestFields);
}
// 没 id 初始化构造一条数据
else {
result = await constructOne({
modelModel: this.model.model,
model: this.model as unknown as IModel,
record: { name: 'xxx' },
fields: requestFields,
variables: {
anyKey: 'anyValue'
},
context: {}
});
}
// 这里 return 出去的值会赋给 formData,同2-2-1,在 vue 的 props 里接一下就能使用
return result;
});
}
}
- 自定义字段:从"拿值"到"算值" ===================
3-1 普通字段(String 等)
3-1-1 自动获取:用 value 就够了
字段的数据由父级表单/表格统一请求,组件内直接用 props.value。 示例代码(TS & VUE)
import { SPI, ViewType, FormFieldWidget, BaseFieldWidget, ModelFieldType } from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
BaseFieldWidget.Token({
viewType: [ViewType.Form, ViewType.Search],
ttype: ModelFieldType.String
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormFieldWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
}
<template>
<div class="Test" style="color: red">
{{ value }}
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'Test',
props: ['value']
});
</script>
3-1-2 值变更触发后端计算
当字段变化需要"算一下再回填表单",走 customQuery 最顺:把整个 formData 带上,后端算好返回,前端用 ObjectUtils.shallowMerge 合一把,再 reloadFormData$ 刷新即可。 示例代码(TS & VUE)
import {
SPI,
ViewType,
FormFieldWidget,
BaseFieldWidget,
ModelFieldType,
Widget,
customQuery,
ObjectUtils
} from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
BaseFieldWidget.Token({
viewType: [ViewType.Form, ViewType.Search],
ttype: ModelFieldType.String
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormFieldWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
// 请求的方法名,可配置
public get methodName() {
return this.getDsl().methodName || 'construct';
}
@Widget.Method()
public async onCalculate() {
// 拿到表单的数据
const formData = this.formData || {};
// 拿到当前视图的字段
const requestFields = this.rootViewRuntimeContext.runtimeContext.getRequestFields();
/**
* 调用自定义方法
* @param modelModel 模型的编码
* @param method 方法名称
* @param record 请求数据,这里把整个表单数据都带上
* @param requestFields 请求字段,默认是所有字段,可以配置成需要的字段,以减少请求体积,提高性能
* @param responseFields 第五个参数是返回字段,默认是所有字段
*/
const result = await customQuery(this.model.model, this.methodName, formData, requestFields, requestFields);
// 合并返回的数据到表单
if (result) {
ObjectUtils.shallowMerge(formData, result as Object);
}
// 重新加载表单数据
this.reloadFormData$.subject.next(true);
}
}
<template>
<div class="Test">
<a-input class="oio-input oio-input-number" v-model:value="realValue" @change="onChange" />
<a-button class="oio-button" type="primary" @click="onCalculate">请求</a-button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref, watch } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'Test',
props: ['value', 'change', 'onCalculate'],
setup(props) {
const realValue = ref<string>(props.value);
watch(
() => props.value,
(newValue) => {
realValue.value = newValue;
}
);
const onChange = () => {
props.change?.(realValue.value);
};
return {
realValue,
onChange
};
}
});
</script>
<style lang="scss">
