如果你没接触过旧版Asp.Net Mvc中的 Authorize 或者 Cookie登陆,那么你一定会疑惑 认证这个名词,这太正式了,这到底代表这什么?
获取资源之前得先过两道关卡Authentication & Authorization
要想了解Identity中用户登录之后,后续的访问时怎样识别用户的,那首先我们得了解下认证(Authentication) 和授权(Authorization)的含义
Authentication
Authentication就是认证的意思,还举之前公园的例子,我们拿到门票之后,去公园,入口门卫A首先要根据门票确认我们是谁?是老王,还是老赵,门票是不是真的,过期没。这个过程,这个识别来访者是谁的过程就叫做Authentication(身份认证过程)
那Authorization 又是啥?
这两个单词太像了,甚至他们的释义都很像,以至于我们在不了解他们的时候总是弄混他们,Authorization是授权的意思,上一小节中,门卫A识别出了我们是谁?Ok,我们是老李,那么门卫B能不能让我们进园呢?不一定,门卫B还要再看,门票过期没,上一步已经看过门票是否过期了,为什么还要看呢?事情是这样的:门卫A看到门票过期了,然后在门票副卡上写上“门票过期”四个大字,再写上“认证失败”,但是负责认证的门卫A没有拦着我们,而是继续让我们前进,因为动物园可能因为活动而允许过期门票进入,或者没有门票也可以,那么接下来授权的人门卫B来看门票,他根据动物园切实的情况看,看看许可范围,再问问后台这个人是不是动物园的管理员。经过种种校验,发现,虽然门票过期了,但是今天是开放日,没门票也行,但是我们是普通游客,却来到了管理员通道,所以没让我们进园——授权失败
小结
好了,这就是认证和授权(Authentication & Authorization),两个不同的事,由两个不同的人(或者组件)来做
- 认证用来确认来者是谁,确认身份(确认之后可能没有身份)
- 授权用来确认持有此身份的来者能不能访问当前请求的资源
现在,我们要记住认证与授权中的一个要点
认证只确定用户是谁即使认证失败,也不会拦截用户访问,拦截用户访问发生在授权阶段
另外要注意的是 Authentication和Authorization并不属于Identity的一部分,都不属于Identity,它和Identity是相互独立的,然后一起协作。也就是说,即便我们没有使用Identity ,我们有我们自己的用户存储,角色等等和身份权限相关的一切,那么我们可以将我们的成员系统完美的与Asp.Net Core 进行集成,我们可以假设,Identity就是我们写的,然后将其与Asp.Net Core进行集成
那么为什么要将这个与Identity无关的认证过程Authentication放在这里呢?因为它们是协作的 Authentication和Authorization本事就是要与成员系统协作的,在代码上,他们解耦并且独立,但是在事实逻辑上,成员系统和认证授权总是一起使用的,所以一起讲容易理解
那么这篇文章只讲 Authentication与Authorization中的第一个 —— Authentication,先来了解一下,asp.net core 是怎样知道我们已经登陆的访客是谁的
身份认证中间件 Authentication Middleware
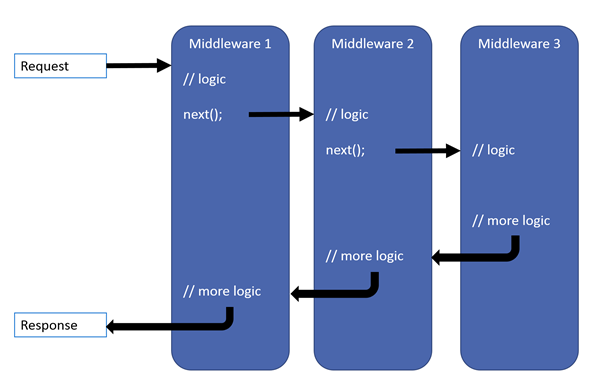
中间件(Middleware)讲起来又是一个长长的故事,如果你完全没概念,那么我建议你先简单学习一下asp.net core 中的中间件,你只要知道它的运行原理即可
在一般的asp.net core web 项目中,我们一般把身份认证中间件放在 静态文件中间件之后,Mvc中间件之前
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
//略...
