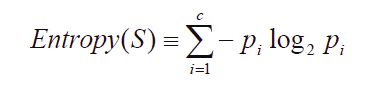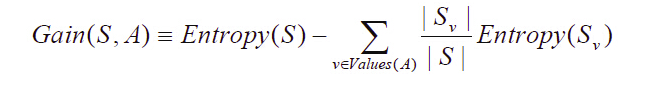1 def createDataSet():
2 dataSet = [[1,1,1,'yes'],
3 [1,1,0,'yes'],
4 [1,0,1,'yes'],
5 [1,0,0,'no'],
6 [0,1,1,'no']] # 我们定义了一个list来表示我们的数据集,这里的数据对应的是上表中的数据
7
8 labels = ['no surfacing','flippers']
9
10 return dataSet, labels
以信息增益度量属性选择,选择分裂后信息增益最大的属性进行分裂。信息熵是用来衡量一个随机变量出现的期望值。如果信息的不确定性越大,熵的值也就越大,出现的各种情况也就越多。
信息增益(information gain)是指信息划分前后的熵的变化,也就是说由于使用这个属性分割样例而导致的期望熵降低。也就是说,信息增益就是原有信息熵与属性划分后信息熵(需要对划分后的信息熵取期望值)的差值,具体计算法如下:
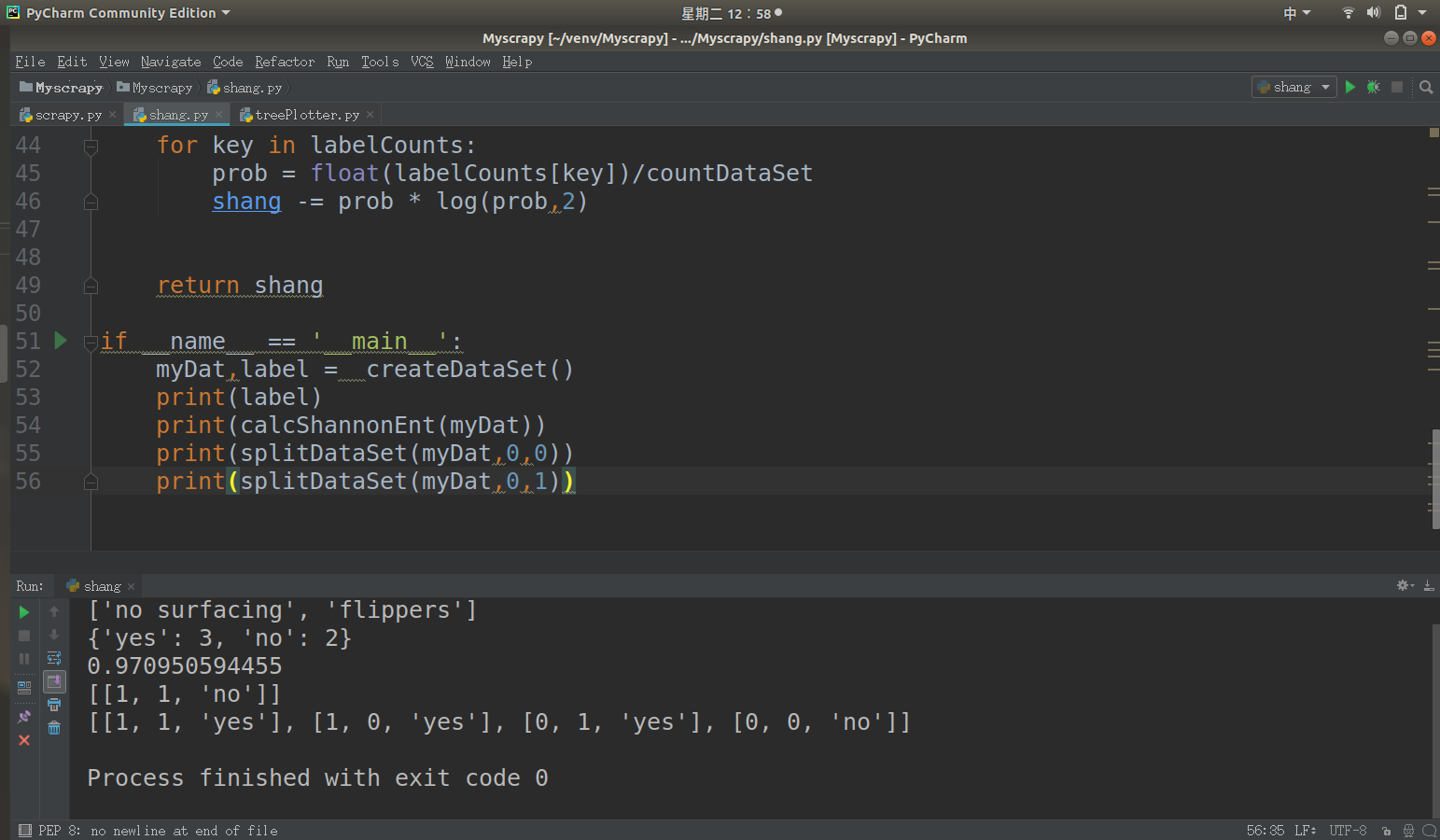
1 from math import log
2
3 def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):#传入数据集
4 # 在这里dataSet是一个链表形式的的数据集
5 countDataSet = len(dataSet)
6 labelCounts={} # 构建字典,用键值对的关系我们表示出 我们数据集中的类别还有对应的关系
7 for featVec in dataSet: 通过for循环,我们每次取出一个数据集,如featVec=[1,1,'yes']
8 currentLabel=featVec[-1] # 取出最后一列 也就是类别的那一类,比如说‘yes’或者是‘no’
9 if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
10 labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
11 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
12
13 print labelCounts
14
15 shang = 0.0
16
17 for key in labelCounts:
18 prob = float(labelCounts[key])/countDataSet
19 shang -= prob * log(prob,2)
20 return shang
1 dataSet = [[1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
2 [1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
3 [1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
4 [1, 0, 0, 'no'],
5 [0, 1, 1, 'no']]
1 def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value):
2 retDataSet = []
3
4 for featVec in dataSet:
5 if featVec[axis] == value:
6 reduceFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
7 reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
8 retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec)
9
10 return retDataSet
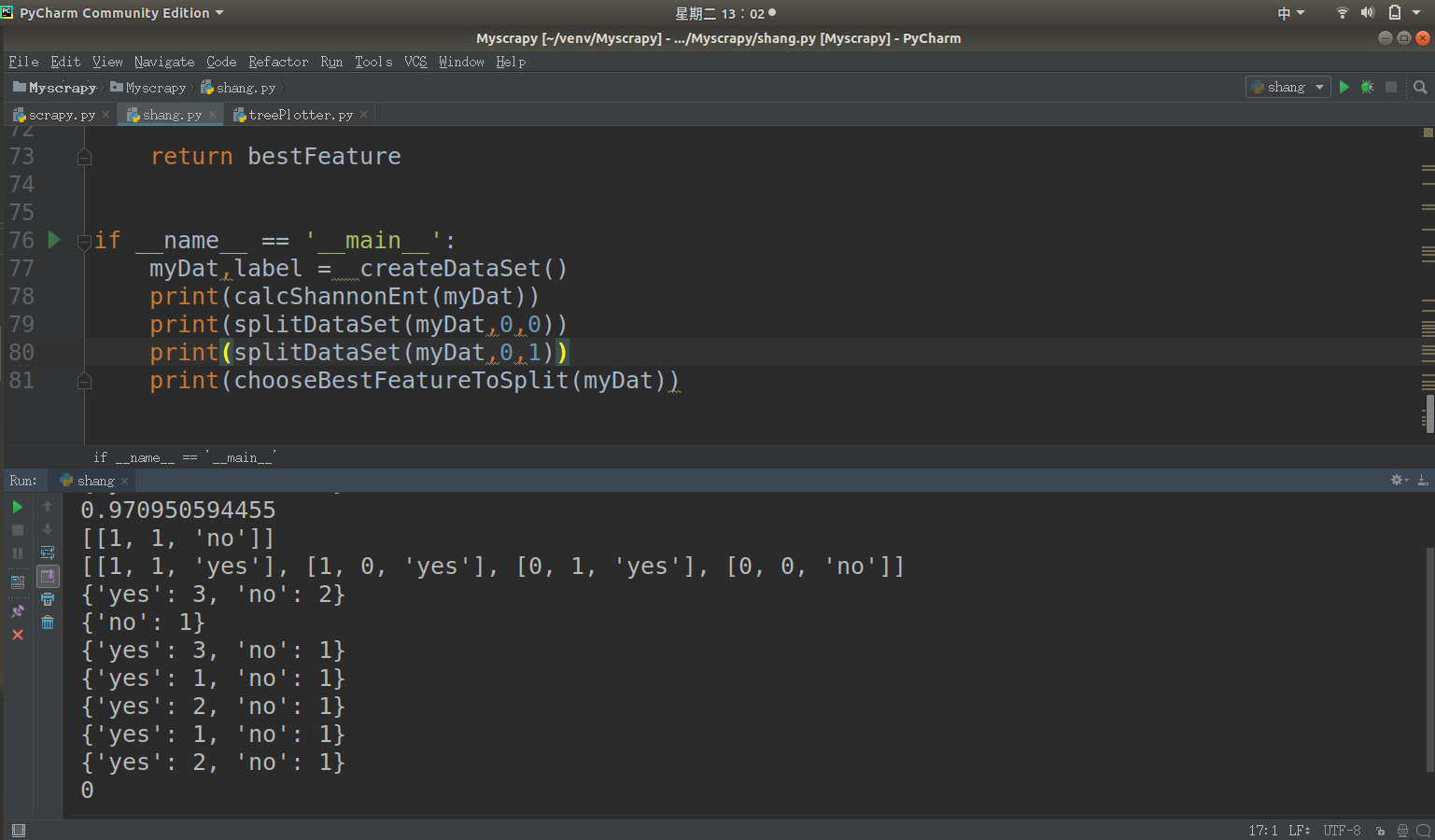
1 def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
2 numFeatures = len(dataSet[0])-1