.Test {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 16px;
.ant-input {
flex: auto;
}
}
</style>
3-2 关系字段(ManyToOne)
这个场景有三种姿势,力度不同、成本不同。
3-2-1 自动获取:用 value
和普通字段一致,拿值展示。 示例代码(TS & VUE)
import { SPI, ViewType, FormFieldWidget, BaseFieldWidget, ModelFieldType } from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
BaseFieldWidget.Token({
viewType: [ViewType.Form, ViewType.Search],
ttype: ModelFieldType.ManyToOne
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormFieldWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
}
<template>
<div class="Test" style="color: red">
{{ value }}
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'Test',
props: ['value']
});
</script>
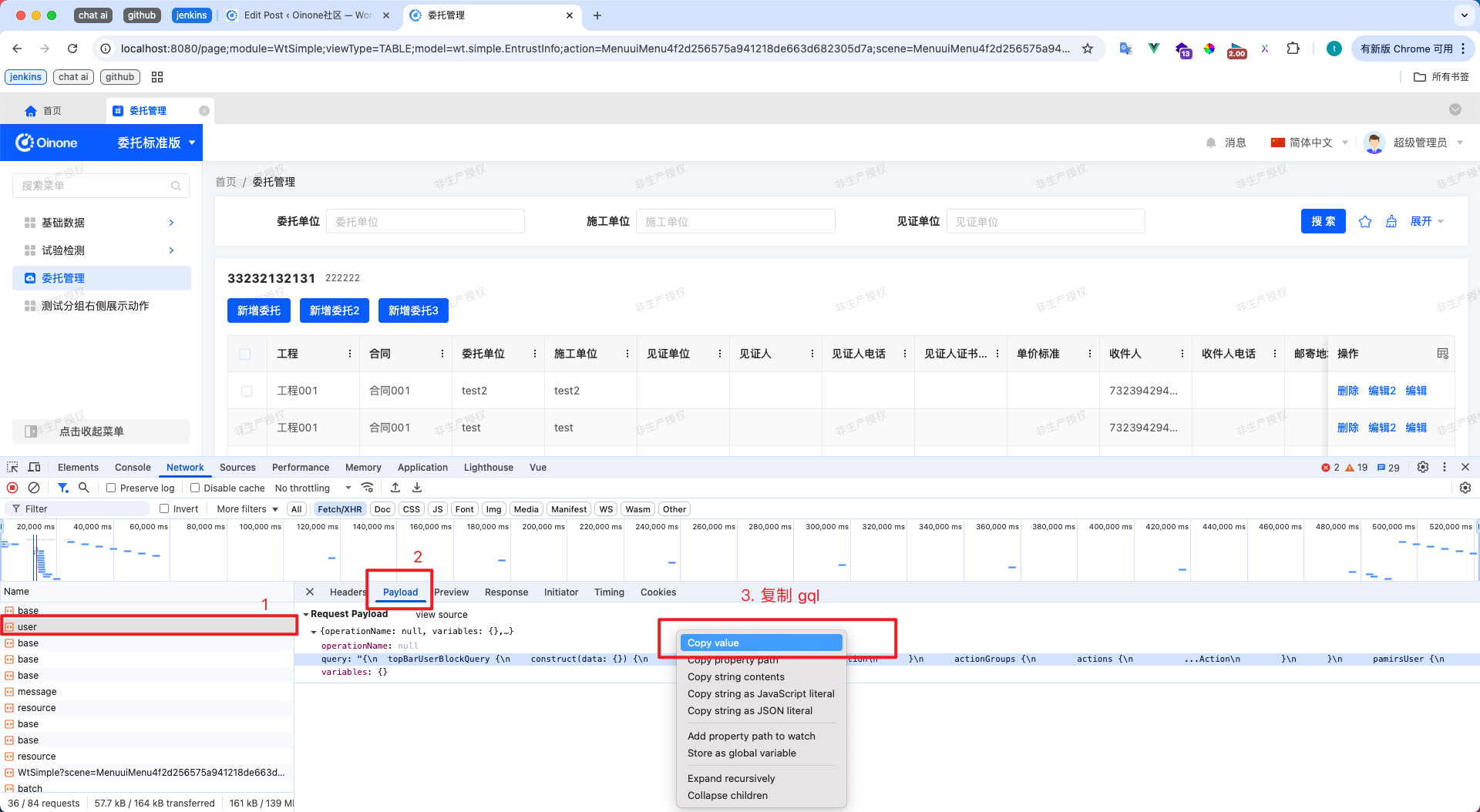
3-2-2 手写 GraphQL 获取数据(弹窗选多对一)
当内置下拉不符合交互预期,需要弹窗 → 搜索 → 点选 → 回填时,手写 GraphQL 能快速落地,也便于精确控制字段与包体。 示例代码(TS)
import {
SPI,
Widget,
FormFieldWidget,
ActiveRecords,
ModelFieldType,
RuntimeRelationField,
ViewType,
http,
Condition,
DEFAULT_TRUE_CONDITION
} from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
FormFieldWidget.Token({
viewType: [ViewType.Form, ViewType.Search],
ttype: ModelFieldType.ManyToOne
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormFieldWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
// 弹窗表格展示的字段
public get searchDialogModelFields() {
// 关系字段关联的字段
return (this.field as RuntimeRelationField)?.referencesModel.modelFields;
}
// 转化成 antd table 的 columns 能展示的结构
@Widget.Reactive()
public get columns() {
return (
this.searchDialogModelFields?.map((field: any) => {
return {
key: field.data,
dataIndex: field.data,
title: field.label
};
}) || []
);
}
// 弹窗输入框搜索的字段编码,逗号分隔
@Widget.Reactive()
public get searchFieldCode() {
return this.getDsl().searchFieldCode || 'name';
}
// 弹窗表格数据查询方法名
public get queryPageFunction() {
return (
// 界面设计器配置的查询方法名
this.getDsl().queryPageFunction ||
// 默认查询方法名
'queryPage'
);
}
// 弹窗表格总页数
@Widget.Reactive()
protected totalPages = 10000;
// 弹窗表格数据
@Widget.Reactive()
public searchDialogData: ActiveRecords | undefined;
// 发起查询弹窗表格数据
@Widget.Method()
public async querySearchDialogData(currentPage: number, pageSize: number, searchValue: string) {
// 根据配置的弹窗输入框搜索的字段编码,构建查询条件
let condition = new Condition(DEFAULT_TRUE_CONDITION);
if (searchValue) {
this.searchFieldCode.split(',').forEach((fieldCode) => {
// like 模糊匹配
condition.and(new Condition(fieldCode).like(searchValue));
});
}
// 手拼 gql
const query = `
{
resourceCountryQuery {
queryPage(
page: {currentPage: ${currentPage}, size: ${pageSize}}
queryWrapper: {rsql: "${condition?.toString()}"}
) {
content {
code
name
id
}
totalPages
totalElements
}
}
}
`;
const r = await http.query('resource', query);
const result = r.data['resourceCountryQuery']['queryPage'];
this.totalPages = result.totalPages as number;
this.searchDialogData = result.content as ActiveRecords;
}
}
示例代码(VUE)
<template>
<div class="test-filed-wrapper">
{{ value }}
