[开源应用]-一个Android平台的 IM 应用
这是一个简单的 IM 应用,写这个应用的本意只是想练练手,暂且实现了私聊和群聊功能,后边再根据用户反馈情况再来更新吧~ 应用完全是以 MVVM 的思想来实现的,使用的是 Google 的 LiveData + ViewModel 框架,使用的后台服务是由腾讯云通信服务提供的 应用完全开源,觉得还不错的同学不如点击应用内的“赞赏支持”来赞助我喝杯咖啡? GitHub主页:Round Apk下载地址:Round QQ交流群:892434439
最初学习Android的时候,是边学习边做着一个小项目的,因为项目需求,需要实现一个底部导航栏的功能,由于基础知识受限,百度了很多博客,大致就找到两种实现方案:第一种就是直接用Fragment实现(点击切换),第二种是ViewPager+Fragment实现(除了点击切换,还支持左右滑动切换)。根据需求使用了第一种方法,后期产生了Fragment重叠的问题,由于这个bug时而出现,也不知道如何定位(学生时期),就暂且放下了。现在因为学习进度(系统学习Fragment),重新捡起这个问题,就想写一篇实现功能+解决bug的博客,如有不足之处,请留言指教。
当我们进入Activity时,首先展示第一个页面,即创建对应Fragment实例,使用add+show方法显示出来,当我们点击进入别的页面时,调用hide方法将已展示的Fragment页面隐藏(实际是设置Visiable属性为不可见),然后显示对应Fragment页面(已创建则直接调用show方法,未创建则创建,然后调用add+show方法显示)。
这里补充一点:切换页面也可以用replace方法,它和hide+show方法的直观区别就是:使用replace方法会先将fragment实例remove掉,然后重新add,这就导致Fragment每次切换都会重新走一遍生命周期,创建一个新的实例,不会保存每个Fragment的状态;而使用hide+show方法则仅仅是将不显示的Fragment设置为不可见,再次显示出来时会保存状态。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorBackGround"
android:paddingTop="5dp"
android:paddingBottom="5dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_clothes"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/ic_clothes"
android:text="@string/clothes"
android:textSize="13sp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_food"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/ic_food"
android:text="@string/food"
android:textSize="13sp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_hotel"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/ic_hotel"
android:text="@string/hotel"
android:textSize="13sp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<View
android:background="@color/colorGray"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0.1dp"/>
<include layout="@layout/bottombar"/>
</LinearLayout>
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import com.example.laughter.testdemo.R;
/**
* A simple {@link Fragment} subclass.
*/
public class ClothesFragment extends Fragment {
public ClothesFragment() {
// Required empty public constructor
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_clothes, container, false);
}
}
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".fragment.ClothesFragment">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/clothes"
android:textSize="72sp"
android:gravity="center"/>
</FrameLayout>
我这里为了区分Fragment页面给每个页面添加了一个TextView,具体就根据自己的需求在Fragment中写代码就行了。
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.example.laughter.testdemo.fragment.ClothesFragment;
import com.example.laughter.testdemo.fragment.FoodFragment;
import com.example.laughter.testdemo.fragment.HotelFragment;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
//底部菜单栏3个TextView
private TextView mTextClothes;
private TextView mTextFood;
private TextView mTextHotel;
//3个Fragment
private Fragment mClothesFragment;
private Fragment mFoodFragment;
private Fragment mHotelFragment;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化
init();
//设置第一个Fragment默认显示
setFragment(0);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
default:
break;
case R.id.text_clothes:
setFragment(0);
break;
case R.id.text_food:
setFragment(1);
break;
case R.id.text_hotel:
setFragment(2);
break;
}
}
private void init(){
//初始化控件
mTextClothes = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text_clothes);
mTextFood = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text_food);
mTextHotel = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text_hotel);
//设置监听
mTextClothes.setOnClickListener(this);
mTextFood.setOnClickListener(this);
mTextHotel.setOnClickListener(this);
}
private void setFragment(int index){
//获取Fragment管理器
FragmentManager mFragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
//开启事务
FragmentTransaction mTransaction = mFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//隐藏所有Fragment
hideFragments(mTransaction);
switch (index){
default:
break;
case 0:
//设置菜单栏为选中状态(修改文字和图片颜色)
mTextClothes.setTextColor(getResources()
.getColor(R.color.colorTextPressed));
mTextClothes.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0,
R.drawable.ic_clothes_pressed,0,0);