3 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
4 bestInfoGain =0.0
5 bestFeature = -1
6 for i in range(numFeatures):
7 featList = [sample[i] for sample in dataSet]
8 uniqueVals = set(featList)
9 newEntropy = 0.0
10 for value in uniqueVals:
11 subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value)
12 prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
13 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
14 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
15 if(infoGain > bestInfoGain):
16 bestInfoGain = infoGain
17 bestFeature = i
18
19 return bestFeature
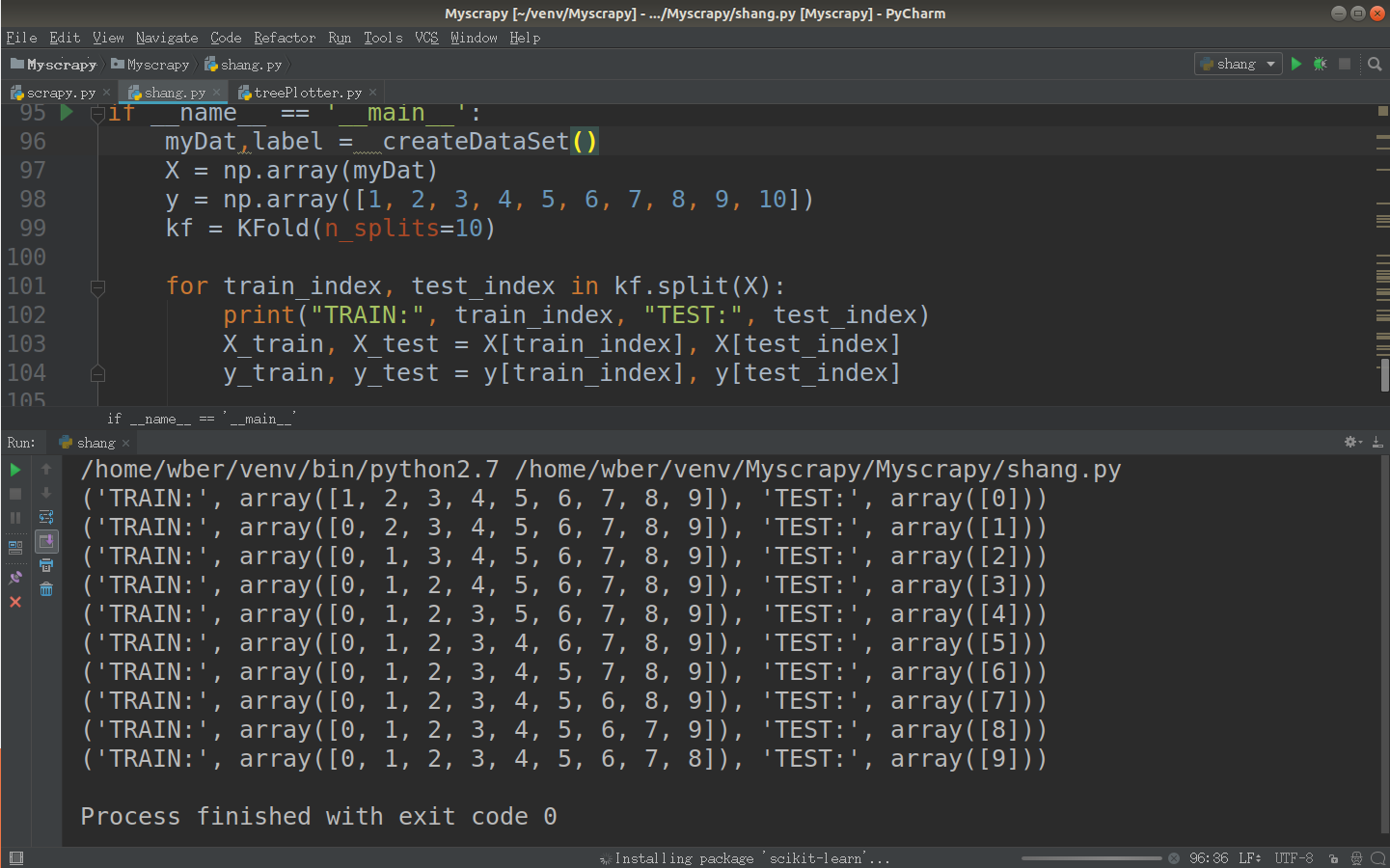
将数据集随机地切分为S个互不相交的大小相同的子集
然后挑选其中S-1个子集作为训练集,训练模型,用剩下的一个子集作测试集,获得测试误差或者评测指标
将上面过程对所有可能的S种选择重复进行,即每次都是用不同的测试集
最后对S次实验所得的数据(测试误差或者评测指标)取均值。
![]()
代码如下:
1 X = np.array(myDat)
2 y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
3 kf = KFold(n_splits=10)
4
5 for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
6 print("TRAIN:", train_index, "TEST:", test_index)
7 X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]
8 y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]
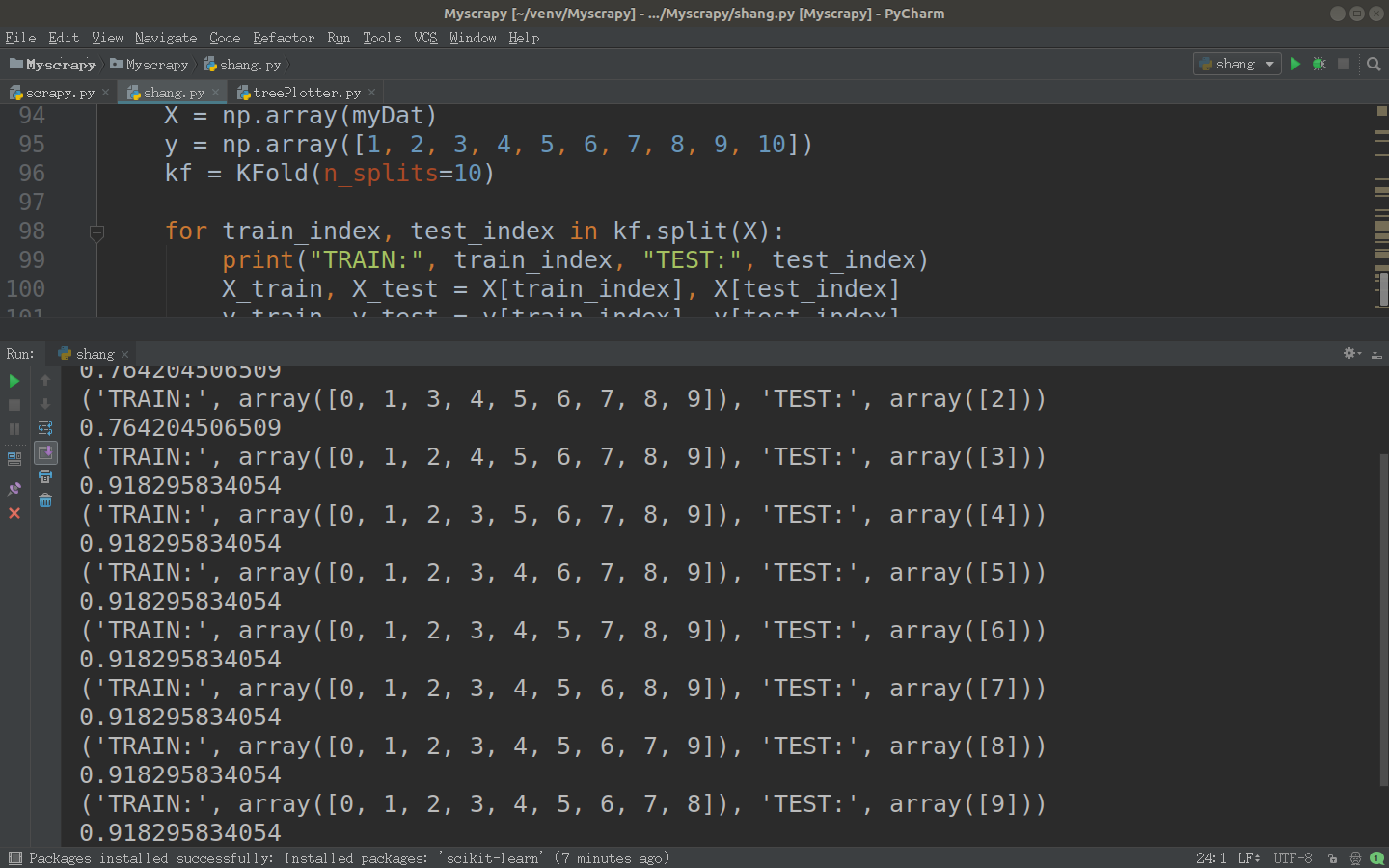
测试:
![]()
完整代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 import csv
3
4 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
5 import requests
6 import mycsv
7 import sys
8
9 reload(sys)
10 sys.setdefaultencoding('utf-8')
11
12 # 请求头设置
13 header = {
14 'Accept': '*/*;',
15 'Connection': 'keep-alive',
16 'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9',
17 'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate, br',
18 'Host': 'book.douban.com',
19 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/67.0.3396.87 Safari/537.36'
20 }
21
22
23 # 初始化csv文件
24 def info(name):
25 csvinfo = open(name + '.mycsv', 'ab')
26 begcsv = csv.writer(csvinfo)
27 begcsv.writerow(['titles', 'authors', 'nums', 'peoples'])
28 csvinfo.close()
29
30
31 # 爬取指定name模块的url,并存储至name.csv文件
