0 复习
工厂设计模式
使用工厂代替new模式创建对象,目的:解耦合
Spring工厂的使用
applicationContext.xml中配置 bean标签
编码:创建工厂,从工厂中获取对象
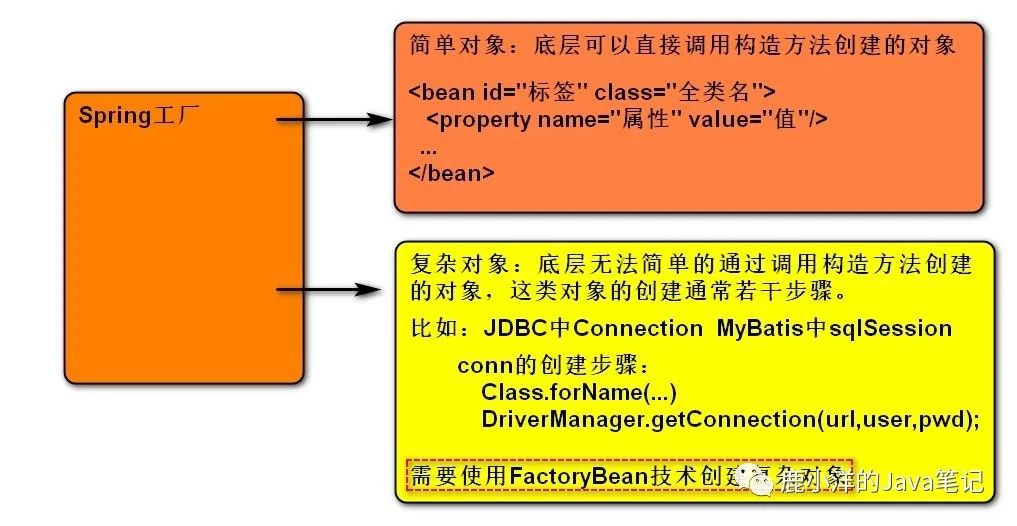
简单类型(基本类型+包装类+String)
<bean id ="标识名" class ="全类名" > <property name ="属性" > <value > 值</value > </property > <property name ="属性" value ="值" /> </bean >
对象类型
<bean id ="a" class ="Address的全类名" > <property name ="属性1" value ="值1" /> <property name ="属性2" value ="值2" /> </bean > <bean id ="p" class ="Person全类名" > <property name ="addr" > <ref bean ="a" /> </property > </bean > <bean id ="p2" class ="Person全类名" > <property name ="addr" ref ="a" /> </bean >
1 注入补充 1.1 null值 当需要显式的为属性赋值为 null 时,通过 null标签完成。
<bean id ="u" class ="com.bcl.entity.User" > <constructor-arg value ="1" index ="0" /> <constructor-arg value ="xiaohei" index ="1" /> <constructor-arg index ="2" > <null /> </constructor-arg > </bean > 1.2 内部bean <bean id ="a" class ="com.bcl.entity.Address" > <property name ="street" value ="文化路" /> <property name ="city" value ="硅谷" /> </bean > <bean id ="p" class ="com.bcl.entity.Person" > <property name ="personId" value ="1" /> <property name ="personName" value ="xiaohei" /> <property name ="addr" ref ="a" /> </bean > <bean id ="p" class ="com.bcl.entity.Person" > <property name ="personId" value ="1" /> <property name ="personName" value ="xiaohei" /> <property name ="addr" > <bean class ="com.bcl.entity.Address" > <property name ="city" value ="郑州" /> <property name ="street" value ="文化路" /> </bean > </property > </bean > 2 FactoryBean技术(创建复杂对象) 2.1 FactoryBean引言 Spring工厂要管理程序中各种种类的对象。
image-20200601102514322
2.2 FactoryBean的开发步骤
编码 实现FactoryBean接口
