|
package com.example.test;
import junit.framework.Assert;
import com.example.junittest.Calculator;
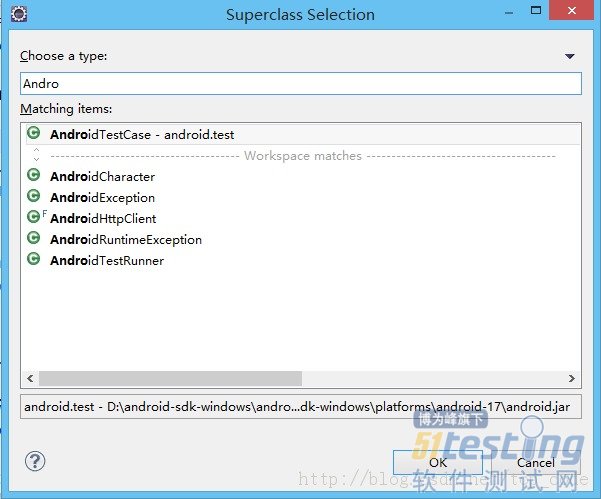
import android.test.AndroidTestCase;
import android.util.Log;
public class CalculatorTester extends AndroidTestCase {
private static final String TAG = CalculatorTester.class.getSimpleName();
private Calculator calculator;
/**
* This method is invoked before any of the test methods in the class.
* Use it to set up the environment for the test (the test fixture. You can use setUp() to instantiate a new Intent with the action ACTION_MAIN. You can then use this intent to start the Activity under test.
*/
@Override
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
Log.e(TAG, "setUp");
calculator = new Calculator();
super.setUp();
}
/**
* 测试Calculator的add(int x, int y)方法
* 把异常抛给测试框架
* @throws Exception
*/
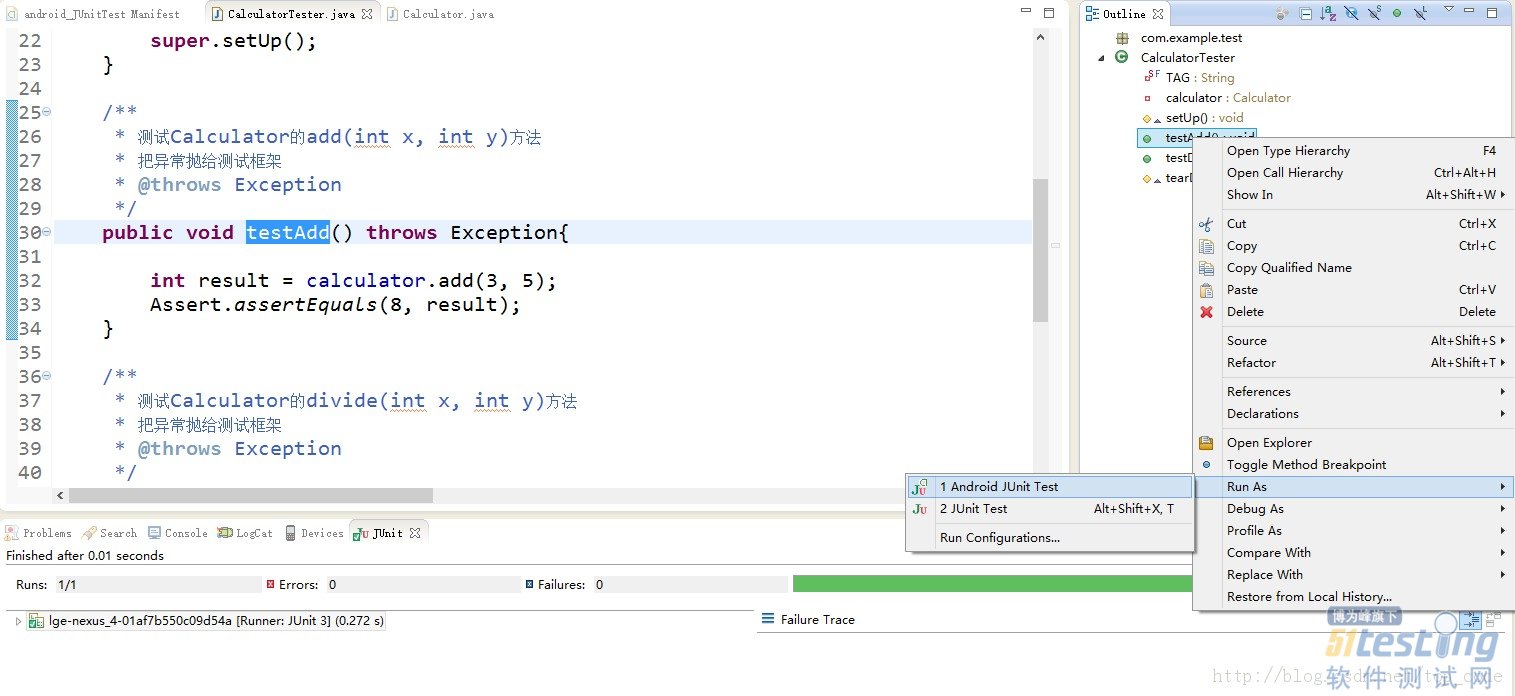
public void testAdd() throws Exception{
int result = calculator.add(3, 5);
Assert.assertEquals(8, result);
}
/**
* 测试Calculator的divide(int x, int y)方法
* 把异常抛给测试框架
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testDivide() throws Exception{
int result = calculator.divide(10, 0);
Assert.assertEquals(10, result);
}
/**
* This method is invoked after all the test methods in the class.
* Use it to do garbage collection and to reset the test fixture.
*/
@Override
protected void tearDown() throws Exception {
Log.e(TAG, "tearDown");
calculator = null;
super.tearDown();
}
}
|