32 def web(url, name):
33 db_data = requests.get(url, headers=header)
34 soup = BeautifulSoup(db_data.text, 'lxml')
35 titles = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > h2 > a')
36 authors = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > div.pub')
37 nums = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > div.star.clearfix > span.rating_nums')
38 peoples = soup.select('#subject_list > ul > li > div.info > div.star.clearfix > span.pl')
39 print(titles[0])
40 for title, author, num, people in zip(titles, authors, nums, peoples):
41 data = [
42 (
43 title.get('title'),
44 author.get_text().replace(' ', '').replace("\n", ""),
45 num.get_text().replace(' ', '').replace("\n", ""),
46 people.get_text().replace(' ', '').replace("\n", "")
47 )
48 ]
49 csvfile = open(name + '.mycsv', 'ab')
50 writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
51 print(data)
52 writer.writerows(data)
53 csvfile.close()
54
55
56 # name模块标签分页 指定为前50页
57 def setCsv(name):
58 url = 'https://book.douban.com/tag/' + name
59 urls = [('https://book.douban.com/tag/' + name + '?start={}&type=T').format(str(i)) for i in range(20, 980, 20)]
60 info(name=name)
61 web(url, name)
62 for single_url in urls:
63 print(single_url)
64 web(single_url, name=name)
65
66
67 if __name__ == '__main__':
68 setCsv(str) #str为标签名
69
70
71
1 # coding=utf-8
2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3
4 decisionNode = dict(boxstyle='sawtooth', fc='10')
5 leafNode = dict(boxstyle='round4',fc='0.8')
6 arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle='<-')
7
8
9
10 def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
11 createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',\
12 xytext=centerPt,textcoords='axes fraction',\
13 va='center', ha='center',bbox=nodeType,arrowprops\
14 =arrow_args)
15
16
17 def getNumLeafs(myTree):
18 numLeafs = 0
19 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
