此文旨在记录与传播在 Docker 上搭建 PostGIS 数据库实现空间数据存储及可视化的知识要点。
PostGIS
已经有PostGIS经验的大佬可以忽略此段了。解释 PostGIS 之前需要介绍 PostgreSQL (简称 postgres ); postgres 是一个数据库服务器软件,由加州大学伯克利分校计算机系开发;部署在服务器上可以由不同数量的客户端连接,进而操作postgres 数据库中的数据。PostGIS 是在 postgres 之上的一款扩展软件,他主要用来存储及操作空间数据(矢量和栅格),还可以对进行空间分析。
Docker
对于一位不熟悉命令行的用户来说可能Docker 是一头野兽;有点吓人吧。 因为他的大部分操作都是基于命令行的;但是它为您提供了一种构建和运行软件的方式,通过构建一种名为LXC容器的技术,以非常一致和可控的方式运行软件。
对于GISer来说,Docker 和 PostGIS 又意味着什么呢? 如果有 Docker 和 PostGIS 技术,GISer或者其他人都能以最小的配置在任何机器上安装软件,而且环境都是一致的,这在开发和运维中至关重要。当然 Docker 这项技术并不限于和 PostGIS 结合。
安装Docker
Docker 是夸平台的可以安装在任何机器上。前面已经有关于 Docker 安装及使用的文章,可以去参考,在这就不去一一解释了,直接给出通过 Vagrant 安装的简略步骤。
环境
| 序号 |
名称 |
版本 |
用途 |
| 1 |
centos |
7 |
系统 |
| 2 |
kartoza/postgis |
9.6-2.4 |
docker镜像 |
| 3 |
Virtual Box |
latest |
虚拟机 |
注: 因为我们安装好的 PostGIS 要和我们本机的软件进行通信,所以需要使用 host-only 网络, 且指定IP为192.168.33.10。
Vagrantfile文件内容
注:假定已安装Virtual Box 及 Vagrant.
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
# All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure
# configures the configuration version (we support older styles for
# backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what
# you're doing.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
# boxes at https://vagrantcloud.com/search.
config.vm.box = "centos/7"
