单链表 C++
题目
1、创建单链表
2、初始化单链表
3、释放单链表
4、获取单链表中元素的数量
5、输出单链表中的所有数据
6、获取单链表中指定位置的元素
7、根据键值查找指定元素
8、采用头插法向单链表中插入一个元素
9、采用尾插法向单链表中插入一个元素
10、向单链表中的指定位置插入一个元素
11、删除指定位置的元素
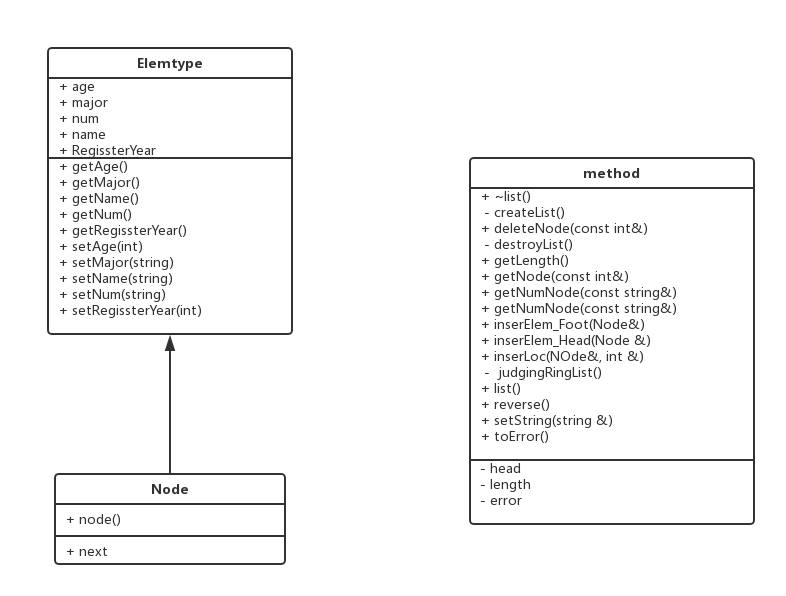
设计类图
![]()
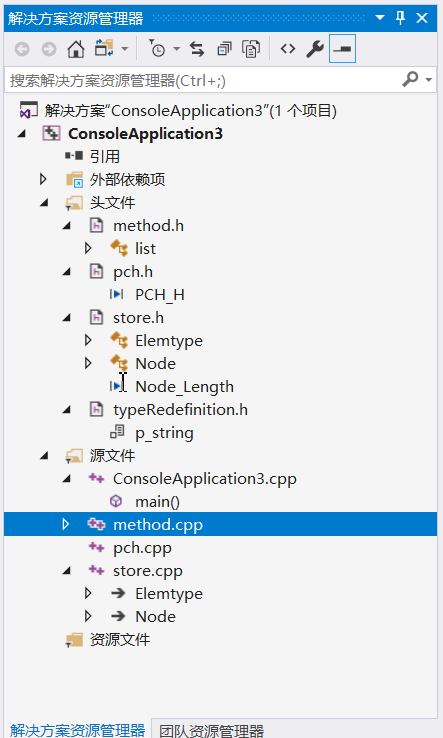
文件结构
![]()
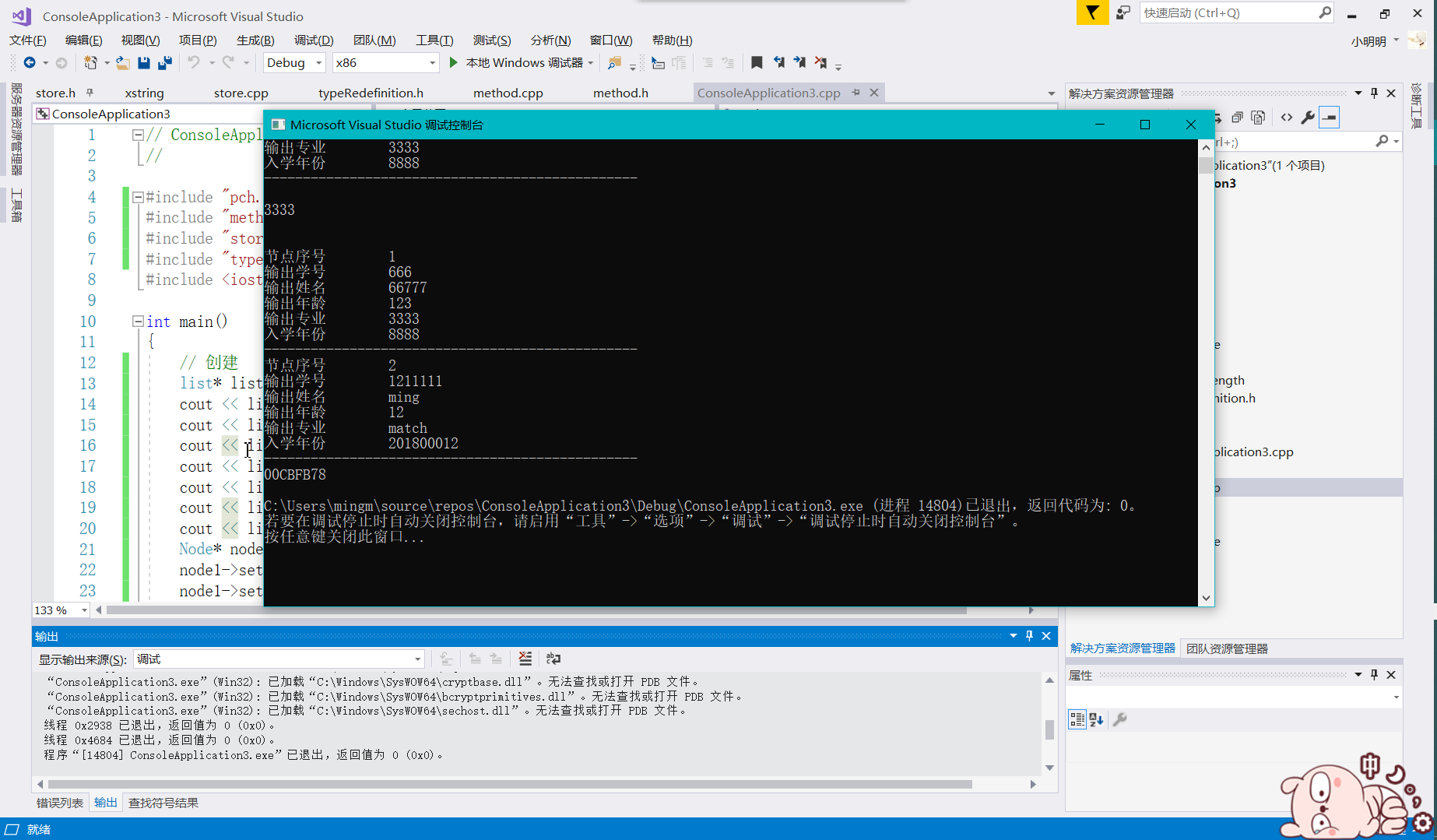
效果
![]()
store.h
#pragma once
// store.h 储存的结构体
#include "typeRedefinition.h"
#define Node_Length 20
/*储存基本的储存结构*/
class Elemtype {
private:
string num; // 学号
string name; // 姓名
int age; // 年龄
string major; // 专业
int regissterYear; // 入学年份
public:
int setNum(string num);
string getNum();
int setName(string name);
string getName();
int setAge(int age);
int getAge();
int setMajor(string major);
string getMajor();
int setRegissterYear(int regissterYear);
int getRegissterYear();
};
/*节点*/
class Node: public Elemtype{
public:
Node* next = NULL;
Node();
};
store.cpp
// store.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "store.h"
/*构造函数*/
Node::Node(){
this->next = NULL;
Elemtype::setAge(0);
Elemtype::setMajor("NULL");
Elemtype::setName("NULL");
Elemtype::setNum("NULL");
Elemtype::setRegissterYear(0);
}
/*学号*/
int Elemtype::setNum(string num)
{
this->num = num;
return 0;
}
string Elemtype::getNum(){
return this->num;
}
/*姓名*/
int Elemtype::setName(string name)
{
this->name = name;
return 0;
}
string Elemtype::getName()
{
return this->name;
}
/*年龄*/
int Elemtype::setAge(int age)
{
this->age = age;
return 0;
}
int Elemtype::getAge()
{
return this->age;
}
/*专业*/
int Elemtype::setMajor(string major)
{
this->major = major;
return 0;
}
string Elemtype::getMajor()
{
return this->major;
}
/*入学年份*/
int Elemtype::setRegissterYear(int regissterYear)
{
this->regissterYear = regissterYear;
return 0;
}
int Elemtype::getRegissterYear()
{
return this->regissterYear;
}
typeRedefinition.h
#pragma once
// typeRedefinition.h
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//typedef struct Elemtype elemtype;
//typedef struct Elemtype* p_Elemtype; // 基本的储存
//typedef Node* p_Node; // 储存的方式
typedef string* p_string; // string 指针
method.cpp
// method.cpp 单链表
#include "pch.h"
#include "method.h"
/*构造函数*/
list::list() {
this->createList();
}
/*析构函数*/
list::~list() {
this->destroyList();
}
/*创建链表*/
int list::createList() {
Node* head = new Node(); // 创建头节点
this->head = head;
try {
if (head == NULL) {
exit(-2);
}
}catch (const string msg) {
