Atomikos-XA事务恢复
说事务恢复流程之前,我们来讨论下,会啥会出现事务恢复?XA二阶段提交协议不是强一致性的吗?要解答这个问题,我们就要来看看XA二阶段协议有什么问题?
问题一 :单点故障
由于协调者的重要性,一旦协调者TM发生故障。参与者RM会一直阻塞下去。尤其在第二阶段,协调者发生故障,那么所有的参与者还都处于锁定事务资源的状态中,而无法继续完成事务操作。(如果是协调者挂掉,可以重新选举一个协调者,但是无法解决因为协调者宕机导致的参与者处于阻塞状态的问题)
问题二 :数据不一致
数据不一致。在二阶段提交的阶段二中,当协调者向参与者发送commit请求之后,发生了局部网络异常或者在发送commit请求过程中协调者发生了故障,这回导致只有一部分参与者接受到了commit请求。而在这部分参与者接到commit请求之后就会执行commit操作。但是其他部分未接到commit请求的机器则无法执行事务提交。于是整个分布式系统便出现了数据不一致性的现象。
如何解决?
解决的方案简单,就是我们在事务的操作的每一步,我们都需要对事务状态的日志进行人为的记录,我们可以把日志记录存储在我们想存储的地方,可以是本地存储,也可以中心化的存储。atomikos的开源版本,我们之前也分析了,它是使用内存 + file的方式,存储在本地,这样的话,如果在一个集群系统里面,如果有节点宕机,日志又存储在本地,所以事务不能及时的恢复(需要重启服务)。
Atomikos 多场景下事务恢复。
Atomikos 提供了二种方式,来应对不同场景下的异常情况。
- 场景一: 服务节点不宕机,因为其他的原因,产生需要事务恢复的情况。 这个时候才要定时任务进行恢复。 具体的代码
com.atomikos.icatch.imp.TransactionServiceImp.init() 方法,会初始化一个定时任务,进行事务的恢复。
public synchronized void init ( Properties properties ) throws SysException
{
shutdownInProgress_ = false;
control_ = new com.atomikos.icatch.admin.imp.LogControlImp ( (AdminLog) this.recoveryLog );
ConfigProperties configProperties = new ConfigProperties(properties);
long recoveryDelay = configProperties.getRecoveryDelay();
recoveryTimer = new PooledAlarmTimer(recoveryDelay);
recoveryTimer.addAlarmTimerListener(new AlarmTimerListener() {
@Override
public void alarm(AlarmTimer timer) {
//进行事务恢复
performRecovery();
}
});
TaskManager.SINGLETON.executeTask(recoveryTimer);
initialized_ = true;
}
- 最终会进入
com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XATransactionalResource.recover() 方法。
public void recover() {
XaResourceRecoveryManager xaResourceRecoveryManager = XaResourceRecoveryManager.getInstance();
if (xaResourceRecoveryManager != null) { //null for LogCloud recovery
try {
xaResourceRecoveryManager.recover(getXAResource());
} catch (Exception e) {
refreshXAResource(); //cf case 156968
}
}
}
- 场景二: 当服务节点宕机重启动过程中进行事务的恢复。具体实现在
com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XATransactionalResource.setRecoveryService()方法里面
@Override
public void setRecoveryService ( RecoveryService recoveryService )
throws ResourceException
{
if ( recoveryService != null ) {
if ( LOGGER.isTraceEnabled() ) LOGGER.logTrace ( "Installing recovery service on resource "
+ getName () );
this.branchIdentifier=recoveryService.getName();
//进行事务恢复
recover();
}
}
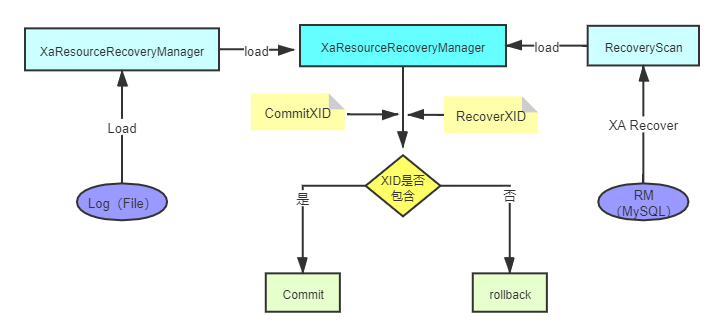
com.atomikos.datasource.xa.XATransactionalResource.recover() 流程详解。
![]()
主代码:
public void recover(XAResource xaResource) throws XAException {
// 根据XA recovery 协议获取 xid
List<XID> xidsToRecover = retrievePreparedXidsFromXaResource(xaResource);
Collection<XID> xidsToCommit;
try {
// xid 与日志记录的xid进行匹配
xidsToCommit = retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog();
for (XID xid : xidsToRecover) {
if (xidsToCommit.contains(xid)) {
//执行 XA commit xid 进行提交
replayCommit(xid, xaResource);
} else {
attemptPresumedAbort(xid, xaResource);
}
}
} catch (LogException couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids) {
LOGGER.logWarning("Transient error while recovering - will retry later...", couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids);
}
}
- 我们来看一下如何根据
XA recovery 协议获取RM端存储的xid。 进入方法 retrievePreparedXidsFromXaResource(xaResource), 最后进入 com.atomikos.datasource.xa.RecoveryScan.recoverXids()方法。
public static List<XID> recoverXids(XAResource xaResource, XidSelector selector) throws XAException {
List<XID> ret = new ArrayList<XID>();
boolean done = false;
int flags = XAResource.TMSTARTRSCAN;
Xid[] xidsFromLastScan = null;
List<XID> allRecoveredXidsSoFar = new ArrayList<XID>();
do {
xidsFromLastScan = xaResource.recover(flags);
flags = XAResource.TMNOFLAGS;
done = (xidsFromLastScan == null || xidsFromLastScan.length == 0);
if (!done) {
// TEMPTATIVELY SET done TO TRUE
// TO TOLERATE ORACLE 8.1.7 INFINITE
// LOOP (ALWAYS RETURNS SAME RECOVER
// SET). IF A NEW SET OF XIDS IS RETURNED
// THEN done WILL BE RESET TO FALSE
done = true;
for ( int i = 0; i < xidsFromLastScan.length; i++ ) {
XID xid = new XID ( xidsFromLastScan[i] );
// our own XID implements equals and hashCode properly
if (!allRecoveredXidsSoFar.contains(xid)) {
// a new xid is returned -> we can not be in a recovery loop -> go on
allRecoveredXidsSoFar.add(xid);
done = false;
if (selector.selects(xid)) {
ret.add(xid);
}
}
}
}
} while (!done);
return ret;
}
- 我们重点关注
xidsFromLastScan = xaResource.recover(flags); 这个方法,如果我们使用MySQL,那么久会进入 MysqlXAConnection.recover()方法。执行 XA recovery xid 语句来获取 xid。
protected static Xid[] recover(Connection c, int flag) throws XAException {
/*
* The XA RECOVER statement returns information for those XA transactions on the MySQL server that are in the PREPARED state. (See Section 13.4.7.2, ???XA
* Transaction States???.) The output includes a row for each such XA transaction on the server, regardless of which client started it.