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
# NOTE: This will enable public access to the opened port
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine and only allow access
# via 127.0.0.1 to disable public access
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
# using a specific IP.
config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
# config.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.141.204"
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
# your network.
# config.vm.network "public_network"
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
# argument is a set of non-required options.
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
# Provider-specific configuration so you can fine-tune various
# backing providers for Vagrant. These expose provider-specific options.
# Example for VirtualBox:
#
# config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
# vb.gui = true
#
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
# vb.memory = "1024"
# end
#
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
# information on available options.
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
# Puppet, Chef, Ansible, Salt, and Docker are also available. Please see the
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
# apt-get update
# apt-get install -y apache2
# SHELL
end
安装 centos 系统
$ vagrant up
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Checking if box 'centos/7' is up to date...
==> default: Clearing any previously set forwarded ports...
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
......
==> default: Rsyncing folder: /cygdrive/c/VM/Vagrant/ => /vagrant
==> default: Machine already provisioned. Run `vagrant provision` or use the `--provision`
==> default: flag to force provisioning. Provisioners marked to run always will still run.
查看虚拟机系统状态
$ vagrant status
Current machine states:
default running (virtualbox)
The VM is running. To stop this VM, you can run `vagrant halt` to
shut it down forcefully, or you can run `vagrant suspend` to simply
suspend the virtual machine. In either case, to restart it again,
simply run `vagrant up`.
连接 centos 虚拟机
$ vagrant ssh
Last login: Wed May 9 07:01:18 2018 from 10.0.2.2
[vagrant@localhost ~]$
安装Docker, 安装参考官网
在刚才连接的虚拟机中执行如下命令
$ sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-selinux \
docker-engine-selinux \
docker-engine
$ sudo yum install -y yum-utils \
device-mapper-persistent-data \
lvm2
$ sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
$ sudo yum install docker-ce