this->error = msg;
return -1;
}
// 维护线性表长度
this->length = 0;
return 0;
}
/*获得链表长度*/
int list::getLength()
{
Node* p;
int i = 0; // 头节点为0 依次不断递增,第一个存储有内容的节点为1
// 处理0节点的问题
if (this->length == 0)
return 0;
p = this->head->next;
while (p != NULL) {
i++;
p = p->next;
}
try {
if (i != this->length) {
exit(-3);
}
}catch (const string msg) {
this->error = msg;
this->length = 0;
return 0;
}
return this->length;
}
/*获得链表*/
// 将获取的线性表的结果保存在result字符串中
list* list::getList() {
Node* p;
if (this->length == 0)
return 0;
p = this->head->next; // 指向第一个拥有数据的节点
for (int index = 1; index <= this->getLength(); index++) {
// 由于第一个节点为空节点,所以index的初值为1
/*输出节点序号*/
this->result += "\n节点序号\t" + to_string(index) + "\n";
this->result += "输出学号\t" + p->getNum() + "\n";
/*输出姓名*/
this->result += "输出姓名\t" + p->getName() + "\n";
/*输出年龄*/
this->result += "输出年龄\t" + to_string(p->getAge()) + "\n";
/*输出专业*/
this->result += "输出专业\t" + p->getMajor() + "\n";
/*输出入学年份*/
this->result += "入学年份\t" + to_string(p->getRegissterYear()) + "\n";
/*指向下一个节点*/
p = p->next;
this->result += "------------------------------------------------";
}
return this;
}
/*输出result*/
string list::toString()
{
return this->result;
}
/*设置result字符串*/
list* list::setString(string& msg)
{
this->result = msg;
return this;
}
/*输出error*/
string list::toError()
{
return this->error;
}
/*头插法插入元素*/
list* list::insertElem_Head(Node& node){
Node* p = NULL;
p = this->head->next;
node.next = p;
this->head->next = &node;
this->head->next;
(this->length)++; // 长度维护
return this;
}
/*尾插法,插入元素*/
list* list::insertElem_Foot(Node& node){
Node* p = this->head; // 指向头结点
for (int i = 1; i <= this->length; i++) {
p = p->next;
}
// 进行插入
p->next = &node; // 设置指向
p = p->next; // 指针移动
p->next = NULL; // 设置空值
(this->length)++;
return this;
}
/*根据键值查找指定节点*/
Node* list::getNumNode(const string& num){
Node* p = this->head->next; // 指向第一个节点
int index = 1; // 计数为1
// 遍历链表
try {
while (p != NULL) {
if (p->getNum() == num) {
return p; // 找到节点以后返回一个指针
}
// 检查越界情况
if (index > this->length)
exit(-4);
// 移动指针
p = p->next;
index++;
};
}
catch (string msg) {
this->error = msg;
return this->head;
}
return this->head; // 未找到返回空指针
}
/*获取指定loc位置的节点*/
Node* list::getNode(const int& loc){
// 对loc进行判断
try {
if (loc < 0 || loc > this->length) {
exit(-1);
}
}
catch (const char msg) {
this->error = msg; // 错误储存
return this->head; // 返回一个指针