*
* XA RECOVER output rows look like this (for an example xid value consisting of the parts 'abc', 'def', and 7):
*
* mysql> XA RECOVER;
* +----------+--------------+--------------+--------+
* | formatID | gtrid_length | bqual_length | data |
* +----------+--------------+--------------+--------+
* | 7 | 3 | 3 | abcdef |
* +----------+--------------+--------------+--------+
*
* The output columns have the following meanings:
*
* formatID is the formatID part of the transaction xid
* gtrid_length is the length in bytes of the gtrid part of the xid
* bqual_length is the length in bytes of the bqual part of the xid
* data is the concatenation of the gtrid and bqual parts of the xid
*/
boolean startRscan = ((flag & TMSTARTRSCAN) > 0);
boolean endRscan = ((flag & TMENDRSCAN) > 0);
if (!startRscan && !endRscan && flag != TMNOFLAGS) {
throw new MysqlXAException(XAException.XAER_INVAL, Messages.getString("MysqlXAConnection.001"), null);
}
//
// We return all recovered XIDs at once, so if not TMSTARTRSCAN, return no new XIDs
//
// We don't attempt to maintain state to check for TMNOFLAGS "outside" of a scan
//
if (!startRscan) {
return new Xid[0];
}
ResultSet rs = null;
Statement stmt = null;
List<MysqlXid> recoveredXidList = new ArrayList<MysqlXid>();
try {
// TODO: Cache this for lifetime of XAConnection
stmt = c.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("XA RECOVER");
while (rs.next()) {
final int formatId = rs.getInt(1);
int gtridLength = rs.getInt(2);
int bqualLength = rs.getInt(3);
byte[] gtridAndBqual = rs.getBytes(4);
final byte[] gtrid = new byte[gtridLength];
final byte[] bqual = new byte[bqualLength];
if (gtridAndBqual.length != (gtridLength + bqualLength)) {
throw new MysqlXAException(XAException.XA_RBPROTO, Messages.getString("MysqlXAConnection.002"), null);
}
System.arraycopy(gtridAndBqual, 0, gtrid, 0, gtridLength);
System.arraycopy(gtridAndBqual, gtridLength, bqual, 0, bqualLength);
recoveredXidList.add(new MysqlXid(gtrid, bqual, formatId));
}
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
throw mapXAExceptionFromSQLException(sqlEx);
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
throw mapXAExceptionFromSQLException(sqlEx);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
throw mapXAExceptionFromSQLException(sqlEx);
}
}
}
int numXids = recoveredXidList.size();
Xid[] asXids = new Xid[numXids];
Object[] asObjects = recoveredXidList.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < numXids; i++) {
asXids[i] = (Xid) asObjects[i];
}
return asXids;
}
这里要注意如果Mysql的版本 <5.7.7 ,则不会有任何数据,在以后的版本中Mysql进行了修复,因此如果我们想要使用MySQL充当RM,版本必须 >= 5.7.7 ,原因是:
MySQL 5.6版本在客户端退出的时候,自动把已经prepare的事务回滚了,那么MySQL为什么要这样做?这主要取决于MySQL的内部实现,MySQL 5.7以前的版本,对于prepare的事务,MySQL是不会记录binlog的(官方说是减少fsync,起到了优化的作用)。只有当分布式事务提交的时候才会把前面的操作写入binlog信息,所以对于binlog来说,分布式事务与普通的事务没有区别,而prepare以前的操作信息都保存在连接的IO_CACHE中,如果这个时候客户端退出了,以前的binlog信息都会被丢失,再次重连后允许提交的话,会造成Binlog丢失,从而造成主从数据的不一致,所以官方在客户端退出的时候直接把已经prepare的事务都回滚了!
Collection<XID> xidsToCommit = retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog();
- 我们来看下获取事务日志里面的XID的
retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog()方法。 然后进入com.atomikos.recovery.imp.RecoveryLogImp.getCommittingParticipants()方法。
public Collection<ParticipantLogEntry> getCommittingParticipants()
throws LogReadException {
Collection<ParticipantLogEntry> committingParticipants = new HashSet<ParticipantLogEntry>();
Collection<CoordinatorLogEntry> committingCoordinatorLogEntries = repository.findAllCommittingCoordinatorLogEntries();
for (CoordinatorLogEntry coordinatorLogEntry : committingCoordinatorLogEntries) {
for (ParticipantLogEntry participantLogEntry : coordinatorLogEntry.participants) {
committingParticipants.add(participantLogEntry);
}
}
return committingParticipants;
}
到这里我们来简单介绍一下,事务日志的存储结构。首先是 CoordinatorLogEntry,这是一次XA事务的所有信息实体类。
public class CoordinatorLogEntry implements Serializable {
//全局事务id
public final String id;
//是否已经提交
public final boolean wasCommitted;
/**
* Only for subtransactions, null otherwise.