# 安装完成后启动 Docker
$ sudo systemctl start docker
解决权限问题
$ sudo groupadd docker
$ sudo gpasswd -a vagrant docker
$ exit
$ vagrant ssh
$ docker version
Client:
Version: 18.03.1-ce
API version: 1.37
Go version: go1.9.5
Git commit: 9ee9f40
Built: Thu Apr 26 07:20:16 2018
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Orchestrator: swarm
Server:
Engine:
Version: 18.03.1-ce
API version: 1.37 (minimum version 1.12)
Go version: go1.9.5
Git commit: 9ee9f40
Built: Thu Apr 26 07:23:58 2018
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
安装 PostGIS 镜像
$ mdkir postgre_data && cd postgre_data
$ pwd
/home/vagrant/postgre_data
$ docker run --name=postgis -d -e POSTGRES_USER=sde -e POSTGRES_PASS=sde -e POSTGRES_DBNAME=gis -e ALLOW_IP_RANGE=0.0.0.0/0 -p 5432:5432 -v $(pwd):/var/lib/postgresql --restart=always kartoza/postgis:9.6-2.4
d6f14f3e815fbca4d644582c45aca90dff2b16aba58f0b5765409a140930a3bb
- docker run --name=postgis 告诉 docker新建一个名为postgis的镜像
- -d 后台运行
- -e POSTGRES_USER=sde 通过 -e 参数向镜像写入POSTGRES_USER=sde的环境变量作为 PostgreSQL的超级用户,你可以在任何地方改变他。
- -e POSTGRES_PASS=sde 通过 -e 参数向镜像写入POSTGRES_PASS=sde的环境变量作为 PostgreSQL的超级用户的密码,你可以在任何地方改变他。
- -e POSTGRES_DBNAME=gis 通过 -e 参数向镜像写入POSTGRES_DBNAME=gis的环境变量作为操作 PostgreSQL 的当前数据库,你可以在任何地方改变他。