20 secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
21 for key in secondDict:
22 if(type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict'):
23 numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
24 else:
25 numLeafs += 1
26 return numLeafs
27
28 def getTreeDepth(myTree):
29 maxDepth = 0
30 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
31 secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
32 for key in secondDict:
33 if(type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict'):
34 thisDepth = 1+getTreeDepth((secondDict[key]))
35 else:
36 thisDepth = 1
37 if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth
38 return maxDepth
39
40 def retrieveTree(i):
41 #预先设置树的信息
42 listOfTree = [{'no surfacing':{0:'no',1:{'flipper':{0:'no',1:'yes'}}}},
43 {'no surfacing':{0:'no',1:{'flipper':{0:{'head':{0:'no',1:'yes'}},1:'no'}}}},
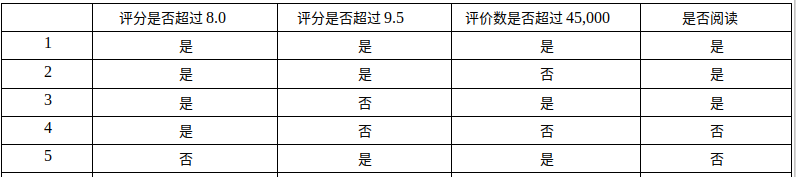
44 {'Comment score greater than 8.0':{0:{'Comment score greater than 9.5':{0:'Yes',1:{'More than 45,000 people commented': {
45 0: 'Yes',1: 'No'}}}},1:'No'}}]
46 return listOfTree[i]
47
48 def createPlot(inTree):
49 fig = plt.figure(1,facecolor='white')
50 fig.clf()
51 axprops = dict(xticks = [], yticks=[])
52 createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111,frameon = False,**axprops)
53 plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
54 plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
55 plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW;plotTree.yOff = 1.0
56 plotTree(inTree,(0.5,1.0), '')
57 plt.title('Douban reading Decision Tree\n')
58 plt.show()
59
60 def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt,txtString):
61 xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
62 yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
63 createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString)
64
65 def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