//显示对应Fragment
if(mClothesFragment == null){
mClothesFragment = new ClothesFragment();
mTransaction.add(R.id.container, mClothesFragment,
"clothes_fragment");
}else {
mTransaction.show(mClothesFragment);
}
break;
case 1:
mTextFood.setTextColor(getResources()
.getColor(R.color.colorTextPressed));
mTextFood.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0,
R.drawable.ic_food_pressed,0,0);
if(mFoodFragment == null){
mFoodFragment = new FoodFragment();
mTransaction.add(R.id.container, mFoodFragment,
"food_fragment");
}else {
mTransaction.show(mFoodFragment);
}
break;
case 2:
mTextHotel.setTextColor(getResources()
.getColor(R.color.colorTextPressed));
mTextHotel.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0,
R.drawable.ic_hotel_pressed,0,0);
if(mHotelFragment == null){
mHotelFragment = new HotelFragment();
mTransaction.add(R.id.container, mHotelFragment,
"hotel_fragment");
}else {
mTransaction.show(mHotelFragment);
}
break;
}
//提交事务
mTransaction.commit();
}
private void hideFragments(FragmentTransaction transaction){
if(mClothesFragment != null){
//隐藏Fragment
transaction.hide(mClothesFragment);
//将对应菜单栏设置为默认状态
mTextClothes.setTextColor(getResources()
.getColor(R.color.colorText));
mTextClothes.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0,
R.drawable.ic_clothes,0,0);
}
if(mFoodFragment != null){
transaction.hide(mFoodFragment);
mTextFood.setTextColor(getResources()
.getColor(R.color.colorText));
mTextFood.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0,
R.drawable.ic_food,0,0);
}
if(mHotelFragment != null){
transaction.hide(mHotelFragment);
mTextHotel.setTextColor(getResources()
.getColor(R.color.colorText));
mTextHotel.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(0,
R.drawable.ic_hotel,0,0);
}
}
}
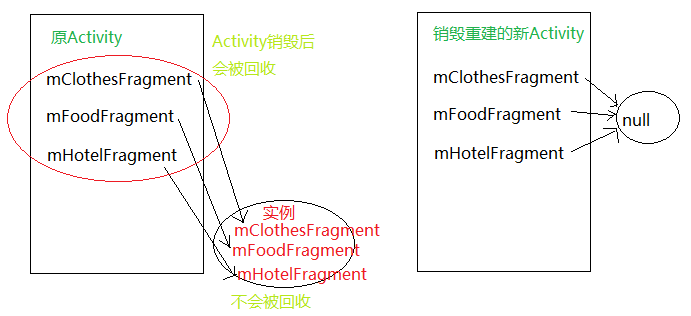
上面代码中逻辑很清晰,根据注释基本可以看明白,具体有些控件的用法自行百度。到这里功能就已经实现了,但是会出现Fragment重叠的bug。具体情况如下图:
所以,在重建后的的Activity中,又会重新创建Fragment的实例,并且显示出来,而之前被系统恢复的Fragment也会恢复之前的显示状态,这就导致了多个Fragment重叠。当然,任何能导致Activity销毁重建的情况都会产生这个bug,比如说应用在后台时,因为内存资源不足导致Activity被kill。既然知道原因了,那么解决起来就不难了。
这里我想到的解决办法是从重新创建Fragment这里着手,既然保存的状态会恢复,那么Activity重建的时候我们不让Fragment重新创建不就行了。具体怎么做呢?这里还是需要熟悉Activity的生命周期。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化
init();
//根据传入的Bundle对象判断Activity是正常启动还是销毁重建
if(savedInstanceState == null){
//设置第一个Fragment默认选中
setFragment(0);
}
}
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
...
//标记当前显示的Fragment
private int fragmentId = 0;
...
@Override
protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
//通过onSaveInstanceState方法保存当前显示的fragment
outState.putInt("fragment_id",fragmentId);
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onRestoreInstanceState(savedInstanceState);
FragmentManager mFragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
//通过FragmentManager获取保存在FragmentTransaction中的Fragment实例
mClothesFragment = (ClothesFragment)mFragmentManager
.findFragmentByTag("clothes_fragment");
mFoodFragment = (FoodFragment)mFragmentManager
.findFragmentByTag("food_fragment");
mHotelFragment = (HotelFragment)mFragmentManager
.findFragmentByTag("hotel_fragment");
//恢复销毁前显示的Fragment
setFragment(savedInstanceState.getInt("fragment_id"));
}
...
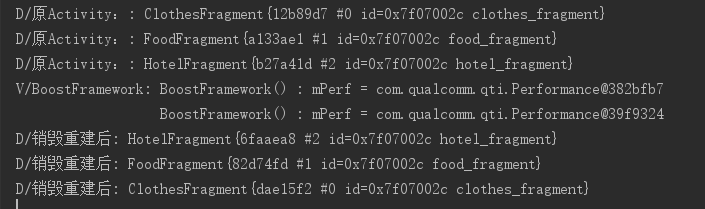
显然,销毁重建后Fragment对象所指向的实例与重建前相同。这样我们的BottomBar就完成了!
如果对Activity生命周期不太了解,可以看一看我的另一篇博客:
Android笔记(一) | Activity的生命周期

微信关注我们
转载内容版权归作者及来源网站所有!
低调大师中文资讯倾力打造互联网数据资讯、行业资源、电子商务、移动互联网、网络营销平台。持续更新报道IT业界、互联网、市场资讯、驱动更新,是最及时权威的产业资讯及硬件资讯报道平台。
马里奥是站在游戏界顶峰的超人气多面角色。马里奥靠吃蘑菇成长,特征是大鼻子、头戴帽子、身穿背带裤,还留着胡子。与他的双胞胎兄弟路易基一起,长年担任任天堂的招牌角色。
为解决软件依赖安装时官方源访问速度慢的问题,腾讯云为一些软件搭建了缓存服务。您可以通过使用腾讯云软件源站来提升依赖包的安装速度。为了方便用户自由搭建服务架构,目前腾讯云软件源站支持公网访问和内网访问。
Rocky Linux(中文名:洛基)是由Gregory Kurtzer于2020年12月发起的企业级Linux发行版,作为CentOS稳定版停止维护后与RHEL(Red Hat Enterprise Linux)完全兼容的开源替代方案,由社区拥有并管理,支持x86_64、aarch64等架构。其通过重新编译RHEL源代码提供长期稳定性,采用模块化包装和SELinux安全架构,默认包含GNOME桌面环境及XFS文件系统,支持十年生命周期更新。
Sublime Text具有漂亮的用户界面和强大的功能,例如代码缩略图,Python的插件,代码段等。还可自定义键绑定,菜单和工具栏。Sublime Text 的主要功能包括:拼写检查,书签,完整的 Python API , Goto 功能,即时项目切换,多选择,多窗口等等。Sublime Text 是一个跨平台的编辑器,同时支持Windows、Linux、Mac OS X等操作系统。