- -e ALLOW_IP_RANGE=0.0.0.0/0 通过 -e 参数向镜像写入ALLOW_IP_RANGE=0.0.0.0/0的环境变量,使任何客户端都可以连接当前数据库的配置,你可以在任何地方改变他。
- -p 5432:5432 因为 PostgreSQL 向外暴露5432,我们要使用外面实体机的 pgAdmin 连接Docker中的数据库,故向外映射5432端口,又因为 centos 虚拟机和实体机质检室host-only网络,故在连接。
- -v $(pwd):/var/lib/postgresql 挂载(bind)当前目录与PostgreSQL生产的数据库,这样两边的数据会同步。
- --restart=always 创建一条自动启动的规则,告诉 Docker , 每次启动的时候 postgis 容器自动启动。
- kartoza/postgis:9.6-2.4 指定 postgis的镜像为 kartoza/postgis, 且版本为 PostgreSQL 9.6 和 PostGIS 2.4
查看运行的镜像
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d6f14f3e815f kartoza/postgis:9.6-2.4 "/bin/sh -c /docker-…" 51 seconds ago Up 50 seconds 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp postgis
查看运行的 postgis 镜像的日志
$ docker logs postgis
Add rule to pg_hba: 0.0.0.0/0
Add rule to pg_hba: replication user
Setup master database
# ......略
Success. You can now start the database server using:
/usr/lib/postgresql/9.6/bin/pg_ctl -D /var/lib/postgresql/9.6/main -l logfile start
WARNING: enabling "trust" authentication for local connections
You can change this by editing pg_hba.conf or using the option -A, or
--auth-local and --auth-host, the next time you run initdb.
2018-05-10 07:08:38.015 UTC [51] LOG: database system was shut down at 2018-05-10 07:08:37 UTC
2018-05-10 07:08:38.015 UTC [52] postgres@postgres FATAL: the database system is starting up