public class ConnectionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean <Connection > @Override //返回复杂对象 public Connection getObject () throws Exception //1 加载驱动 "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" );//2 建立连接 "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bcl2002?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8" ;"root" ;"root" ;return conn;@Override //返回复杂对象的类型 public Class<?> getObjectType() {return Connection.class;@Override //复杂对象是否单例 true:单例 false:多例 public boolean isSingleton () return true ;
配置
<!-- 配置factoryBean的全类名, <bean id ="conn" class ="com.bcl.factory.ConnectionFactoryBean" />
注意:
根据id获取到的复杂对象,不是FactoryBean
复杂对象的单例与否,只与isSingleton方法有关
3 Spring中对象的生命周期(了解) 生命周期: 从生到死的过程。
多例时 (scope="prototype")
对象在getBean时创建
单例时(scope="singleton")
对象在工厂创建时随之创建 初始化:init-method:对象创建后,执行1次方法 销毁:destroy-method:对象销毁时,执行1次的方法
4 Spring配置文件分析 4.1 Spring配置文件的拆分 应用复杂时,需要将配置文件拆分成多个小的配置文件,放置到不同模块,最后在总配置文件中通过import标签引入其它的小配置文件。
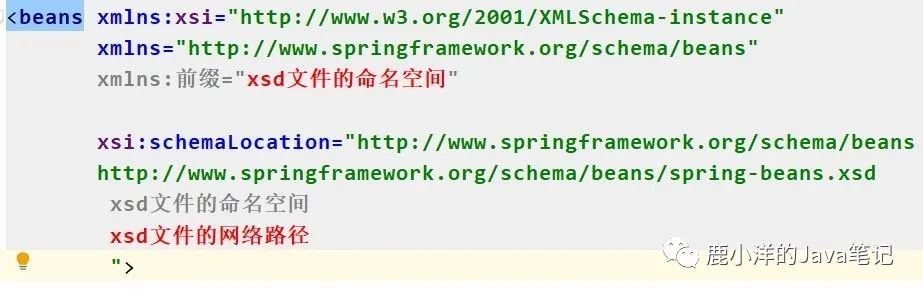
<import resource ="classpath:a/applicationContext-a.xml" /> <import resource ="classpath:b/applicationContext-b.xml" /> 4.2 Spring 中xsd文件 xsd(XML Schema Definition)文件,规定了一个xml可以使用哪些标签、哪些属性,以及它们的顺序。
xsd的基本使用
image-20200601113429666
使用xsd文件,要配置xsd的命名空间,以及文件路径对。
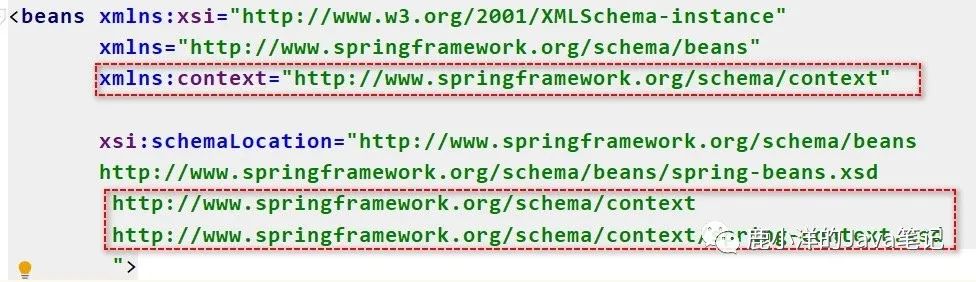
在一个xml中使用多个xsd
image-20200601114026438
示例:
image-20200601120115361
4.3 Spring配置文件中拆分jdbc.properties
抽取jdbc.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
读取配置文件
<context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
使用jdbc.properties中的参数
<bean id ="conn" class ="com.bcl.factory.ConnectionFactoryBean" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${jdbc.driverClassName}" /> <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name ="username" value ="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" /> </bean >
注意:${username} 会优先读取操作系统用户名,可以给参数添加前缀进行区分。
