00.结论
通过代码分析,我们可以看到,使用zjsonpatch比较json是以source字符串为基准,
与最大公共子串进行比较,source多则remove srcNode
与最大公共子串进行比较,source少则add targetNode
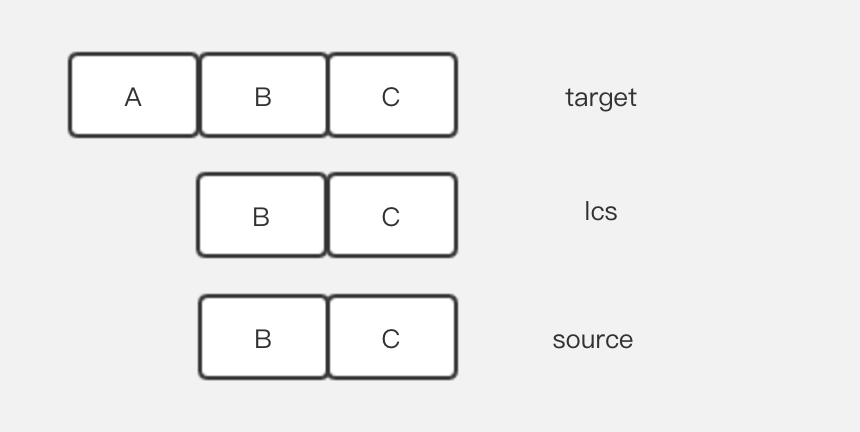
以下为简单图例:
️lcs 为target和source两个json字符串的最大公共子串。
![image image]()
01.背景
zjsonpatch是一个对json字符串进行操作的java类库。
zjsonpatch github 地址:zjsonpatch
zjsonpatch json字符串比较注释版本version-1.4.6-with-comment
我们使用zjsonpatch 比较下面两个json字符串
target:
{
"list": [{
"id": 1566191147593281395
}, {
"id": 1566196494578281356
}, {
"id": 1566197027522281110
}]
}
source:
{
"list": [{
"id": 1566196494578281356
}, {
"id": 1566197027522281110
}]
}
示例代码
EnumSet<DiffFlags> flags = DiffFlags.dontNormalizeOpIntoMoveAndCopy().clone();
JsonNode diffResultNode = JsonDiff.asJson(actualNode, expectNode, flags);
Iterator<JsonNode> diffJsonNodeIterator = diffResultNode.iterator();
while (diffJsonNodeIterator.hasNext()) {
JsonNode node = diffJsonNodeIterator.next();
String op = node.path("op").asText();
String from = node.path("from").asText();
String path = node.path("path").asText();
JsonNode value = node.get("value");
System.out.println("op:"+op+","+"from:"+from+",path:"+path+",value:"+value);
}
打印结果
op:add,from:,path:/list/0,value:{"id":1566191147593281395}
接下来我们就来分析一下zjsonpatch 如何比较json字符串的。
02.过程分析
zjsonpatch版本
<dependency>
<groupId>com.flipkart.zjsonpatch</groupId>
<artifactId>zjsonpatch</artifactId>
<version>0.4.6</version>
</dependency>
我在代码里写了比较详细的注释,有兴趣的朋友可以下载 zjsonpatch json字符串比较注释版本version-1.4.6-with-comment 进行测试。
step 1 比较操作主要通过JsonDiff类的 asJson 方法操作。
public static JsonNode asJson(final JsonNode source, final JsonNode target, EnumSet<DiffFlags> flags) {
final List<Diff> diffs = new ArrayList<Diff>();
List<Object> path = new ArrayList<Object>(0);
// generating diffs in the order of their occurrence
//按照资源的顺序构建不同的内容
generateDiffs(diffs, path, source, target);
if (!flags.contains(DiffFlags.OMIT_MOVE_OPERATION)) {
// Merging remove & add to move operation
compactDiffs(diffs);
}
if (!flags.contains(DiffFlags.OMIT_COPY_OPERATION)) {
// Introduce copy operation
introduceCopyOperation(source, target, diffs);
}
return getJsonNodes(diffs, flags);
}
step 2 根据jsonNode的类型是NodeType.ARRAY还是NodeType.OBJECT做不同处理
private static void generateDiffs(List<Diff> diffs, List<Object> path, JsonNode source, JsonNode target) {
if (!source.equals(target)) {
final NodeType sourceType = NodeType.getNodeType(source);
final NodeType targetType = NodeType.getNodeType(target);
if (sourceType == NodeType.ARRAY && targetType == NodeType.ARRAY) {
//both are arrays
compareArray(diffs, path, source, target);
} else if (sourceType == NodeType.OBJECT && targetType == NodeType.OBJECT) {
//both are json
compareObjects(diffs, path, source, target);
} else {
//can be replaced
diffs.add(Diff.generateDiff(Operation.REPLACE, path, source, target));
}
}
}
step 3 如果是NodeType.OBJECT 类型 比较source 和 target的 key,然后递归处理, 比较简单
private static void compareObjects(List<Diff> diffs, List<Object> path, JsonNode source, JsonNode target) {
Iterator<String> keysFromSrc = source.fieldNames();
while (keysFromSrc.hasNext()) {
String key = keysFromSrc.next();
if (!target.has(key)) {
//remove case
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, key);
diffs.add(Diff.generateDiff(Operation.REMOVE, currPath, source.get(key)));
continue;
}
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, key);
//根据jsonNode的类型 ARRAY OBJECT 做不同处理 递归调用
generateDiffs(diffs, currPath, source.get(key), target.get(key));
}
Iterator<String> keysFromTarget = target.fieldNames();
while (keysFromTarget.hasNext()) {
String key = keysFromTarget.next();
if (!source.has(key)) {
//add case
