clop
![Go]()
![codecov]()
![Go Report Card]()
clop (Command Line Option Parse)是一款基于struct的命令行解析器,麻雀虽小,五脏俱全(从零实现)。
![]()
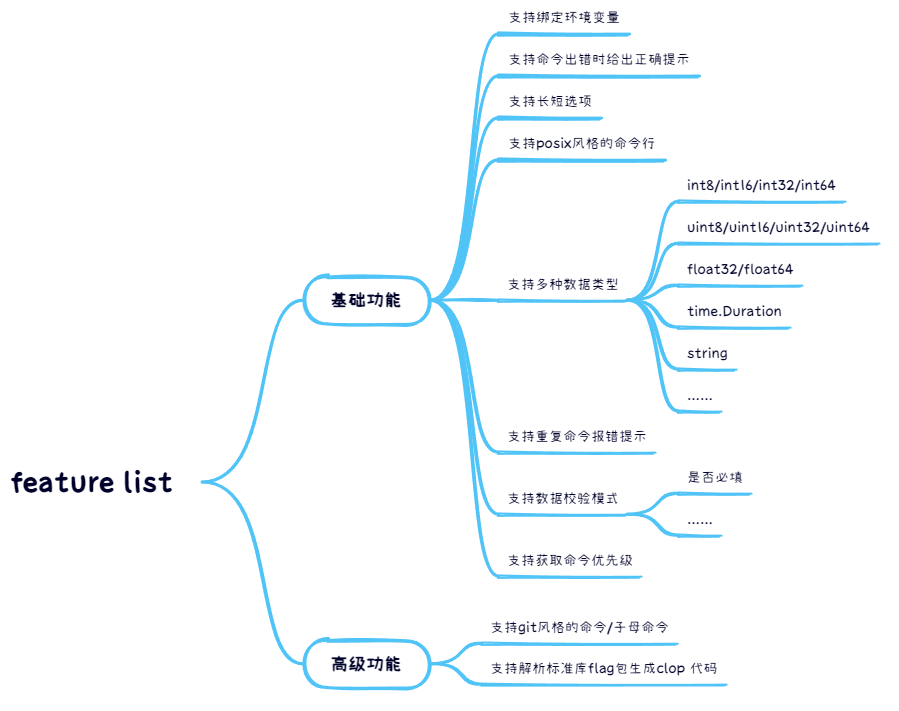
feature
- 支持环境变量绑定
env DEBUG=xx ./proc
- 支持参数搜集
cat a.txt b.txt,可以把a.txt, b.txt散装成员归归类,收集到你指定的结构体成员里
- 支持短选项
proc -d 或者长选项proc --debug不在话下
- posix风格命令行支持,支持命令组合
ls -ltr是ls -l -t -r简写形式,方便实现普通posix 标准命令
- 子命令(
subcommand)支持,方便实现git风格子命令git add ,简洁的子命令注册方式,只要会写结构体就行,3,4,5到无穷尽子命令也支持,只要你喜欢,用上clop就可以实现
- 默认值支持
default:"1",支持多种数据类型,让你省去类型转换的烦恼
- 贴心的重复命令报错
- 严格的短选项,长选项报错。避免二义性选项诞生
- 效验模式支持,不需要写一堆的
if x!= "" or if y!=0浪费青春的代码
- 可以获取命令优先级别,方便设置命令别名
- 解析flag包代码生成clop代码
![]()
内容
Installation
go get github.com/guonaihong/clop
Quick start
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type Hello struct {
File string `clop:"-f; --file" usage:"file"`
}
func main() {
h := Hello{}
clop.SetVersion("v0.2.0")
clop.SetAbout("这是一个简单的示例demo")
clop.Bind(&h)
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", h)
}
// ./one -f test
// main.Hello{File:"test"}
// ./one --file test
// main.Hello{File:"test"}
example
base type
int
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type IntDemo struct {
Int int `clop:"short;long" usage:"int"`
}
func main() {
id := &IntDemo{}
clop.Bind(id)
fmt.Printf("id = %v\n", id)
}
// ./int -i 3
// id = &{3}
// ./int --int 3
// id = &{3}
float64
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type Float64Demo struct {
Float64 float64 `clop:"short;long" usage:"float64"`
}
func main() {
fd := &Float64Demo{}
clop.Bind(fd)
fmt.Printf("fd = %v\n", fd)
}
// ./float64 -f 3.14
// fd = &{3.14}
// ./float64 --float64 3.14
// fd = &{3.14}
duration
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type DurationDemo struct {
Duration time.Duration `clop:"short;long" usage:"duration"`
}
func main() {
dd := &DurationDemo{}
clop.Bind(dd)
fmt.Printf("dd = %v\n", dd)
}
// ./duration -d 1h
// dd = &{1h0m0s}
// ./duration --duration 1h
// dd = &{1h0m0s}
string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type StringDemo struct {
String string `clop:"short;long" usage:"string"`
}
func main() {
s := &StringDemo{}
clop.Bind(s)
fmt.Printf("s = %v\n", s)
}
// ./string --string hello
// s = &{hello}
// ./string -s hello
// s = &{hello}
array
similar to curl command
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type ArrayDemo struct {
Header []string `clop:"-H;long" usage:"header"`
}
func main() {
h := &ArrayDemo{}
clop.Bind(h)
fmt.Printf("h = %v\n", h)
}
// ./array -H session:sid --header token:my
// h = &{[session:sid token:my]}
similar to join command
加上greedy属性,就支持数组贪婪写法。类似join命令。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type test struct {
A []int `clop:"-a;greedy" usage:"test array"`
B int `clop:"-b" usage:"test int"`
}
func main() {
a := &test{}
clop.Bind(a)
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", a)
}
/*
运行