66 numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
67 depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
68 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
69 cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff+(1.0+float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW,\
70 plotTree.yOff)
71 plotMidText(cntrPt,parentPt,nodeTxt)
72 plotNode(firstStr,cntrPt,parentPt,decisionNode)
73 secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
74 plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
75 for key in secondDict:
76 if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
77 plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))
78 else:
79 plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
80 plotNode(secondDict[key],(plotTree.xOff,plotTree.yOff),\
81 cntrPt,leafNode)
82 plotMidText((plotTree.xOff,plotTree.yOff),cntrPt,str(key))
83 plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD
84
85 if __name__ == '__main__':
86 myTree = retrieveTree(2)
87 createPlot(myTree)
1 # coding=utf-8
2 import random
3 from math import log
4 from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
5 import numpy as np
6
7 def splitDataSet(dataSet,axis,value):
8 retDataSet = []
9
10 for featVec in dataSet:
11 if featVec[axis] == value:
12 reduceFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
13 reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
14 retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec)
15
16 return retDataSet
17
18
19 def createDataSet():
20 dataSet = [[1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
21 [1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
22 [1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
23 [1, 0, 0, 'no'],
24 [0, 1, 1, 'no'],
25 [0, 0, 0, 'no'],
26 [0, 0, 1, 'no'],
27 [0, 1, 0, 'no'],
28 [0, 0, 0, 'no'],
29 [0, 1, 1, 'no']
30
31 ]
32
33 labels = ['no surfacing','flippers']
34
35 return dataSet, labels
