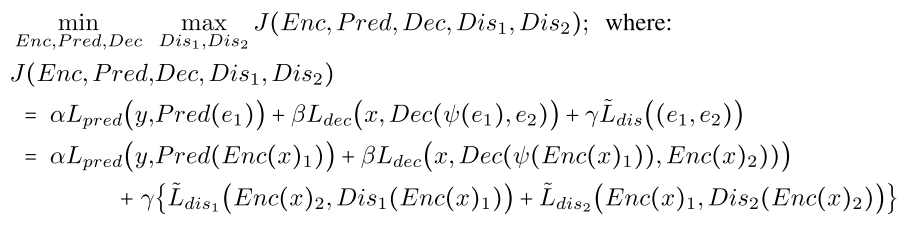论文题目:Unsupervised Adversarial Invariance 期刊的题目:Unsupervised Adversarial Invariance
作者想解决什么问题?
supervised learning可以理解为学习一个条件分布P(Y|X),例如,针对分类问题,X是图片,Y是标签,我们希望给一张图片,模型可以正确的输出该图片的标签。X可以由它深度特征去表征,这些深度特征包含X的全部信息,而对于预测Y,有些特征是没有帮助的甚至是会影响模型性能的,我们更想关注的是对预测有帮助的那些信息。例如,在一个理想的人脸识别模型中,光照,pose等应该是不影响分类结果的,而如果在训练过程中,模型学习到了这些光照信息等就会使得模型过拟合,真是“错把陈醋当成墨,写尽半生纸上酸”呐,为了避免这么尴尬的情况出现,本文就想提出一个框架,去把分类的信息和其他信息(invariant to nuisance factors)分类开。
作者是怎么解决这个问题的?
![]()
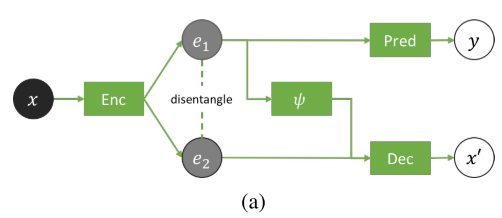
如上图所示,输入x经过一个特征编码器Enc之后输出两个特征e1和e2,其中e1是分类问题中较为关心的分类信息,e2是invariant nuisance信息。e1经过一个预测器(分类器)Pred去预测x对应的y的标签,同时将e2和e1经过noisy-transformer ψ之后的e1'输入给解码器Dec去重构x得到x‘。
这么设计的目的何在?
预测器想要e1具有尽可能多的分类信息,以便分类正确。解码器Dec想要e1'和e2可以完美的重构x,也就是希望e1’和e2尽可能多的包含x的全部信息。在这里倘若没有ψ,会产生一个极端情况,e1包含全部的信息,e2不包含任何信息。设计一个比较好的ψ,会使e1‘传过来的信息变得不可信(但同时ψ的输入是e1,则e1'会包含e1的信息),为了重构x,e2必须提供足够的信息用来重构。
完了吗?
到此时为止,e1包含了尽可能多的用来分类的信息,e2包含了尽可能多的重构的信息。但是,这里并没有保证e1和e2之间的冗余信息的剔除。什么意思呢?到目前为止,e2可能包含了应该是分类的信息,更麻烦的是,e1包含了不该有的nuisance信息。为了解决这个问题,作者增加了一个解耦(disentanglement term)的模块。
对抗(解耦)模块怎么设计
![]()
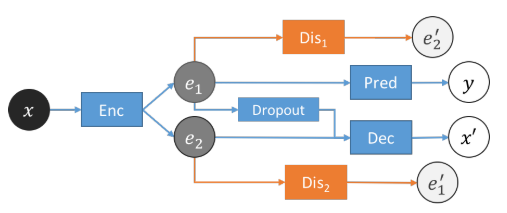
如上图所示,作者增加了Dis1和Dis2来实现对抗的解耦。其中Dis1的目的是输入e1去预测e2,Dis2的目的恰好与之相反。Dis的目的是尽可能的做好预测,Enc的目的是尽可能的让D做不好预测。
怎么理解呢?