./use_array -a 12 34 56 78 -b 100
输出
&main.test{A:[]int{12, 34, 56, 78}, B:100}
*/
required flag
package main
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type curl struct {
Url string `clop:"-u; --url" usage:"url" valid:"required"`
}
func main() {
c := curl{}
clop.Bind(&c)
}
// ./required
// error: -u; --url must have a value!
// For more information try --help
set default value
可以使用default tag设置默认值,普通类型直接写,复合类型用json表示
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type defaultExample struct {
Int int `default:"1"`
Float64 float64 `default:"3.64"`
Float32 float32 `default:"3.32"`
SliceString []string `default:"[\"one\", \"two\"]"`
SliceInt []int `default:"[1,2,3,4,5]"`
SliceFloat64 []float64 `default:"[1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5]"`
}
func main() {
de := defaultExample{}
clop.Bind(&de)
fmt.Printf("%v\n", de)
}
// run
// ./use_def
// output:
// {1 3.64 3.32 [one two] [1 2 3 4 5] [1.1 2.2 3.3 4.4 5.5]}
Support environment variables
custom environment variable name
// file name use_env.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type env struct {
OmpNumThread string `clop:"env=omp_num_thread" usage:"omp num thread"`
Path string `clop:"env=XPATH" usage:"xpath"`
Max int `clop:"env=MAX" usage:"max thread"`
}
func main() {
e := env{}
clop.Bind(&e)
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", e)
}
// run
// env XPATH=`pwd` omp_num_thread=3 MAX=4 ./use_env
// output
// main.env{OmpNumThread:"3", Path:"/home/guo", Max:4}
Quick writing of environment variables
使用env tag会根据结构体名, 生成一个环境变量名, 规则就是驼峰命令名, 改成大写下划线
// file name use_env.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type env struct {
OmpNumThread string `clop:"env" usage:"omp num thread"`
Xpath string `clop:"env" usage:"xpath"`
Max int `clop:"env" usage:"max thread"`
}
func main() {
e := env{}
clop.Bind(&e)
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", e)
}
// run
// env XPATH=`pwd` OMP_NUM_THREAD=3 MAX=4 ./use_env
// output
// main.env{OmpNumThread:"3", Xpath:"/home/guo", Max:4}
subcommand
Sub command implementation method 1
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type add struct {
All bool `clop:"-A; --all" usage:"add changes from all tracked and untracked files"`
Force bool `clop:"-f; --force" usage:"allow adding otherwise ignored files"`
Pathspec []string `clop:"args=pathspec"`
}
type mv struct {
Force bool `clop:"-f; --force" usage:"allow adding otherwise ignored files"`
}
type git struct {
Add add `clop:"subcommand=add" usage:"Add file contents to the index"`
Mv mv `clop:"subcommand=mv" usage:"Move or rename a file, a directory, or a symlink"`
}
func main() {
g := git{}
clop.Bind(&g)
fmt.Printf("git:%#v\n", g)
fmt.Printf("git:set mv(%t) or set add(%t)\n", clop.IsSetSubcommand("mv"), clop.IsSetSubcommand("add"))
switch {
case clop.IsSetSubcommand("mv"):
fmt.Printf("subcommand mv\n")