});
}
这样做的目的很简单,仅对需要认证的部分做认证
在http请求到达 mvc中间件之前,也就是进入我们写的逻辑代码之前,身份认证就结束了,也就是说,身份认证不能在 controller action中控制
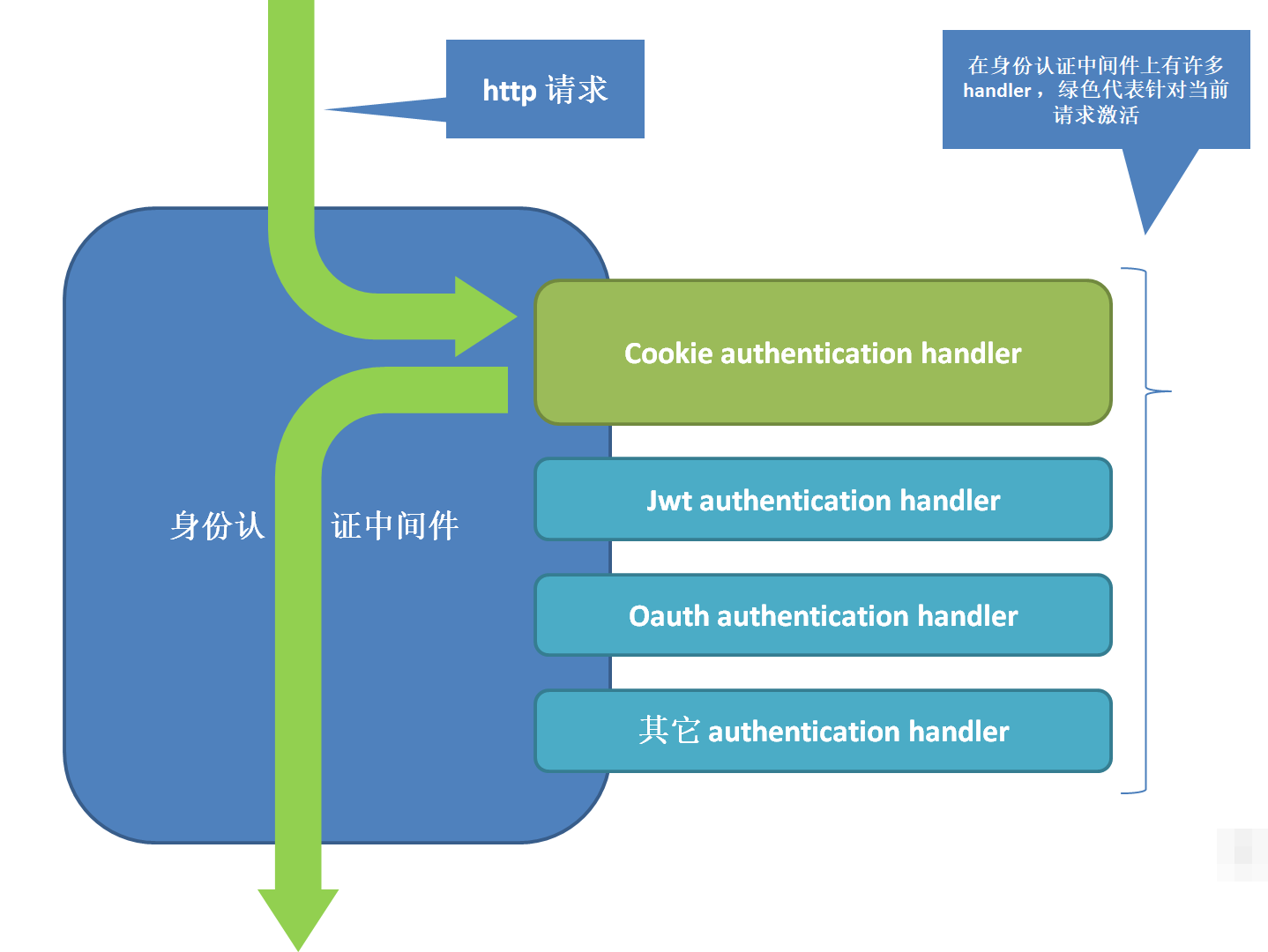
我们用一张图来简化发生在身份认证中间件中的认证过程,注意,这里马上要引入一个新的概念
![img_5fe0b9cccda041fcd7e5f61381d1d93e.png]()
身份认证 handler
中间件是嵌在中间件管道中的一个一个模块,http请求有条件的流经他们
![img_a2c16845b96d5fdecdd25846f8824898.png]()
另一个相似的东西,有很多 handler 嵌在身份认证中间件上,那么http是流经所有的handler吗?