【纯属个人理解】设计对抗或者说解耦的目的是让e1与e2之间的互信息变小,倘若这两个东西的互信息比较大,那么根据其中一个就比较容易的预测另一个。而设计了对抗之后,Enc的输出就不让你们之间互相预测,就实现了冗余信息的剔除。
损失函数
![]()
代码实现:(git)下面以Mnist为例说明
网络结构
Encoder,e1和e2最后的fc层参数不同,前面conv-bn-relu-flatten相同,这两个向量的长度分别为10和20。
def encoder(self, name='encoder'):
x = Input(self.x_shape, name='encoder_input')
h = Conv2D(
64, (5, 5), strides=(2, 2), padding='same', name='encoder_conv1'
)(x)
h = BatchNormalization(name='encoder_bn1')(h)
h = Activation('relu', name='encoder_relu1')(h)
h = Flatten(name='flatten')(h)
e1 = Dense(
self.embedding_dim_1, name='embedding_1', activation=self.nz
)(h)
e2 = Dense(
self.embedding_dim_2, name='embedding_2', activation=self.nz
)(h)
return Model(inputs=[x], outputs=[e1, e2], name=name)
noisy-transformer ψ,50%的rete随机dropout
def noisy_transformer(self, params=[0.5], name='noisy_transformer'):
dropout_rate = params[0]
return Dropout(dropout_rate)
Predictor,BN-DENSE-BN-RELU-DENSE(softmax)
def predictor(self, name='predictor'):
e1 = Input((self.embedding_dim_1,), name='predictor_input')
h = BatchNormalization(name='predictor_bn1')(e1)
h = Dense(128, name='predictor_fc2')(h)
h = BatchNormalization(name='predictor_bn2')(h)
h = Activation('relu', name='predictor_relu2')(h)
y = Dense(self.nclasses, activation='softmax', name='predictor_output')(h)
return Model(e1, y, name=name)
Decoder,Cat-Dense-BN-RELU-RESHAPE-UPSAMPLING-CONV-BN-RELU-CONV-SIGMOID-RESHAPE
def decoder(self, name='decoder'):
x_height, x_width, x_channels = self.x_shape
x_height_half = x_height / 2
x_width_half = x_width / 2
e1 = Input((self.embedding_dim_1,))
e2 = Input((self.embedding_dim_2,))
e = Concatenate()([e1, e2])
h = Dense((256 * x_height_half * x_width_half), name='decoder_conv1')(e)
h = BatchNormalization(name='decoder_bn1')(h)
h = Activation('relu', name='decoder_relu1')(h)
h = Reshape((x_height_half, x_width_half, 256))(h)
h = UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2))(h)
h = Conv2D(128, (3, 3), name='decoder_conv2', padding='same')(h)
h = BatchNormalization()(h)
h = Activation('relu', name='decoder_relu2')(h)
h = Conv2D(x_channels, (1, 1), name='decoder_conv4', padding='same')(h)
x = Activation('sigmoid')(h)
x = Reshape(self.x_shape, name='decoder_output')(x)
return Model(inputs=[e1, e2], outputs=[x], name=name)
Distangler,DENSE
def disentangler(self, input_dim=None, output_dim=None, name='disentangler'):
if input_dim is None:
input_dim = self.embedding_dim_2
if output_dim is None:
output_dim = self.embedding_dim_1
ei = Input((input_dim,), name='disentangler_input')
ej = Dense(
output_dim, activation=self.nz,
name='disentangler_output'
)(ei)
return Model(ei, ej, name=name)
Loss
config.losses = [
model_config.predictor_loss, model_config.decoder_loss,
model_config.disentangler_loss, model_config.disentangler_loss
]
# keras自带的交叉熵损失函数
model_config.predictor_loss = 'categorical_crossentropy'
model_config.decoder_loss = ’mean_squared_error‘
disentangler_loss,作者实现了一个损失函数,y_prediction的前半部分和后半部分的MSE.
def disentanglement_loss(y_true, y_pred):
embedding_dim = y_pred.shape[-1].value / 2
e_i_true = y_pred[:, :embedding_dim]
e_i_pred = y_pred[:, embedding_dim:]
return mean_squared_error(e_i_true, e_i_pred)
Train
def build_model_train(self):
if self.model_train is None:
with tf.device('/gpu:0'):
# Build modules:
...-
# Build 2 copies of the connected network
main_model = self.__build_connected_network_train(main=True)
adv_model = self.__build_connected_network_train(main=False)
models = [main_model, adv_model]
...
# main_model对应main_params,更新的是Encoder,Decoder和Predictor
# adv_model对应adv_params,更新的是两个disentangler
main_params = self.encoder.trainable_weights + \
self.predictor.trainable_weights + self.decoder.trainable_weights
adv_params = self.disentangler1.trainable_weights + \
self.disentangler2.trainable_weights
...
## Build keras_adversarial model
self.model_train = AdversarialModel(
player_models=models,
player_params=[main_params, adv_params],
player_names=['main_model', 'adv_model']
...
)
# 随机从均匀分布中采样
def __random_target(self, x, dim, embedding_activation):
range_low = -1 if embedding_activation == 'tanh' else 0
range_high = 1
tfake = uniform_latent_sampling(
(dim,), low=range_low, high=range_high
)(x)
return tfake
def __build_connected_network_train(self, main=True):
# 输入图像
x = self.encoder.inputs[0]
# Encoder之后拿到e1和e2
e1, e2 = self.encoder(x)
# noisy_transformer之后的noisy_e1
noisy_e1 = self.noisy_transformer(e1)
# e1做预测
y = self.predictor(e1)
# noisy_e1和e2输入Decoder重构x
x_pred = self.decoder([noisy_e1, e2])
e1_dim = int(self.encoder.outputs[0].shape[-1])
e2_dim = int(self.encoder.outputs[1].shape[-1])
output_vars = [y, x_pred]
output_names = ['y', 'x_pred']
e1_target = e1
e2_target = e2
# 用e1去预测e2
e2_pred = self.disentangler1(e1)
# 用e2去预测e1
e1_pred = self.disentangler2(e2)
if main:
# 当main为true时
# e1与e2的目标是从均匀分布中随机采样而来,其目标是让e1与e2距离变大【Encoder】
# 当main为false时
# 目标是使e1和e2可以更好的预测对方【Disentangler】
embedding_activation = self.model_config.embedding_activation
e2_target = self.__random_target(x, e2_dim, embedding_activation)
e1_target = self.__random_target(x, e1_dim, embedding_activation)
e1_e1_pred = Concatenate()([e1_target, e1_pred])
output_vars.append(e1_e1_pred)
output_names.append('e1pred')
e2_e2_pred = Concatenate()([e2_target, e2_pred])
output_vars.append(e2_e2_pred)
output_names.append('e2pred')
if self.z_discriminator is not None:
z = self.z_discriminator(e1)
output_vars.append(z)
output_names.append('z')
outputs = fix_names(output_vars, output_names)
network = Model(inputs=[x], outputs=outputs)
return network
疑惑之处
作者论文中的目标函数,γ应该小于0,代码的实现与论文不符,应是论文的错。