case clop.IsSetSubcommand("add"):
fmt.Printf("subcommand add\n")
}
}
// run:
// ./git add -f
// output:
// git:main.git{Add:main.add{All:false, Force:true, Pathspec:[]string(nil)}, Mv:main.mv{Force:false}}
// git:set mv(false) or set add(true)
// subcommand add
Sub command implementation method 2
使用clop实现子命令的第2种做法, 子命令结构体只要实现SubMain方法, 该方法clop库会帮你自动调用. 省去在main里面写一堆if else判断(相对方法1来说), 特别是子命令特别多的情况, 推荐用这种方法.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type add struct {
All bool `clop:"-A; --all" usage:"add changes from all tracked and untracked files"`
Force bool `clop:"-f; --force" usage:"allow adding otherwise ignored files"`
Pathspec []string `clop:"args=pathspec"`
}
func (a *add) SubMain() {
// 当add子命令被设置时
// clop会自动调用这个函数
}
type mv struct {
Force bool `clop:"-f; --force" usage:"allow adding otherwise ignored files"`
}
func (m *mv) SubMain() {
// 当mv 子命令被设置时
// clop会自动调用这个函数
}
type git struct {
Add add `clop:"subcommand=add" usage:"Add file contents to the index"`
Mv mv `clop:"subcommand=mv" usage:"Move or rename a file, a directory, or a symlink"`
}
func main() {
g := git{}
clop.Bind(&g)
}
Get command priority
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type cat struct {
NumberNonblank bool `clop:"-b;--number-nonblank"
usage:"number nonempty output lines, overrides"`
ShowEnds bool `clop:"-E;--show-ends"
usage:"display $ at end of each line"`
}
func main() {
c := cat{}
clop.Bind(&c)
if clop.GetIndex("number-nonblank") < clop.GetIndex("show-ends") {
fmt.Printf("cat -b -E\n")
} else {
fmt.Printf("cat -E -b \n")
}
}
// cat -be
// 输出 cat -b -E
// cat -Eb
// 输出 cat -E -b
Can only be set once
指定选项只能被设置一次,如果命令行选项,使用两次则会报错。
package main
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type Once struct {
Debug bool `clop:"-d; --debug; once" usage:"debug mode"`
}
func main() {
o := Once{}
clop.Bind(&o)
}
/*
./once -debug -debug
error: The argument '-d' was provided more than once, but cannot be used multiple times
For more information try --help
*/
quick write
快速写法,通过使用固定的short, long tag生成短,长选项。可以和 cat 例子直观比较下。命令行选项越多,越能节约时间,提升效率。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type cat struct {
NumberNonblank bool `clop:"-c;long"
usage:"number nonempty output lines, overrides"`
ShowEnds bool `clop:"-E;long"
usage:"display $ at end of each line"`
Number bool `clop:"-n;long"
usage:"number all output lines"`
SqueezeBlank bool `clop:"-s;long"
usage:"suppress repeated empty output lines"`
ShowTab bool `clop:"-T;long"
usage:"display TAB characters as ^I"`
ShowNonprinting bool `clop:"-v;long"
usage:"use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB" `
Files []string `clop:"args=files"`
}
func main() {
c := cat{}
err := clop.Bind(&c)
fmt.Printf("%#v, %s\n", c, err)
}
Multi structure series
多结构体串联功能. 多结构体统一组成一个命令行视图
如果命令行解析是要怼到多个(>=2)结构体里面, 可以使用结构体串联功能, 前面几个结构体使用clop.Register()接口, 最后一个结构体使用clop.Bind()函数.