<a-button class="oio-button" @click="opendialog"> 打开弹窗 </a-button>
<a-modal wrap-class-name="test-dialog" v-model:visible="data.dialogTableVisible" :title="data.title" width="100%">
<a-input-search
v-model:value="data.input3"
placeholder="请输入"
@search="inputSearchButtonClick"
style="width: 20%"
/>
<a-table :dataSource="searchDialogData" :columns="columns" :pagination="false" bordered :customRow="customRow" />
<oio-pagination
v-model:current-page="data.currentPage4"
v-model:page-size="data.pageSize4"
:total="totalPages"
@change="handleChange"
/>
</a-modal>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { OioPagination } from '@kunlun/vue-ui-antd';
import { defineComponent, reactive } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
inheritAttrs: false,
name: 'Test',
components: {
OioPagination
},
props: ['value', 'searchDialogData', 'columns', 'totalPages', 'querySearchDialogData', 'change'],
setup(props) {
const data = reactive({
dialogTableVisible: false,
input3: '',
title: '名称',
currentPage4: 1,
pageSize4: 15
});
const customRow = (record: any, index: number) => {
return {
onclick: (event: Event) => {
data.dialogTableVisible = false;
console.log(record, index);
props.change?.(record);
}
};
};
const opendialog = () => {
if (!props.searchDialogData) {
props.querySearchDialogData?.(data.currentPage4, data.pageSize4, data.input3);
}
data.dialogTableVisible = true;
};
const handleChange = (currentPage: number, pageSize: number) => {
props.querySearchDialogData?.(data.currentPage4, data.pageSize4, data.input3);
};
const inputSearchButtonClick = () => {
props.querySearchDialogData?.(data.currentPage4, data.pageSize4, data.input3);
};
return {
data,
opendialog,
handleChange,
customRow,
inputSearchButtonClick
};
}
});
</script>
<style lang="scss">
.test-filed-wrapper {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 6px;
}
.test-dialog {
.ant-modal-body {
padding: 20px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
row-gap: 16px;
}
}
</style>
3-2-3 调平台 API 获取数据(通用且稳)
当你想去模板化 又不愿每次都手拼 GraphQL,用平台封装的 customQueryPage 等 API 更平衡。它保留了字段/分页/条件的控制权,同时具备方法名约定 与类型提示的优势。
平台请求相关的 API 用法详见:https://doc.oinone.top/frontend/17638.html 示例代码(TS)
import {
SPI,
Widget,
FormFieldWidget,
ActiveRecords,
ModelFieldType,
RuntimeRelationField,
ViewType,
buildSelectSearchCondition,
customQueryPage,
IModelField
} from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
FormFieldWidget.Token({
viewType: [ViewType.Form, ViewType.Search],
ttype: [ModelFieldType.ManyToOne]
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormFieldWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
// 弹窗表格所属的模型
public get searchDialogModel() {
// 关系字段关联的模型
return (this.field as RuntimeRelationField)?.references;
}
// 弹窗表格展示的字段
public get searchDialogModelFields() {
// 关系字段关联的字段
return (this.field as RuntimeRelationField)?.referencesModel.modelFields;
}