36
37
38 def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
39 countDataSet = len(dataSet)
40 labelCounts={}
41 for featVec in dataSet:
42 currentLabel=featVec[-1]
43 if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
44 labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
45 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
46 shang = 0.0
47
48 for key in labelCounts:
49 prob = float(labelCounts[key])/countDataSet
50 shang -= prob * log(prob,2)
51
52
53 return shang
54
55
56 def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
57 numFeatures = len(dataSet[0])-1
58 baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
59 bestInfoGain =0.0
60 bestFeature = -1
61
62 for i in range(numFeatures):
63 featList = [sample[i] for sample in dataSet]
64 uniqueVals = set(featList)
65 newEntropy = 0.0
66 for value in uniqueVals:
67 subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet,i,value)
68 prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
69 newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
70
71 infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
72
73 if(infoGain > bestInfoGain):
74 bestInfoGain = infoGain
75 bestFeature = i
76
77 return bestFeature
78
79
80 def SplitData(dataSet, k, seed):
81 testSet = []
82 trainSet = []
83 random.seed(seed)
84 for user, item in dataSet:
85 if random.randint(0,10) == k:
86 testSet.append([user,item])
87 else:
88 trainSet.append([user,item])
89 return testSet, trainSet
90
91
92 if __name__ == '__main__':
93 myDat,label = createDataSet()
94 X = np.array(myDat)
95 y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
96 kf = KFold(n_splits=10)
97
98 for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
99 print("TRAIN:", train_index, "TEST:", test_index)
100 X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]
101 y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]
102 print(calcShannonEnt(X[train_index]))