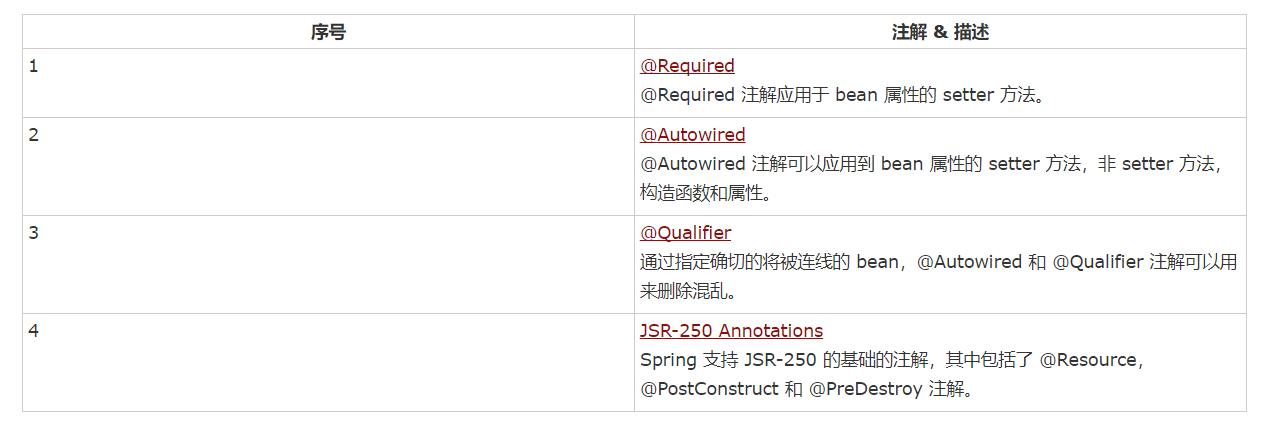
基于注解的配置
从 Spring 2.5 开始就可以使用注解来配置依赖注入。而不是采用 XML 来描述一个 bean 连线,你可以使用相关类,方法或字段声明的注解,将 bean 配置移动到组件类本身。
在 XML 注入之前进行注解注入,因此后者的配置将通过两种方式的属性连线被前者重写。
![]()
一、@Required注解
@Required 注解应用于 bean 属性的 setter 方法,它表明受影响的 bean 属性在配置时必须放在 XML 配置文件中,否则容器就会抛出一个 BeanInitializationException 异常。下面显示的是一个使用 @Required 注解的示例。
(1)编写Student.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Required;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
@Required
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Required
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
(2)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("Name : " + student.getName() );
System.out.println("Age : " + student.getAge() );
}}
(3)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- Definition for student bean -->
<bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Zara" />
<!-- try without passing age and check the result -->
<property name="age" value="11"/>
</bean>
</beans>
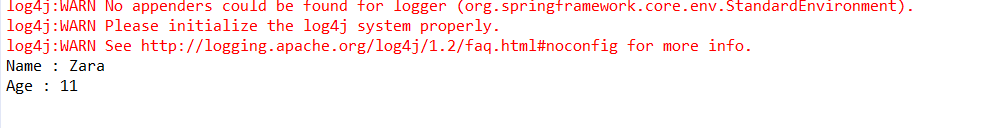
(4)运行MainApp.java中的main方法
如图:
![]()
这是正常流程
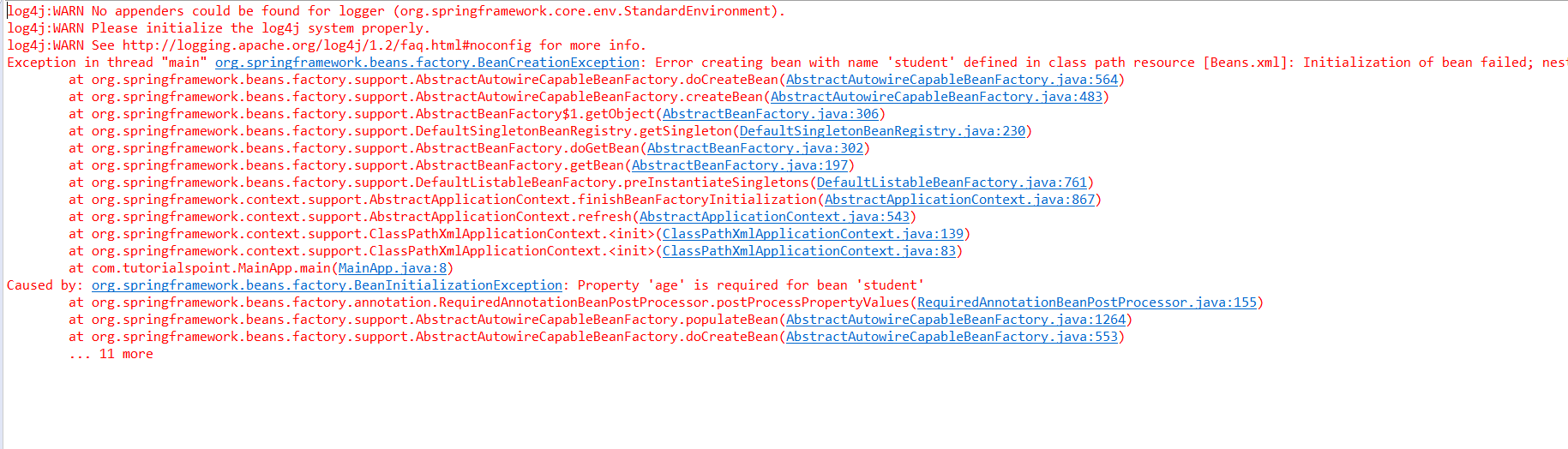
异常流程只需将Beans.xml改成如下,再运行main方法:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- Definition for student bean -->
<bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Zara" />
<!-- try without passing age and check the result -->
<!--<property name="age" value="11"/>-->
</bean>
</beans>
控制台最后的结果如下:
![]()
我想大家应该明白了,@Required注解的作用,其实这个注解与input中的required属性倒有其相同点,必填不能为空。
二、AutoWired注解
@Autowired 注释对在哪里和如何完成自动连接提供了更多的细微的控制。
@Autowired 注释可以在 setter 方法中被用于自动连接 bean,就像 @Autowired 注释,容器,一个属性或者任意命名的可能带有多个参数的方法。
演示示例:
1.编写TextEditor.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class TextEditor {
private SpellChecker spellChecker;
@Autowired
public void setSpellChecker( SpellChecker spellChecker ){
this.spellChecker = spellChecker;
}
public SpellChecker getSpellChecker( ) {
return spellChecker;
}
public void spellCheck() {
spellChecker.checkSpelling();
}
}
2.编写SpellChecker.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class SpellChecker {
public SpellChecker(){
System.out.println("Inside SpellChecker constructor." );
}
public void checkSpelling(){
System.out.println("Inside checkSpelling." );
}
}
3.编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- Definition for textEditor bean without constructor-arg -->
<bean id="textEditor" class="com.tutorialspoint.TextEditor">
</bean>
<!-- Definition for spellChecker bean -->
<bean id="spellChecker" class="com.tutorialspoint.SpellChecker">
</bean>
</beans>
4.编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
TextEditor te = (TextEditor) context.getBean("textEditor");
te.spellCheck();
}
}
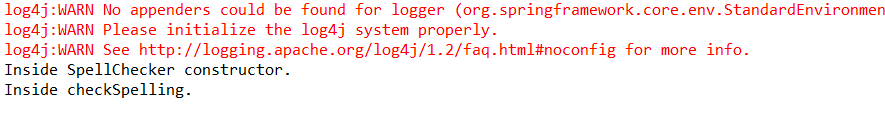
5.运行MainApp.java中的main方法
结果如下:
![]()