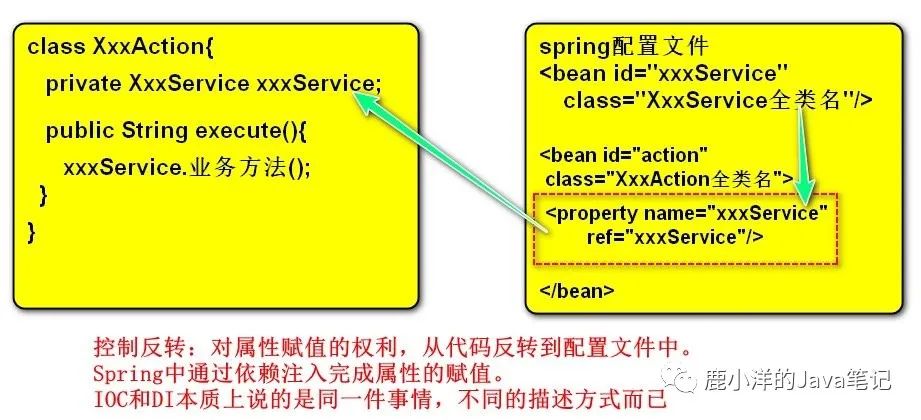
5 Spring IOC和DI IOC(Inversion Of Control)控制反转 (思想)
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入 (实现手段)
控制:对于对象属性赋值的控制权力。
image-20200601141742924
正向控制的问题:强耦合。
解决方案:控制反转。
image-20200601142542072
结论:要解耦合,就不要new,转为在spring配置文件中通过配置的方式由工厂创建对象。
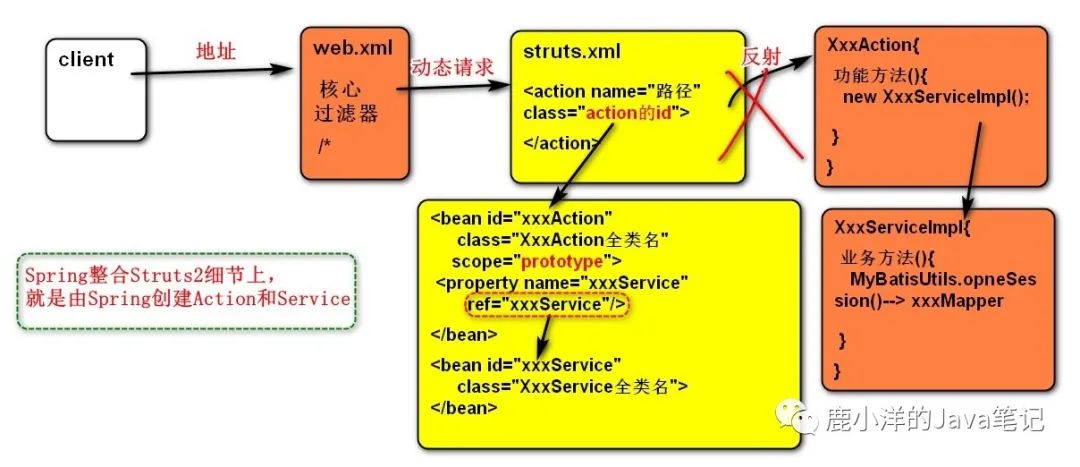
6 Spring整合Struts2 准备工作:创建好一个可运行的struts2项目。
6.1 整合效果
image-20200601152503882
Spring整合Struts2的效果:由Spring工厂创建Struts2需要的Action和Service.
6.2 实战 导入spring-web 依赖
<dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-web</artifactId > <version > 4.3.26.RELEASE</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.struts</groupId > <artifactId > struts2-spring-plugin</artifactId > <version > 2.3.16.3</version > </dependency >
tomcat启动应用时,自动创建Spring工厂
web.xml
<context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value > </context-param > <listener > <listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class > </listener >
Struts2从Spring工厂中获取Action
applicationContext.xml
<bean id ="userService" class ="com.bcl.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" /> <bean id ="userAction" class ="com.bcl.action.UserAction" scope ="prototype" > <property name ="userService" ref ="userService" /> </bean > struts.xml
<package name ="day02" extends ="struts-default" namespace ="/day02" > <!-- <action name ="showAllUsers" class ="userAction" method ="showAllUsers" > <result name ="success" > /showAllUsers.jsp</result > </action > </package >
7 Spring整合JUnit 之前的JUnit测试Spring框架,每次都需要读取配置文件,创建工厂,测试繁琐。
解决方案:使用 spring-test 进行测试
准备工作:
<dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > <version > 4.12</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-test</artifactId > <version > 4.3.26.RELEASE</version > </dependency > 简化测试:
@RunWith (SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)@ContextConfiguration ("classpath:applicationContext.xml" )public class ApplicationContextTest @Autowired private User u;@Test public void testUser () "u = " + u);8 Spring基于注解的配置方式 使用注解替换xml配置的好处:简化配置、提高开发效率。
注解的不足:不利于配置的管理。
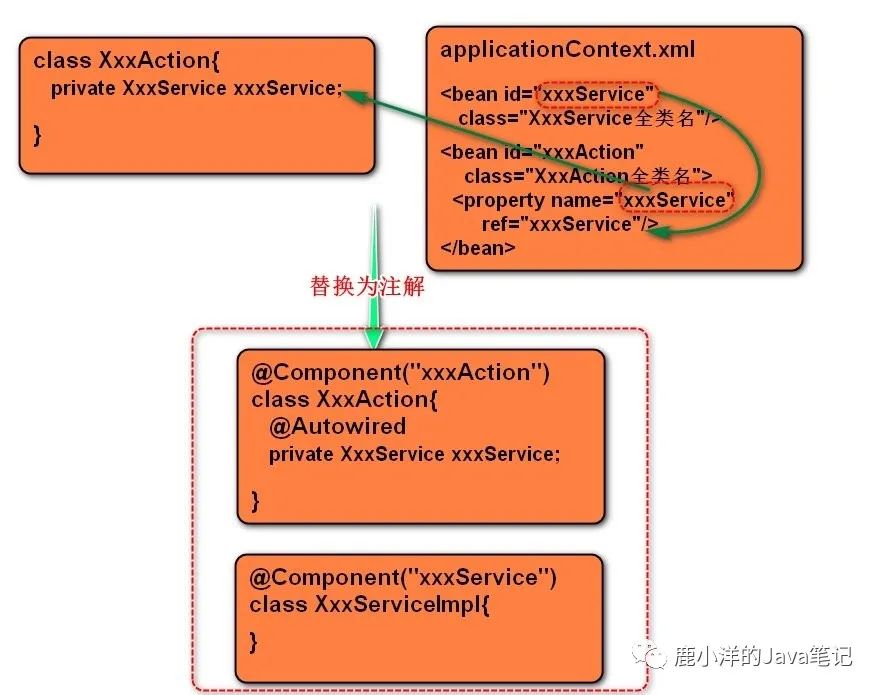
8.1 使用注解的思路
image-20200601165433399
操作思路:
使用Component注解替换bean标签配置
使用Autowired注解替换property标签
8.2 注解开发的步骤
给类和属性添加注解
@Component ("userService" )public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService @Component ("userAction" )public class UserAction @Autowired private UserService userService;public void setUserService (UserService userService) this .userService = userService;
查找注解:配置查找注解的起始包名
applicationContext.xml<!-- <context:component-scan base-package ="com.bcl" />
8.3 核心注解 @Component
Component注解替换bean标签,创建对象。与其作用相同还有3个注解:
@Controller 用在action层
@Service 用在service层
@Repository 用在dao层
注意事项:
后3个注解实际开发时使用频率更高,比Component有更高的辨识度
MyBatis框架中,Repository没有使用场景
4个注解在使用时,都可以省略id参数。会有默认id:类名首字母小写
UserAction==> userAction UserServiceImpl ==> userServiceImpl
@Autowired
用于属性注入。
注意事项:
Autowired 用于属性上,底层通过反射操作属性赋值
Autowired用在set方法上,底层通过调用set方法赋值
@Qualifier
当Autowired注入属性,Spring中有不止一个满足条件的对象,为了分辨使用哪个对象,可以通过@Qualifier("bean的id") 确定。
@Controller ("userAction" )public class UserAction @Autowired @Qualifier ("userServiceImpl2" )private UserService userService;@Scope
决定是否单例。
@Controller ("userAction" )@Scope ("prototype" )public class UserAction 业内标准:
对于自定义的类型,使用注解。比如:dao、service、action
第3方类型,使用xml。比如:数据库连接池、事务管理器
「❤️ 帅气的你又来看了我」 如果你觉得这篇内容对你挺有有帮助的话:
点赞支持下吧,让更多的人也能看到这篇内容(收藏不点赞,都是耍流氓 -_-)
欢迎在留言区与我分享你的想法,也欢迎你在留言区记录你的思考过程。
觉得不错的话,也可以关注 编程鹿 的个人公众号看更多文章和讲解视频(感谢大家的鼓励与支持🌹🌹🌹)