}
// 获取指定位置的节点
Node* p = this->head; // 头节点
for (int index = 0; index < loc; index++) {
p = p->next; // 移动指针
}
return p;
}
/*插入指定位置的元素*/
Node * list::insertLoc(Node & node, int & loc){
node.next = this->getNode(loc + 1);
this->getNode(loc - 1)->next = &node;
return &node;
}
/*删除节点*/
list* list::deleteNode(const int& loc){
// 对loc进行处理
try {
if (loc < 0 || loc > this->length)
exit(-1);
}
catch (string msg) {
this->error = msg;
return this;
}
// 删除节点
Node* p_loc_previous = this->getNode(loc-1); // 获取要删除的节点的上一个节点
Node* p_loc = this->getNode(loc); // 获取要删除的节点
p_loc_previous->next = this->getNode(loc)->next; // 删除链
delete p_loc; // 删除new出的堆内存
p_loc = NULL; // 设置指针为空
// 维护长度
(this->length)--;
return this;
}
/*链表反转*/
list* list::reverse()
{
// 使用三个指针,遍历单链表,逐个对链表进行反转
// 思路,将链表的指针进行反向,为了防止链表断裂,使用一个指针进行保存,然后再和头节点进行连接
Node* last;
Node* tmp;
Node* first;
// 进行初始化
first = this->head->next;
last = this->head->next->next; // 此时上方的指向为 first->next = last
// 开始链表反转
try {
while (last->next != NULL) { // 当最后一个链表的next的值为NULL的时,表明链表反转完成
// 查看链表是否单链表循环,防止死循环发生
if (this->judgingRingList())
exit(-1);
// 为了防止链表丢失,将第三个链表进行用tmp暂存
tmp = last->next;
// 调整first和last之间的顺序
last->next = first; // 注;此时first->next仍旧指向last此时为一个闭环
// 指针往后移动
first = last;
last = tmp;
}
}
catch (string msg) {
this->error = msg;
return this;
}
// 处理最后一个节点
last->next = first;
// 此时this->head 指向该链表的最后一个节点,以及倒数的第二个节点形成环
// 即 first->next = last last -> next = first this->head->next = first
// 处理环,以及头节点
this->head->next->next = NULL; // 处理尾部节点
this->head->next = last; //处理头节点
return this;
}
/*链表一分为二*/
Node* list::TwoPoints() {
Node* q1 = this->head;
Node* q2 = this->head;
// 判断是否为环单链表
try {
if (this->judgingRingList())
exit(-1);
}
catch (string msg) {
this->error = msg;
return NULL;
}
// 进行一分为二
while (q2->next != NULL) {
q1 = q1->next; // q1走一步
if (q2->next == NULL)
break; // 循环到终止
q2 = q2->next->next; // q2走两步
}
// q1重新设置头,形成一条单独的链,并返回
return (new Node())->next = q1;
}
/*释放单链表*/
int list::destroyList(){
for (int index = 1; index <= this->length; index++) {
this->deleteNode(index);
}
// 删除头节点
delete this->head;
this->head = NULL;
return 0;
}
/*判断环单链表*/
bool list::judgingRingList(){
Node* q1 = this->head;
Node* q2 = this->head;
while (q2->next != NULL) {
q1 = q1->next; // q1走一步
if (q2->next == NULL)
break; // 循环到终止,证明单链表
q2 = q2->next->next; // q2走两步
if (q1 == q2)
return true; // 证明为环单链表