// 转化成 antd table 的 columns 能展示的结构
@Widget.Reactive()
public get columns() {
return (
this.searchDialogModelFields?.map((field: any) => {
return {
key: field.data,
dataIndex: field.data,
title: field.label
};
}) || []
);
}
// 弹窗输入框搜索的字段编码,逗号分隔
@Widget.Reactive()
public get searchFieldCode() {
return this.getDsl().searchFieldCode || 'name';
}
// 弹窗表格数据查询方法名
public get queryPageFunction() {
return (
// 界面设计器配置的查询方法名
this.getDsl().queryPageFunction ||
// 默认查询方法名
'queryPage'
);
}
// 弹窗表格总页数
@Widget.Reactive()
protected totalPages = 10000;
// 弹窗表格数据
@Widget.Reactive()
public searchDialogData: ActiveRecords | undefined;
// 发起查询弹窗表格数据
@Widget.Method()
public async querySearchDialogData(currentPage: number, pageSize: number, searchValue: string) {
if (this.searchDialogModel) {
const condition = buildSelectSearchCondition(
(this.field as RuntimeRelationField).referencesModel,
this.searchFieldCode,
searchValue
);
// 这样把模型和方法写死,效果就相当于手写 GraphQL,不能通用了
// const result = await customQueryPage(
// "resource.ResourceCountry",
// "queryPage",
// {
// currentPage,
// pageSize,
// condition
// },
// this.searchDialogModelFields as unknown as IModelField[],
// this.searchDialogModelFields as unknown as IModelField[]
// );
const result = await customQueryPage(
this.searchDialogModel,
this.queryPageFunction,
{
currentPage,
pageSize,
condition
},
this.searchDialogModelFields as unknown as IModelField[],
this.searchDialogModelFields as unknown as IModelField[]
);
this.totalPages = result.totalPages;
this.searchDialogData = result.content;
}
}
}
替换效果可在:资源应用 → 省菜单 → 创建表单 → 国家/地区 字段 看到。
3-2-4 继承基类拿数据(最省心,功能全)
如果你熟悉平台组件 ,推荐直接继承 FormM2OSelectFieldWidget。弹窗和下拉在数据请求面上等价,复用基类的分页、搜索、联动能力,你只需改展示。 示例代码(TS)
import { SPI, Widget, FormFieldWidget, ModelFieldType, ViewType, FormM2OSelectFieldWidget } from '@kunlun/dependencies';
import Test from './Test.vue';
@SPI.ClassFactory(
FormFieldWidget.Token({
viewType: [ViewType.Form, ViewType.Search],
ttype: [ModelFieldType.ManyToOne]
})
)
export class TestWidget extends FormM2OSelectFieldWidget {
public initialize(props) {
super.initialize(props);
this.setComponent(Test);
return this;
}
// 转化成 antd table 的 columns 能展示的结构
@Widget.Reactive()
public get columns() {
return (
this.field.referencesModel.modelFields?.map((field) => {
return {
key: field.data,
dataIndex: field.data,
title: field.label
};
}) || []
);
}
// 弹窗表格总页数,这里重写为响应式的
@Widget.Reactive()
protected totalPages = 10000;
// 弹窗表格数据,这里重写为响应式的
@Widget.Reactive()
protected dataList: Record<string, unknown>[] = [];
// 发起查询弹窗表格数据
@Widget.Method()
public async querySearchDialogData(currentPage: number, pageSize: number, searchValue: string) {
this.currentPage = currentPage;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.searchValue = searchValue;
// 只需调用基类的加载数据方法
await this.initLoadOptions();
}
}
示例代码(VUE)
<template>
<div class="test-filed-wrapper">
{{ value }}
