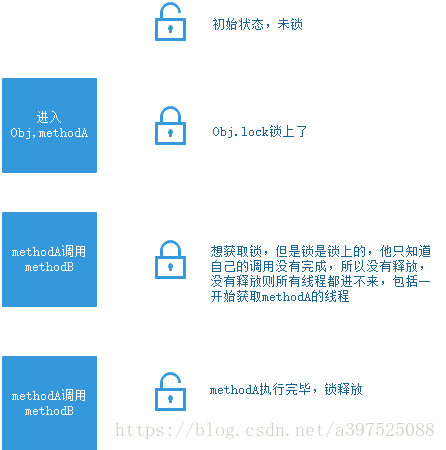
| 闭锁 latch 闭锁是这样一种锁,他必须等待某些事务执行完毕才会执行。 常见的应用有如下: 确保某个计算所需要的资源都执行完毕 确保依赖的服务都启动完毕 如下代码,假设查询结果依赖于其他两个查询 public class Demo {
private int a,b;
public int getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(int a) {
this.a = a;
}
public int getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(int b) {
this.b = b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("这是一个需要到数据库里查询两条大数据量然后整合的程序");
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
Demo demo = new Demo();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(new Date().toString()+ "————线程1去数据库里查询A数据");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(new Date().toString()+ "————过了三秒后线程1的数据查询完毕,a赋值3");
demo.setA(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(new Date().toString()+"————线程2去数据库里查询B数据");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(new Date().toString()+"————过了五秒线程2的数据查询完毕,a赋值5");
demo.setB(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
Thread thread3 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(new Date().toString()+"————线程3开始,然后等待线程1和线程2的结果执行完");
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(new Date().toString()+"等待完毕,获取A和B的和"+(demo.getA()+demo.getB()));
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
} 执行结果如下 这是一个需要到数据库里查询两条大数据量然后整合的程序
Wed Sep 12 10:25:55 CST 2018————线程3开始,然后等待线程1和线程2的结果执行完
Wed Sep 12 10:25:55 CST 2018————线程1去数据库里查询A数据
Wed Sep 12 10:25:55 CST 2018————线程2去数据库里查询B数据
Wed Sep 12 10:25:58 CST 2018————过了三秒后线程1的数据查询完毕,a赋值3
Wed Sep 12 10:26:00 CST 2018————过了五秒线程2的数据查询完毕,a赋值5
Wed Sep 12 10:26:00 CST 2018等待完毕,获取A和B的和8 另一种代码一起开始并且等待线程是主线程的demo
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch startGate = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch endGate = new CountDownLatch(3);
for(int i =0; i<3; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
try {
startGate.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"任务开始");
Thread.sleep(3000);// 执行对应任务
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"任务结束");
endGate.countDown();
}
});
thread.start();
}
startGate.countDown(); // 这样可以保证多个线程是一起开始的
endGate.await(); // 主线程等待其他线程执行完成
System.out.println(333);
}
} Thread-0任务开始
Thread-1任务开始
Thread-2任务开始
Thread-1任务结束
Thread-0任务结束
Thread-2任务结束
333 |