/*
┌────────────────┐
│ │
│ │
│ ServerAddress │ ┌─────────────────────┐
├────────────────┤ │ │
│ │ ──────────────────► │ │
│ │ │ clop.MustRegitser()│
│ Rate │ │ │
│ │ └─────────────────────┘
└────────────────┘
┌────────────────┐
│ │
│ ThreadNum │
│ │ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ │ │ │
├────────────────┤ ──────────────────► │ │
│ │ │ clop.Bind() │
│ OpenVad │ │ │
│ │ │ │
└────────────────┘ └─────────────────────┘
*/
type Server struct {
ServerAddress string `clop:"long" usage:"Server address"`
Rate time.Duration `clop:"long" usage:"The speed at which audio is sent"`
}
type Asr struct{
ThreadNum int `clop:"long" usage:"thread number"`
OpenVad bool `clop:"long" usage:"open vad"`
}
func main() {
asr := Asr{}
ser := Server{}
clop.MustRegister(&asr)
clop.Bind(&ser)
}
// 可以使用如下命令行参数测试下效果
// ./example --server-address", ":8080", "--rate", "1s", "--thread-num", "20", "--open-vad"
Advanced features
高级功能里面有一些clop包比较有特色的功能
Parsing flag code to generate clop code
让你爽翻天, 如果你的command想迁移至clop, 但是面对众多的flag代码, 又不想花费太多时间在无谓的人肉code转换上, 这时候你就需要clop命令, 一行命令解决你的痛点.
1.安装clop命令
go get github.com/guonaihong/clop/cmd/clop
2.使用clop解析包含flag包的代码
就可以把main.go里面的flag库转成clop包的调用方式
main.go代码如下
package main
import "flag"
func main() {
s := flag.String("string", "", "string usage")
i := flag.Int("int", "", "int usage")
flag.Parse()
}
输出代码如下
package main
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type flagAutoGen struct {
Flag string `clop:"--string" usage:"string usage" `
Flag int `clop:"--int" usage:"int usage" `
}
func main() {
var flagVar flagAutoGen
clop.Bind(&flagVar)
}
Implementing linux command options
cat
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/clop"
)
type cat struct {
NumberNonblank bool `clop:"-c;--number-nonblank"
usage:"number nonempty output lines, overrides"`
ShowEnds bool `clop:"-E;--show-ends"
usage:"display $ at end of each line"`
Number bool `clop:"-n;--number"
usage:"number all output lines"`
SqueezeBlank bool `clop:"-s;--squeeze-blank"
usage:"suppress repeated empty output lines"`
ShowTab bool `clop:"-T;--show-tabs"
usage:"display TAB characters as ^I"`
ShowNonprinting bool `clop:"-v;--show-nonprinting"
usage:"use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB" `
Files []string `clop:"args=files"`
}
func main() {
c := cat{}
err := clop.Bind(&c)
fmt.Printf("%#v, %s\n", c, err)
}
/*
Usage:
./cat [Flags] <files>
Flags:
-E,--show-ends display $ at end of each line
-T,--show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I
-c,--number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides
-n,--number number all output lines
-s,--squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-v,--show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
Args:
<files>
*/