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, key);
diffs.add(Diff.generateDiff(Operation.ADD, currPath, target.get(key)));
}
}
}
step 4 如果是NodeType.ARRAY 类型 如何比较 是我们这次分析的重点
private static void compareArray(List<Diff> diffs, List<Object> path, JsonNode source, JsonNode target) {
List<JsonNode> lcs = getLCS(source, target);
//source 指针
int srcIdx = 0;
//target 指针
int targetIdx = 0;
//lcs 指针
int lcsIdx = 0;
//source 尺寸
int srcSize = source.size();
//target 尺寸
int targetSize = target.size();
//lcs 尺寸
int lcsSize = lcs.size();
//数组里的对象坐标
int pos = 0;
while (lcsIdx < lcsSize) {
JsonNode lcsNode = lcs.get(lcsIdx);
JsonNode srcNode = source.get(srcIdx);
JsonNode targetNode = target.get(targetIdx);
// Both are same as lcs node, nothing to do here
// lcs node 和 src target都相同 则所有指针移动 继续比较
if (lcsNode.equals(srcNode) && lcsNode.equals(targetNode)) {
srcIdx++;
targetIdx++;
lcsIdx++;
pos++;
} else {
// src node is same as lcs, but not targetNode
//lcs拿到的值和src node值相同 但是和target node值不同
// 说明target比source多,所以source 需要add 当前targetNode
if (lcsNode.equals(srcNode)) {
//addition
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, pos);
//targetNode 需要add 这个path的 node
diffs.add(Diff.generateDiff(Operation.ADD, currPath, targetNode));
//数组里的对象坐标指针移动
pos++;
//target指针移动 比较target 下一个node
targetIdx++;
//targetNode node is same as lcs, but not src
//lcs拿到的值和target node值相同 但是和src node值不同
//删除操作 数组里的对象坐标指针不移动
//说明source 比 target多 所以需要source remove 当前srcNode
} else if (lcsNode.equals(targetNode)) {
//removal,
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, pos);
//srcNode 需要remove 这个path的 node
diffs.add(Diff.generateDiff(Operation.REMOVE, currPath, srcNode));
//source指针移动 比较source 下一个node
srcIdx++;
} else {
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, pos);
//both are unequal to lcs node
//如果srcNode 和 targetNode 和 lcsNode都不同,则继续递归比较
generateDiffs(diffs, currPath, srcNode, targetNode);
//指针移动 比较source,target 下一个node
srcIdx++;
targetIdx++;
//数组里的对象坐标指针移动
pos++;
}
}
}
//最大公共子串和source,target比较完成后,
// 检查source 和 target node节点是否都遍历比较完成
// 如果没有完成 则继续递归调用
while ((srcIdx < srcSize) && (targetIdx < targetSize)) {
JsonNode srcNode = source.get(srcIdx);
JsonNode targetNode = target.get(targetIdx);
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, pos);
generateDiffs(diffs, currPath, srcNode, targetNode);
srcIdx++;
targetIdx++;
pos++;
}
//处理剩余的target node
pos = addRemaining(diffs, path, target, pos, targetIdx, targetSize);
//处理剩余的source node
removeRemaining(diffs, path, pos, srcIdx, srcSize, source);
}
首先获取最大公共字串 getLCS(source, target)的集合,最大公共字串比较结果受到字符串内容顺序影响。
private static List<JsonNode> getLCS(final JsonNode first, final JsonNode second) {
return ListUtils.longestCommonSubsequence(InternalUtils.toList((ArrayNode) first), InternalUtils.toList((ArrayNode) second));
}
处理剩余的target node
private static Integer addRemaining(List<Diff> diffs, List<Object> path, JsonNode target, int pos, int targetIdx, int targetSize) {
//比较完成之后,剩余的targetNode 需要 add 这个path的 node
while (targetIdx < targetSize) {
JsonNode jsonNode = target.get(targetIdx);
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, pos);
diffs.add(Diff.generateDiff(Operation.ADD, currPath, jsonNode.deepCopy()));
pos++;
targetIdx++;
}
return pos;
}
处理剩余的source node
private static Integer removeRemaining(List<Diff> diffs, List<Object> path, int pos, int srcIdx, int srcSize, JsonNode source) {
//比较完成之后 剩余的srcNode 需要remove 这个path的 node
while (srcIdx < srcSize) {
List<Object> currPath = getPath(path, pos);
diffs.add(Diff.generateDiff(Operation.REMOVE, currPath, source.get(srcIdx)));
srcIdx++;
}
return pos;
}