*/
public final String superiorCoordinatorId;
//参与者集合
public final ParticipantLogEntry[] participants;
}
- 再来看一下参与者实体类
ParticipantLogEntry :
public class ParticipantLogEntry implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1728296701394899871L;
/**
* The ID of the global transaction as known by the transaction core.
*/
public final String coordinatorId;
/**
* Identifies the participant within the global transaction.
*/
public final String uri;
/**
* When does this participant expire (expressed in millis since Jan 1, 1970)?
*/
public final long expires;
/**
* Best-known state of the participant.
*/
public final TxState state;
/**
* For diagnostic purposes, null if not relevant.
*/
public final String resourceName;
}
- 回到
com.atomikos.recovery.xa.DefaultXaRecoveryLog.getExpiredCommittingXids() 方法,可以到获取了一次XA事务过程中,存储的事务日志中的xid。
public Set<XID> getExpiredCommittingXids() throws LogReadException {
Set<XID> ret = new HashSet<XID>();
Collection<ParticipantLogEntry> entries = log.getCommittingParticipants();
for (ParticipantLogEntry entry : entries) {
if (expired(entry) && !http(entry)) {
XID xid = new XID(entry.coordinatorId, entry.uri);
ret.add(xid);
}
}
return ret;
}
- 如果从RM中通过XA recovery取出的XID,包含在从事务日志中取出的XID,则进行commit,否则进行rollback.
List<XID> xidsToRecover = retrievePreparedXidsFromXaResource(xaResource);
Collection<XID> xidsToCommit;
try {
xidsToCommit = retrieveExpiredCommittingXidsFromLog();
for (XID xid : xidsToRecover) {
if (xidsToCommit.contains(xid)) {
replayCommit(xid, xaResource);
} else {
attemptPresumedAbort(xid, xaResource);
}
}
} catch (LogException couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids) {
LOGGER.logWarning("Transient error while recovering - will retry later...", couldNotRetrieveCommittingXids);
}
private void replayCommit(XID xid, XAResource xaResource) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) LOGGER.logDebug("Replaying commit of xid: " + xid);
try {
//进行事务提交
xaResource.commit(xid, false);
//更新事务日志
log.terminated(xid);
} catch (XAException e) {
if (alreadyHeuristicallyTerminatedByResource(e)) {
handleHeuristicTerminationByResource(xid, xaResource, e, true);
} else if (xidTerminatedInResourceByConcurrentCommit(e)) {
log.terminated(xid);
} else {
LOGGER.logWarning("Transient error while replaying commit - will retry later...", e);
}
}
}
- attemptPresumedAbort(xid, xaResource); 方法如下:
private void attemptPresumedAbort(XID xid, XAResource xaResource) {
try {
log.presumedAborting(xid);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) LOGGER.logDebug("Presumed abort of xid: " + xid);
try {
//进行回滚
xaResource.rollback(xid);
//更新日志状态
log.terminated(xid);
} catch (XAException e) {
if (alreadyHeuristicallyTerminatedByResource(e)) {
handleHeuristicTerminationByResource(xid, xaResource, e, false);
} else if (xidTerminatedInResourceByConcurrentRollback(e)) {
log.terminated(xid);
} else {
LOGGER.logWarning("Unexpected exception during recovery - ignoring to retry later...", e);
}
}
} catch (IllegalStateException presumedAbortNotAllowedInCurrentLogState) {
// ignore to retry later if necessary
} catch (LogException logWriteException) {
LOGGER.logWarning("log write failed for Xid: "+xid+", ignoring to retry later", logWriteException);
}
}
文章到此,已经写的很长很多了,我们分析了ShardingSphere对于XA方案,提供了一套SPI解决方案,对Atomikos进行了整合,也分析了Atomikos初始化流程,开始事务流程,获取连接流程,提交事务流程,回滚事务流程,事务恢复流程。 希望对大家理解XA的原理有所帮助。
作者介绍: 肖宇,Apache ShardingSphere Committer,开源hmily分布式事务框架作者, 开源soul网关作者,热爱开源,追求写优雅代码。目前就职入京东数科,参与ShardingSphere的开源建设,以及分布式数据库的研发工作。