psql: FATAL: the database system is starting up
2018-05-10 07:08:38.023 UTC [51] LOG: MultiXact member wraparound protections are now enabled
2018-05-10 07:08:38.026 UTC [39] LOG: database system is ready to accept connections
2018-05-10 07:08:38.026 UTC [57] LOG: autovacuum launcher started
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+-----------+---------+-------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
template0 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(3 rows)
postgres ready
# .....略
Setup postgres User:Password
CREATE ROLE
Check default db exists
Create default db gis
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
------------------+----------+-----------+---------+-------+-----------------------
gis | sde | UTF8 | C | C |
postgres | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
template0 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template_postgis | postgres | UTF8 | C | C |
(5 rows)
2018-05-10 07:08:41.291 UTC [39] LOG: received smart shutdown request
2018-05-10 07:08:41.291 UTC [57] LOG: autovacuum launcher shutting down
2018-05-10 07:08:41.293 UTC [54] LOG: shutting down
2018-05-10 07:08:41.300 UTC [39] LOG: database system is shut down
/docker-entrypoint.sh: ignoring /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/*
Postgres initialisation process completed .... restarting in foreground
2018-05-10 07:08:41.328 UTC [231] LOG: database system was shut down at 2018-05-10 07:08:41 UTC
2018-05-10 07:08:41.329 UTC [231] LOG: MultiXact member wraparound protections are now enabled
2018-05-10 07:08:41.330 UTC [228] LOG: database system is ready to accept connections
2018-05-10 07:08:41.331 UTC [235] LOG: autovacuum launcher started
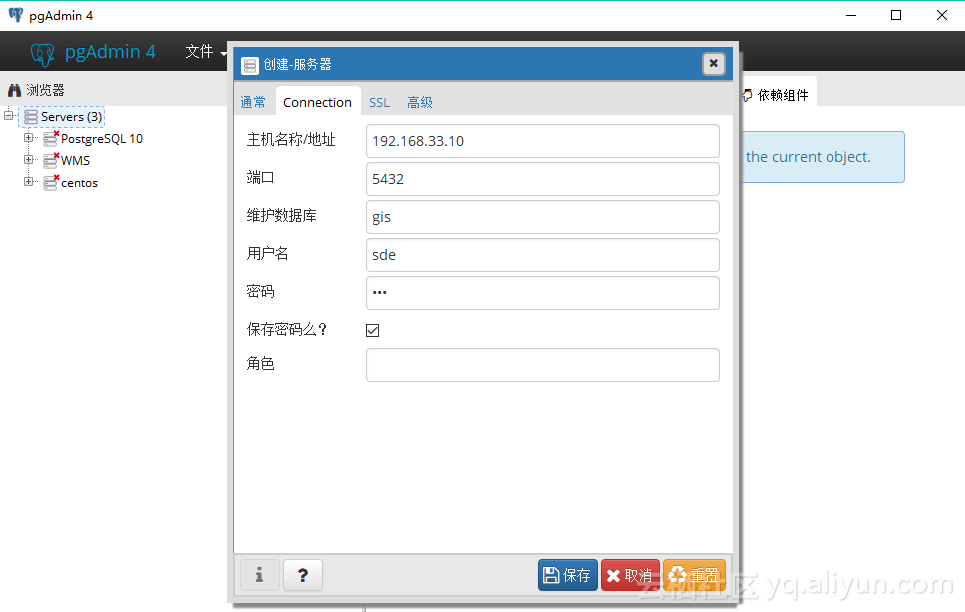
主机 pgAdmin 连接 postgis 容器
连接信息
| 名称 |
值 |
| 名称 |
docker_postgis |
| ip |
192.168.33.10 |
| 端口 |
5432 |
| 维护数据库 |
gis |
| 用户名 |
sde |
| 密码 |
sde |
![postgres_docker_postgis postgres_docker_postgis]()
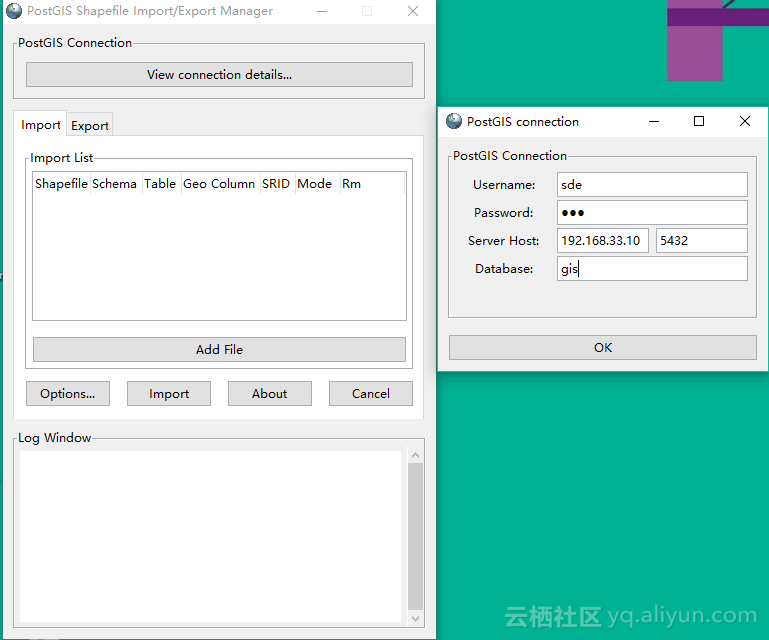
导入 ShapeFile 数据
使用主机上的PostGIS Shapefile Import/Export Manager 连接 Docker 中的 PostgreSql数据库
连接信息
| 名称 |
值 |
| 用户名 |
sde |
| 密码 |
sde |
| ip |
192.168.33.10 |
| 端口 |
5432 |
| 数据库 |
gis |
![shapefile_manager shapefile_manager]()
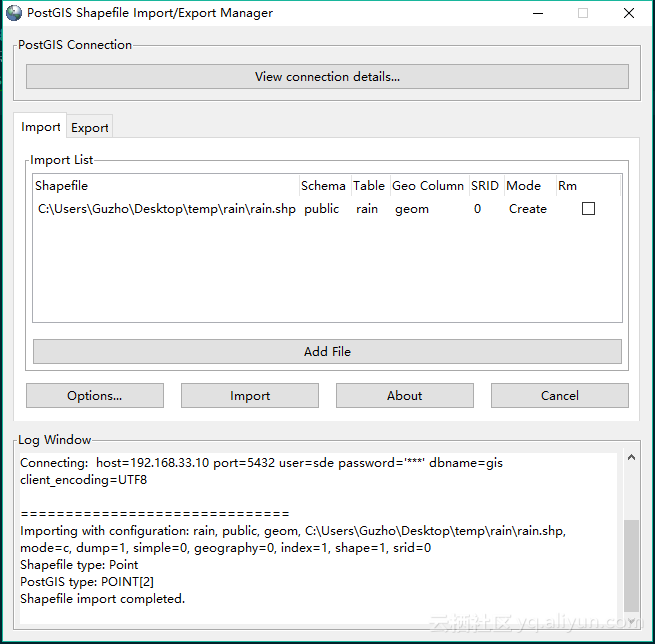
添加文件后点击导入(import)
![import import]()
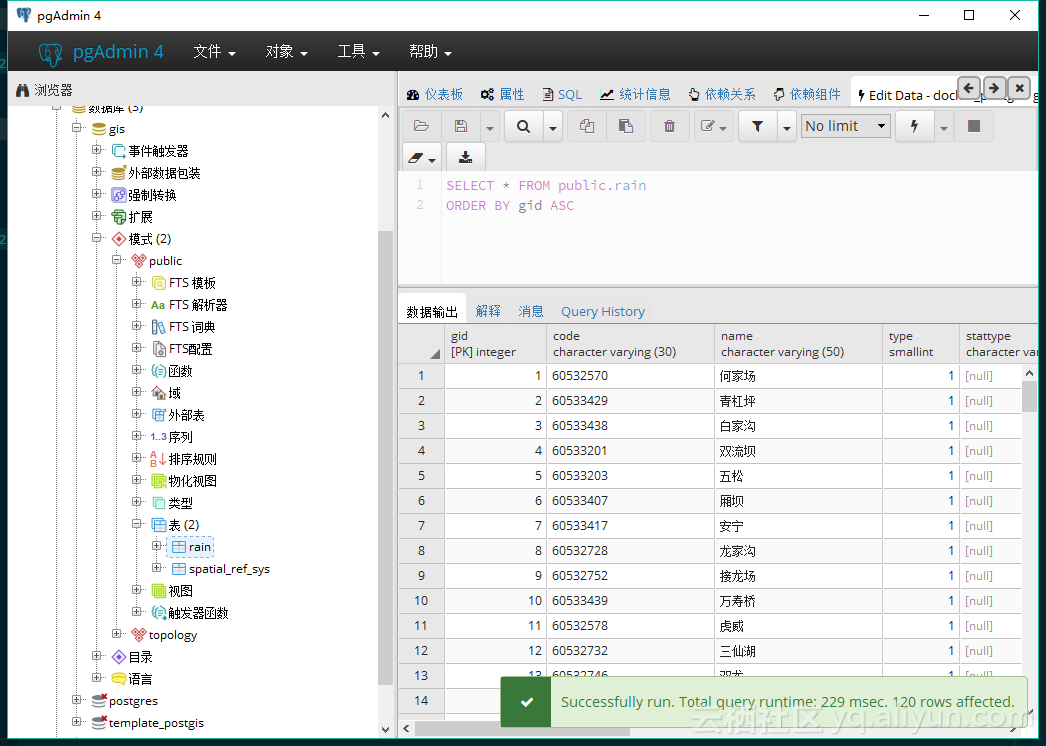
在数据库中查看导入的 shape 数据
![shape_database shape_database]()
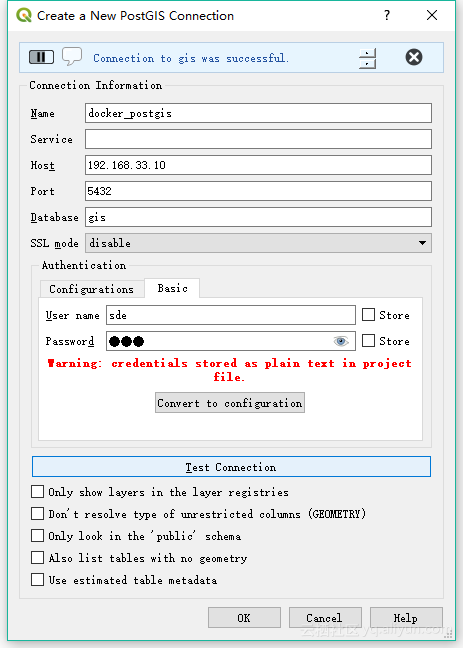
连接QGIS
![qgis_connect qgis_connect]()
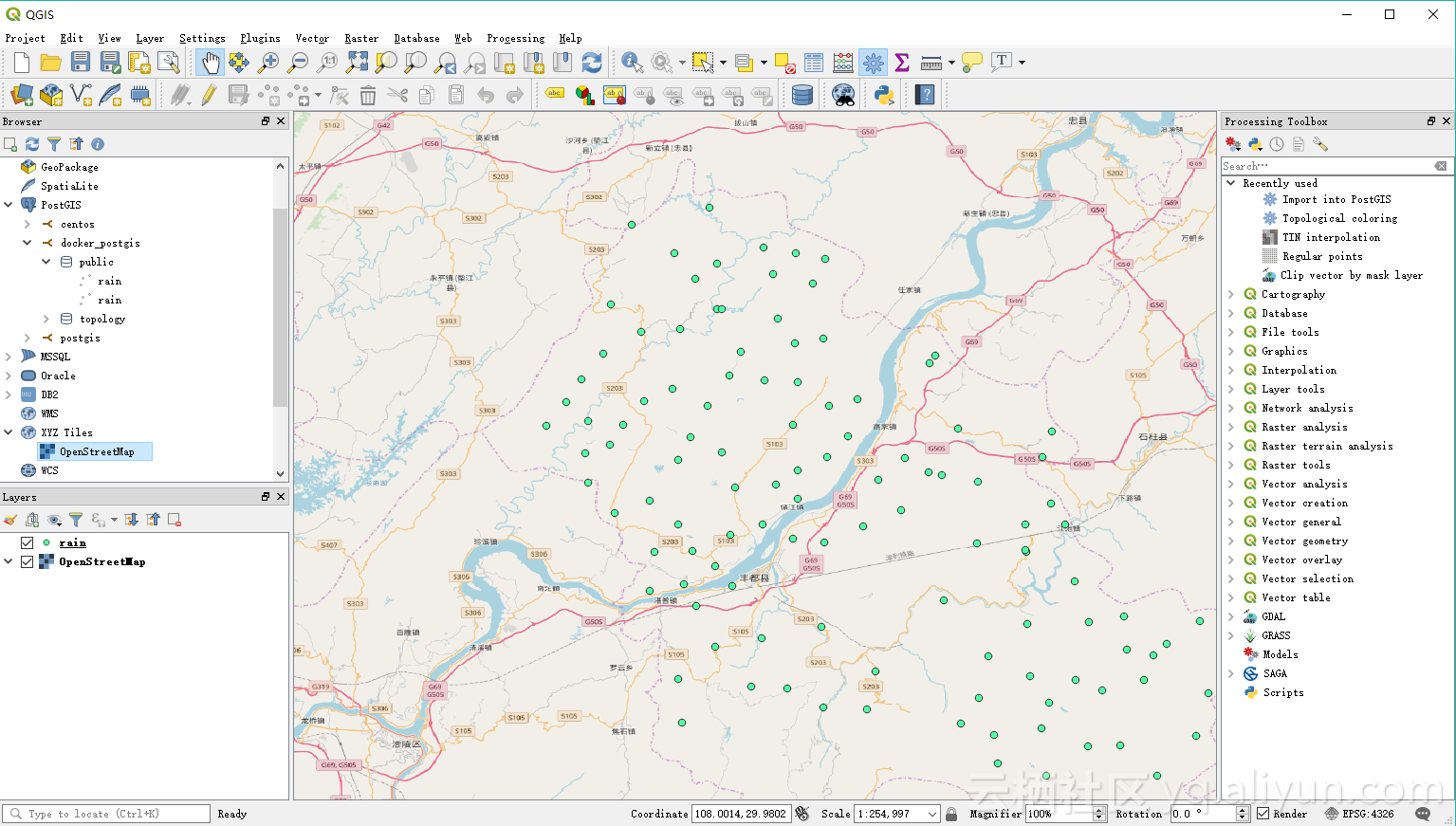