Authentication Handler
Authentication Hander 顾名思义,他就是切实处理身份认证的组件,它附加在 authentication middleware 上,在请求到来时, middleware 会在所有附加在它之上的handler中选取一个用来做身份认证
那么当我们使用Identity时,哪些 authentication handler 被附加了呢?当请求到来时,authentication middleware 如何知道要选择哪个handler呢?
接下来,我们一一解答
Cookie Authentication Handler
Identity只添加了一种类型的 handler ——CookieAuthenticationHandler
在我们的StartUp类中的ConfigureServices方法中,我们添加了Identity的Service
services.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, IdentityRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
但事情没这么简单,在添加Identity的同时,Identity还未我们的项目添加了AuthenticationService和CookieAuthenticationHandler
public static IdentityBuilder AddIdentity<TUser, TRole>(
{
// Services used by identity
services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
options.DefaultAuthenticateScheme = IdentityConstants.ApplicationScheme;
// 略...
})
.AddCookie(IdentityConstants.ApplicationScheme, o =>
{
// 略...
在services.AddAuthentication的内部添加了AuthenticationService
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection
{
public static class AuthenticationCoreServiceCollectionExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddAuthenticationCore(this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.TryAddScoped<IAuthenticationService, AuthenticationService>();
services.TryAddScoped<IAuthenticationHandlerProvider, AuthenticationHandlerProvider>();
services.TryAddSingleton<IAuthenticationSchemeProvider, AuthenticationSchemeProvider>();
注意上面代码的最后三行,后面涉及到他们的获取,他们就是在此处添加的
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection
{
public static class CookieExtensions
{
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddCookie(this AuthenticationBuilder builder, string authenticationScheme, string displayName, Action<CookieAuthenticationOptions> configureOptions)
{
builder.Services.TryAddEnumerable(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<IPostConfigureOptions<CookieAuthenticationOptions>, PostConfigureCookieAuthenticationOptions>());
return builder.AddScheme<CookieAuthenticationOptions, CookieAuthenticationHandler>(authenticationScheme, displayName, configureOptions);
上方的代码添加了 CookieAuthenticationHandler
在添加Authentication service的同时,制定默认的 authentication scheme(这个概念在之前的文章中提到过,如果你还有印象的话) 是谁(就是下方的cookie authentication handler)
这时候另一个问题浮现了,只添加了一个 cookie authentication handler,为什么还要将他制定成默认值,是否有有点多此一举呢?
虽然Identity只添加了一种类型的 handler(cookie authentication handler),但是他同时添加了多个
在 authentication 中间件上,区分各个handler的方法是指定不同的 authentication scheme,而不是通过 handler 的类型
其实它添加了这么多:
services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
options.DefaultAuthenticateScheme = IdentityConstants.ApplicationScheme;
options.DefaultChallengeScheme = IdentityConstants.ApplicationScheme;
options.DefaultSignInScheme = IdentityConstants.ExternalScheme;
})
.AddCookie(IdentityConstants.ApplicationScheme, 略)
.AddCookie(IdentityConstants.ExternalScheme, 略)
.AddCookie(IdentityConstants.TwoFactorRememberMeScheme, 略)
.AddCookie(IdentityConstants.TwoFactorUserIdScheme,略);
不过我们暂时不用关心这些是什么
目前为止我们已经知道了这样几件事:
添加Identity时,Identity添加了用于身份认证的服务,以及默认激活的用于认证的handler——CookieAuthenticationHandler
- Identity的身份认证基于cookie (上篇文章我们了解到 Identity在登陆时将票据加密写入了cookie)
所以用户登录后再次访问的时候,会通过cookie来识别当前用户是谁
动手实践
这一小节中我们先编写测试代码,来看看认证过程产生了哪些结果
创建一个名为TestAuthController的控制器,代码大致如下:
namespace IdentityInAction.Controllers
{
public class TestAuthController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
return Json(new
{
User.Identity.IsAuthenticated,
User.Identity.AuthenticationType,
Claims=User.Claims.Select(c => new { c.Type, c.Value })
// 略...