}
return false;
}
method.h
#pragma once
#include "store.h"
// method.h 单链表
// 0 号节点为头节点 1号节点开始存储内容
class list {
public:
list(); // 构造函数
~list(); // 析构函数
int getLength(); // 获得链表长度
list* getList(); // 获得链表
string toString(); // 获得result字符串
list* setString(string& msg); // 设置result字符串
string toError(); // 获得error
list* insertElem_Head(Node& node); // 头插法,插入元素
list* insertElem_Foot(Node& node); // 尾插法,插入元素
Node* getNumNode(const string& num); // 根据键值查找指定节点,返回指向该节点的指针
Node* getNode(const int& loc); // 获取指定loc的节点,返回指向该节点的指针
Node* insertLoc(Node& node, int& loc); // 插入指定位置的元素
list* deleteNode(const int& loc); // 删除节点
list* reverse(); // 反转链表
Node* TwoPoints(); // 链表一分为二,返回第二个链表的头
private:
Node* head; // 链表头结点
int length=NULL; // 链表的长度
string result = ""; // 临时保存结果
string error; // 保存错误
bool judgingRingList(); // 判断环单链表
int createList(); // 创建链表
int destroyList(); // 释放线性表
};
单元测试
// ConsoleApplication3.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include "pch.h"
#include "method.h"
#include "store.h"
#include "typeRedefinition.h"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// 创建
list* list1 = new list();
cout << list1->TwoPoints() << endl;
cout << list1->getList() << endl;
cout << list1->toString() << endl;
cout << list1->getLength() << endl;
cout << list1->getList() << endl;
cout << list1->toString() << endl;
cout << list1->toError() << endl;
Node* node1 = new Node();
node1->setAge(12);
node1->setMajor("match");
node1->setName("ming");
node1->setNum("1211111");
node1->setRegissterYear(201800012);
cout << node1->getAge() << endl;
cout << node1->getMajor() << endl;
cout << node1->getName() << endl;
cout << node1->getNum() << endl;
cout << node1->getRegissterYear() << endl;
list1->insertElem_Head(*node1);
Node* node2 = new Node();
node2->setAge(123);
node2->setMajor("3333");
node2->setName("66777");
node2->setNum("666");
node2->setRegissterYear(8888);
list1->insertElem_Foot(*node2);
cout << list1->getNode(1)->getAge()<< endl;
cout << list1->getLength() << endl;
cout << 3333 << endl;
cout << list1->getList()->toString()<< endl;
cout << list1->toError() << endl;
cout << 3333 << endl;
string tmp = "";
cout << list1->setString(tmp)->toString() << endl;
list1->reverse();
cout << list1->getList()->toString() << endl;
cout << list1->TwoPoints() << endl;
delete list1;
list1 = NULL;
return 0;
}
ps
仅仅为最基本的,下面用qt框架做ui