将数据导入 QGIS 查看
![look_data look_data]()
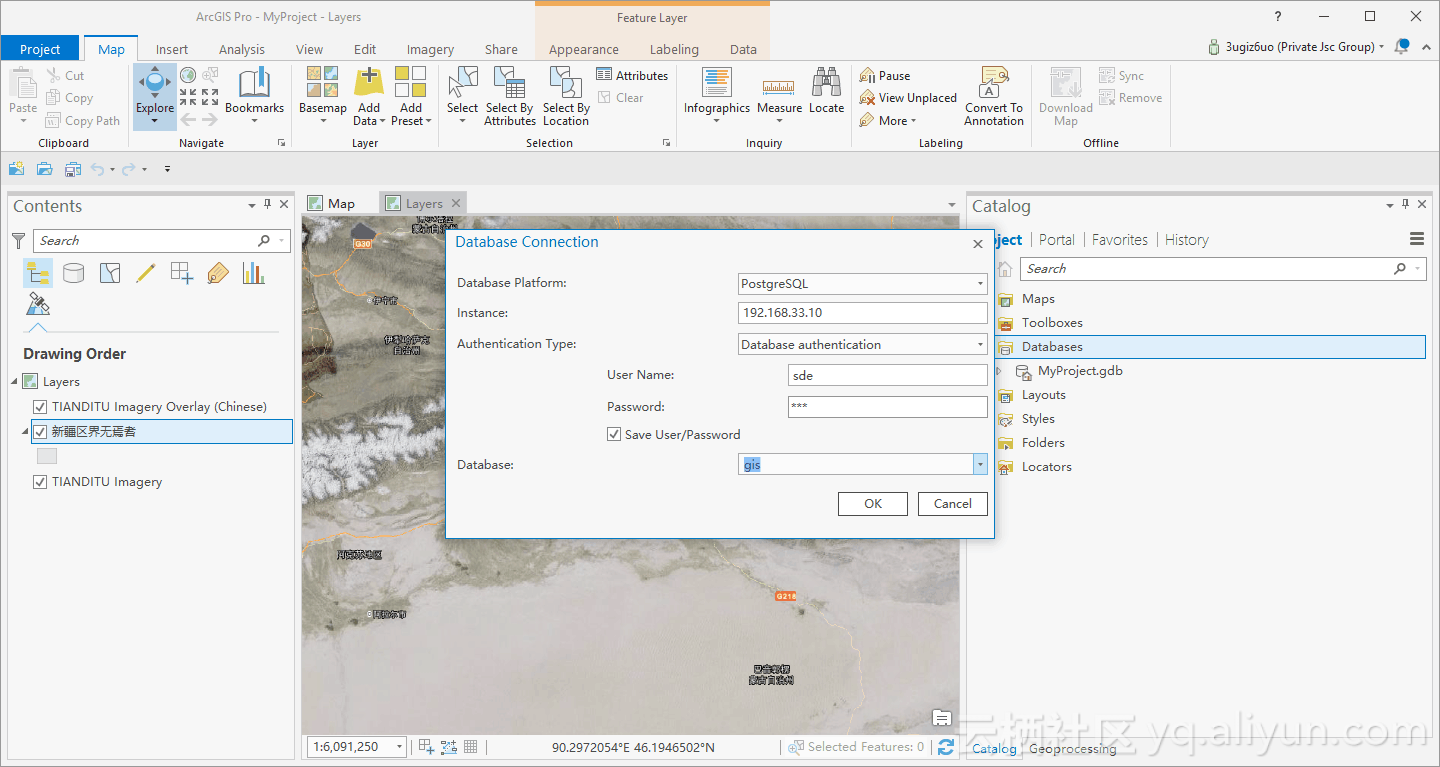
连接 ArcGIS Pro
连接信息
| 名称 |
值 |
| 数据库平台 |
PostgreSQL |
| 实例 |
192.168.33.10 |
| 认证类 |
数据库认证 |
| 用户名 |
sde |
| 密码 |
sde |
| 数据库 |
gis |
![arcgis_pro_connect arcgis_pro_connect]()
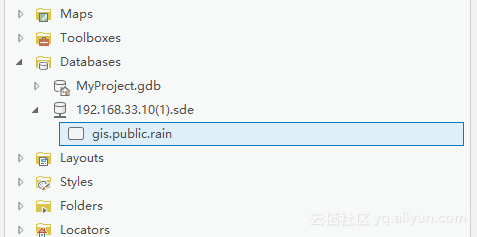
查看数据记录
注: 通过PostGIS Shapefile Import/Export Manager 导入的数据加载到ArcGIS Pro 中没有空间参考,故添加到地图中没有意义,但可以在 Catalog 中看到。
![data_in_arcgis data_in_arcgis]()
导入新数据到sde中
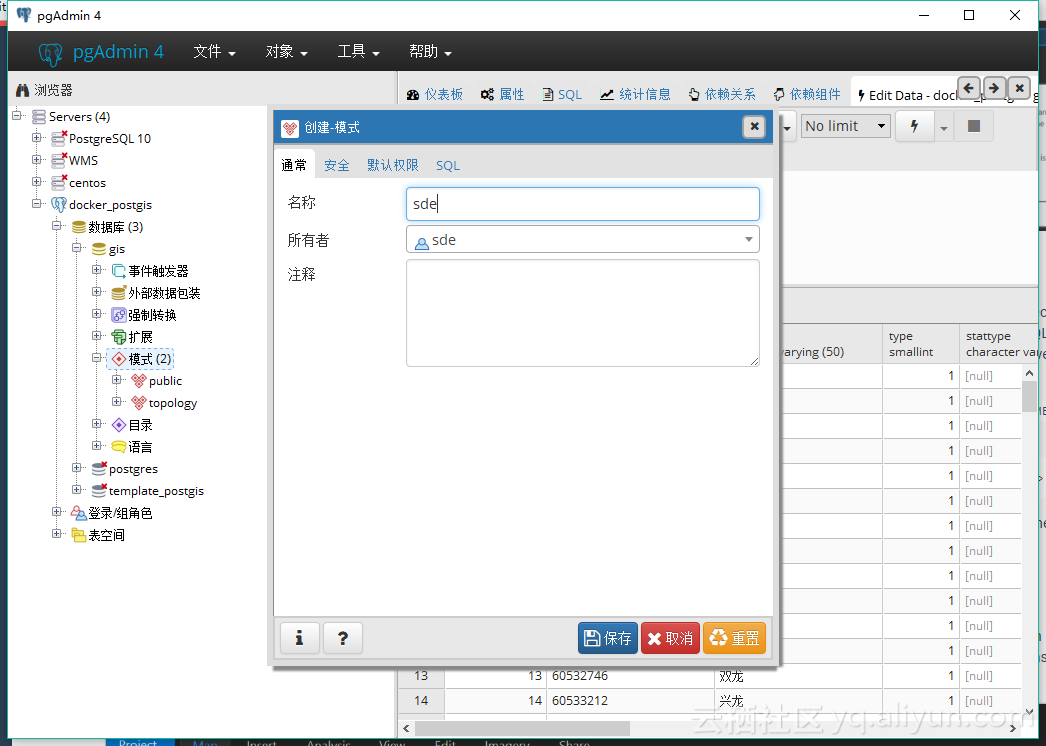
在导入之前需要在连接的数据库中创建与用户名一致的模式,在这我们是sde。
创建 sde 模式
![create_sde_schame create_sde_schame]()
![create sde schame create sde schame]()
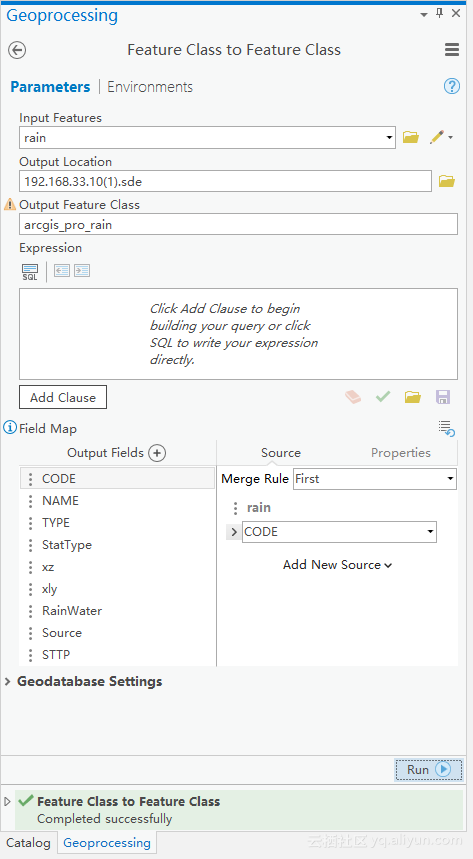
导入数据
![import_to_sde import_to_sde]()
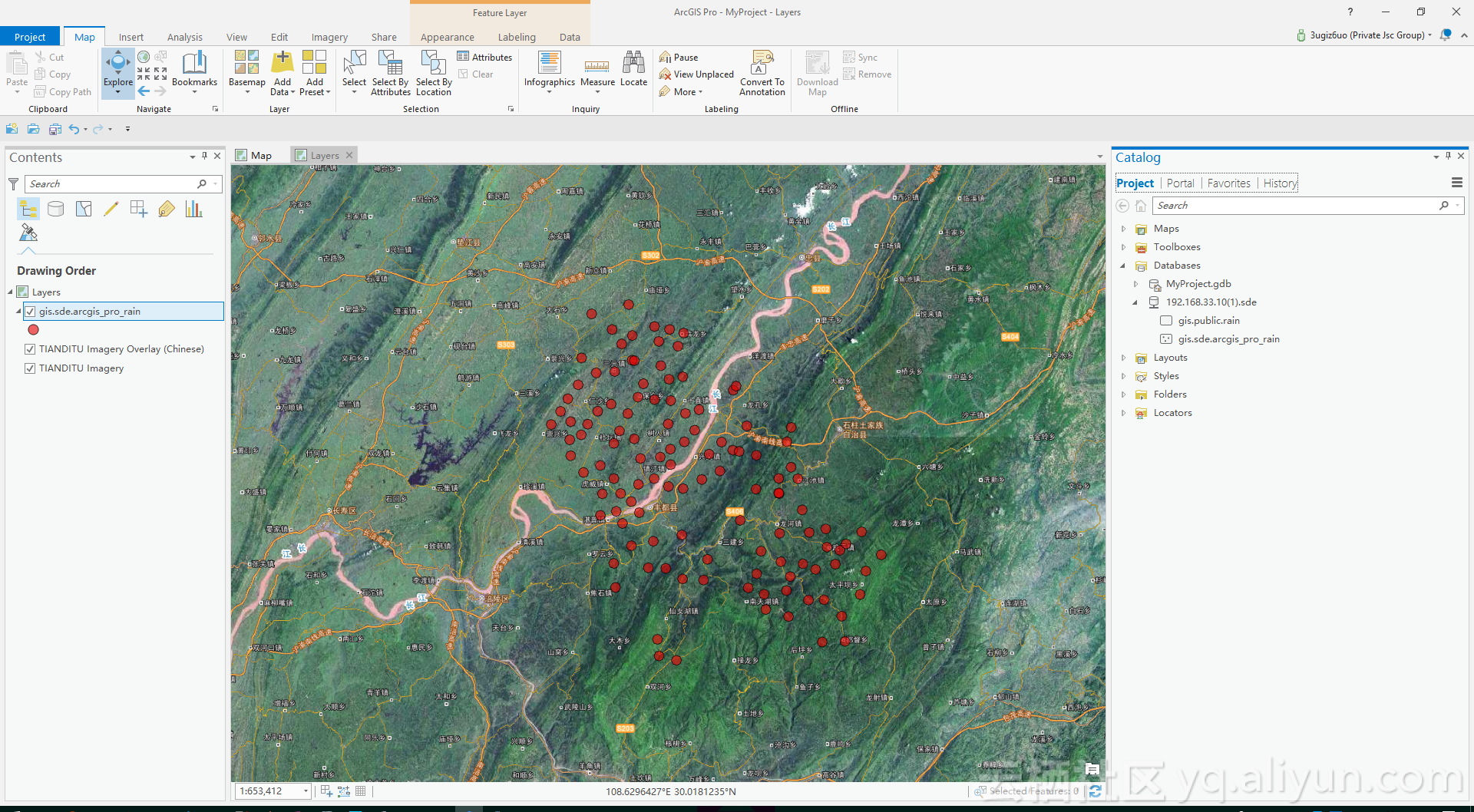
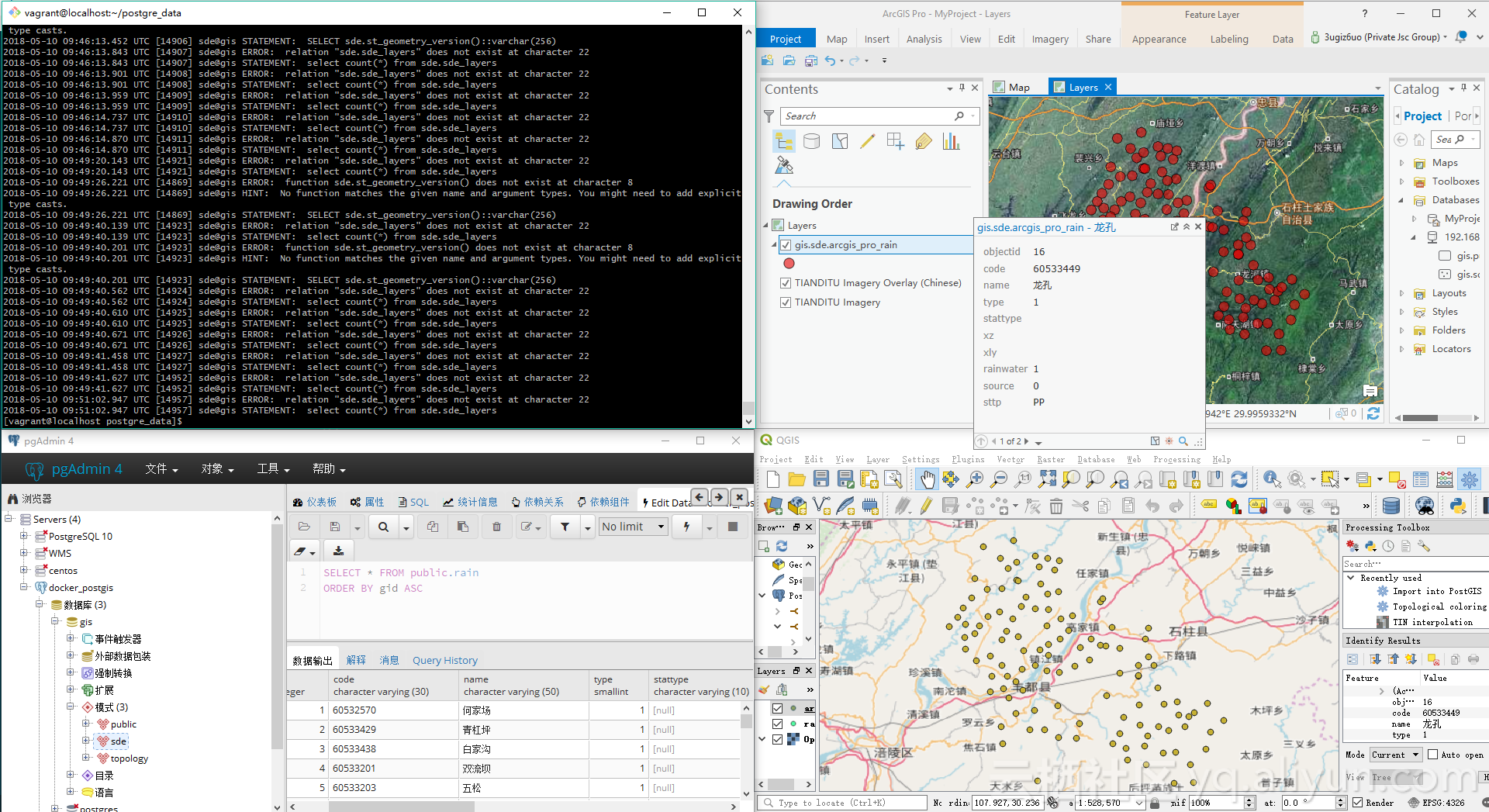
在 ArcGIS Pro 中查看数据
![view_in_arcgis_pro view_in_arcgis_pro]()
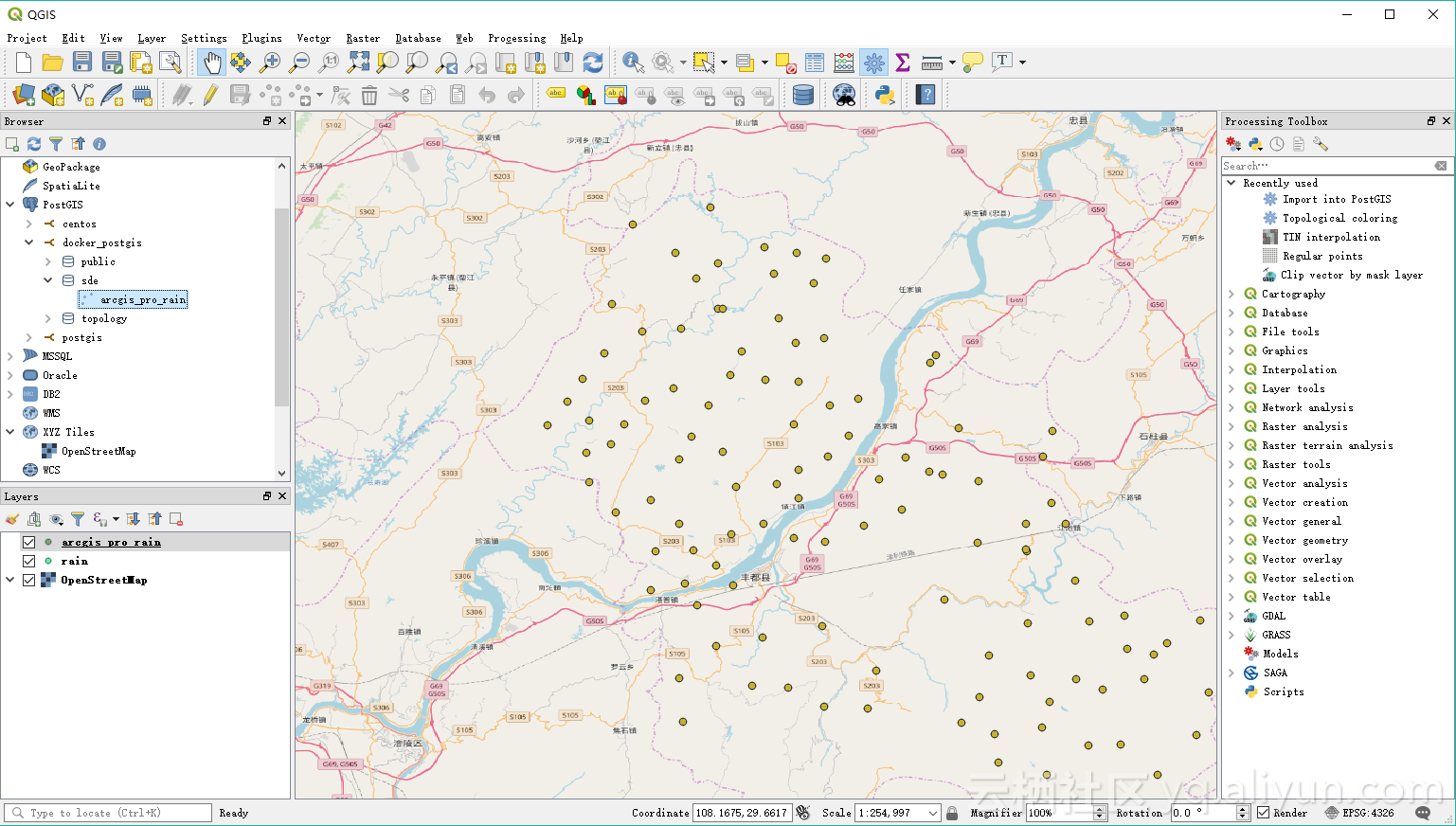
在 QGIS 中查看数据
![view_data_in_qgis view_data_in_qgis]()
总的效果
![final final]()
总结
整个过程通过使用 Vagrant 创建Centos系统,在创建的系统之上安装 Docker, 然后在Docker的基础上安装整合好的 PostGIS 镜像,并运行容器,接着使用 QGIS 和 ArcGIS Pro 连接PostGIS容器导入各种格式的数据、查看数据等。说了这么多,那这样做究竟有什么好处呢? 个人认为有以下几方面的好处。
- 解决开发和部署环境不一致性的问题;
- 快速安装所需软件,避免一个一个安装,节省时间;
- 数据库数据是存储在Linux上且绑定到容器里面的,保证了数据的安全性,同时可以多次挂载、测试及连接(link),即使是在原有镜像基础上增加了新的功能;
- 跨平台
参考