<a-button class="oio-button" @click="opendialog"> 打开弹窗 </a-button>
<a-modal wrap-class-name="test-dialog" v-model:visible="data.dialogTableVisible" :title="data.title" width="100%">
<a-input-search
v-model:value="data.input"
placeholder="请输入"
@search="inputSearchButtonClick"
style="width: 20%"
/>
<a-table :dataSource="dataList" :columns="columns" :pagination="false" bordered :customRow="customRow" />
<oio-pagination
v-model:current-page="data.currentPage"
v-model:page-size="data.pageSize"
:total="totalPages"
@change="handleChange"
/>
</a-modal>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { OioPagination } from '@kunlun/vue-ui-antd';
import { defineComponent, reactive } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
inheritAttrs: false,
name: 'Test',
components: { OioPagination },
props: ['value', 'dataList', 'columns', 'totalPages', 'querySearchDialogData', 'change'],
setup(props) {
const data = reactive({
dialogTableVisible: false,
input: '',
title: '名称',
currentPage: 1,
pageSize: 15
});
const customRow = (record: any, index: number) => {
return {
key: record.id || index,
onClick: (event: Event) => {
data.dialogTableVisible = false;
console.log(record, index);
props.change?.(record);
}
};
};
const opendialog = () => {
if (!props.dataList || !props.dataList.length) {
props.querySearchDialogData?.(data.currentPage, data.pageSize, data.input);
}
data.dialogTableVisible = true;
};
const handleChange = (currentPage: number, pageSize: number) => {
props.querySearchDialogData?.(data.currentPage, data.pageSize, data.input);
};
const inputSearchButtonClick = () => {
data.currentPage = 1;
props.querySearchDialogData?.(data.currentPage, data.pageSize, data.input);
};
return { data, opendialog, handleChange, customRow, inputSearchButtonClick };
}
});
</script>
<style lang="scss">
.test-filed-wrapper { display: flex; align-items: center; gap: 6px; }
.test-dialog { .ant-modal-body { padding: 20px; display: flex; flex-direction: column; row-gap: 16px; } }
</style>
实测:复用基类不止更省代码,联动/懒加载/缓存等能力也直接到手。
- 性能与可维护性:三件小事 ===============
- 字段裁剪 :尽量用
getRequestFields() 控制请求/返回字段,避免"全字段走起"。
- 方法命名约定 :与后端约好
queryPage / queryOne / construct / xxxCalculate,统一口径减少沟通成本。
- 生命周期分层 :一次性数据(如 mask)放
mounted 拉;表格分页走 load 包装,保住交互体验。
- 决策小抄(30 秒选型) ===============
- 只在顶栏/独立组件用一次 → 手写 GraphQL。
- 要分页/筛选/字段控制,后续还会复用 → 平台 API。
- 多对一、下拉/弹窗、需要联动与缓存 → 继承基类。
- 常见坑位 =======
- 条件拼错 :
Condition 组合后别忘了 .toString() 注入到 GraphQL。
- 字段不匹配 :
columns 从 modelFields 派生,避免硬编码。
- 刷新缺失 :表单合并回写后记得
reloadFormData$.subject.next(true)。
- 分页状态丢失 :自定义弹窗记得双向维护
currentPage / pageSize。
- 团队协作建议 =========
- DSL 配置兜底 :把
methodName / queryPageFunction / searchFieldCode 开成可配置,便于不同页面复用同一个组件。
- 命名前缀 :通用方法统一前缀(如
calc* / build* / query*),日志检索更高效。
- 代码分层 :
Widget 里做数据编排,Vue 里专注展示和交互。
让前端自定义请求"像水一样"------该轻则轻,该刚则刚。一次写死、可复用、借基类三种姿势配合使用,你就能在 Oinone 的默认能力和个性化需求之间,找到那个稳妥的甜点位。
 示例代码(TS)
示例代码(TS)