@AutoWired 自动装配 它的一个属性叫required,属性值是boolean类型,默认为true,必须,也可以修改为false,非必须。
三、Qualifier注解
可能会有这样一种情况,当你创建多个具有相同类型的 bean 时,并且想要用一个属性只为它们其中的一个进行装配,在这种情况下,你可以使用 @Qualifier 注释和 @Autowired 注释通过指定哪一个真正的 bean 将会被装配来消除混乱。下面显示的是使用 @Qualifier 注释的一个示例。
(1)编写Student.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
(2)编写Profile.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
public class Profile {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("student1")
private Student student;
public Profile(){
System.out.println("Inside Profile constructor." );
}
public void printAge() {
System.out.println("Age : " + student.getAge() );
}
public void printName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + student.getName() );
}
}
(3)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Profile profile = (Profile) context.getBean("profile");
profile.printAge();
profile.printName();
}
}
(4)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- Definition for profile bean -->
<bean id="profile" class="com.tutorialspoint.Profile">
</bean>
<!-- Definition for student1 bean -->
<bean id="student1" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Zara" />
<property name="age" value="11"/>
</bean>
<!-- Definition for student2 bean -->
<bean id="student2" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Nuha" />
<property name="age" value="2"/>
</bean>
</beans>
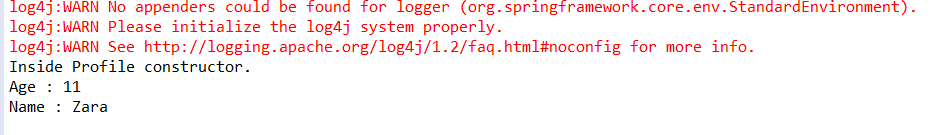
(5)运行MainApp.java对应的main方法
![]()
四、Spring JSR-250 注释
Spring还使用基于 JSR-250 注释,它包括 @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy 和 @Resource 注释。因为你已经有了其他的选择,尽管这些注释并不是真正所需要的,但是关于它们仍然让我给出一个简短的介绍。
@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注释:
为了定义一个 bean 的安装和卸载,我们使用 init-method 和/或 destroy-method 参数简单的声明一下 。init-method 属性指定了一个方法,该方法在 bean 的实例化阶段会立即被调用。同样地,destroy-method 指定了一个方法,该方法只在一个 bean 从容器中删除之前被调用。
你可以使用 @PostConstruct 注释作为初始化回调函数的一个替代,@PreDestroy 注释作为销毁回调函数的一个替代,其解释如下示例所示。
演示示例:
(1)编写HelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import javax.annotation.*;
public class HelloWorld {
private String message;
public void setMessage(String message){
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage(){
System.out.println("Your Message : " + message);
return message;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Bean is going through init.");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Bean will destroy now.");
}
}
(2)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="helloWorld"
class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="message" value="Hello World!"/>
</bean>
</beans>
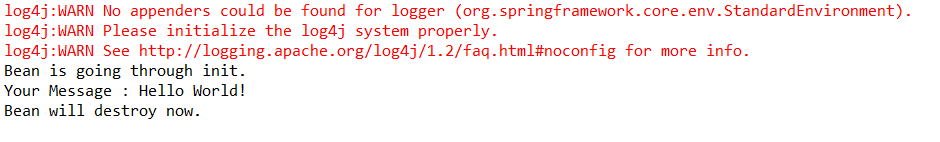
(3)编写MainApp.java并运行对应的main方法
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
obj.getMessage();
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
结果如图:
![]()