这些代码将返回一个json字符串,内容是 authentication的部分结果和用户的claims信息,这三行核心代码的意思分别是:
- 用户是否已经通过身份认证
- 对次请求进行认证的handler的名称(在上篇文章中我们有提到 authentication scheme 就是 authentication type的另一个名字,记住这件事对我们的理解很有帮助)
- 这个用户的Claims信息
运行程序,不要进行登陆,如果已经登陆了则退出登陆,退出登陆的链接是右上角的LogOut
然后访问http://localhost:{你的端口}/testauth/index,得到的结果如下:
{
"isAuthenticated": false,
"authenticationType": null,
"claims": []
}
由于没有用户登陆,所以结果里几乎什么都没有,然后再尝试登陆后再次访问这个地址,结果如下:
{
"isAuthenticated": true,
"authenticationType": "Identity.Application",
"claims": [
{
"type": "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/nameidentifier",
"value": "78a032c7-0d67-4cec-b031-2d15a7bac755"
},
{
"type": "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name",
"value": "abc@abc.com"
},
{
"type": "AspNet.Identity.SecurityStamp",
"value": "babbb46b-6ba0-4b87-875a-92088197dfbf"
}
]
}
"isAuthenticated": true 这代表认证成功
"authenticationType": "Identity.Application"这是对该请求进行认证的handler的名字,由前文我们知道,我们默认的handler是名为IdentityConstants.ApplicationScheme的cookie handler,我们看一小段源代码证实一下:
public class IdentityConstants
{
private static readonly string CookiePrefix = "Identity";
public static readonly string ApplicationScheme = CookiePrefix + ".Application";
正如所料,接下来就是claims了,再上篇文章中提到再登陆过程中加入到Identity的claims有这些:
- UserName |
http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/nameidentifier
- UserId|
http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name
- SecurityStamp(如果支持的话)|
AspNet.Identity.SecurityStamp
- 存储在数据库中的额外Claims(如果支持的话)(注:支持,但当前用户没有)
这些claims随着票据一起加密写到了cookie中,现在他们又随着cookie一起传了回来
要注意的是,即便我们退出登陆后没有身份认证失败了,但是我们仍然获得了这个Uri的访问权限,原因在于认证并不阻止用户,授权才会阻止用户,而我们没又做授权方面的限制
看到这里,我们的认证过程的大体已经清楚了,接下来我们要看下整个认证过程的一点细节,整个过程是自上而下的,看标题为工作的那一列
| 工作 |
注释 |
| 获取IAuthenticationHandlerProvider的实例 |
|
| 获取默认的AuthenticationScheme |
|
| 使用上一步的scheme获取IAuthenticationService实例 |
|
| 上一步的service通过第一步的IAuthenticationHandlerProvider获取handler |
handler 是 cookie authentication handler |
| handler 调用 AuthenticateAsync,这个方法最终调用了handler的HandleAuthenticateAsync① |
这个方法是事实上执行认证的方法 |
| 获取 CookieAuthenticationOptions.Cookie.Name指定的存储票据的cookie的原始字符串 |
这个Name的默认值是`.AspNetCore.Identity.Application` |
| 解密cookie字符串获得AuthenticationTicket的实例 |
|
| 检查是否使用了session存储,如果有则验证是否存在对应的session |
|
| 检查cookie 是否过期 |
|
| 检查是否需要刷新cookie |
|
| 创建新的AuthenticationTicket |
|
| 将AuthenticationTicket中的Principal设置到HttpContext.User上,认证结束 |
在动手做一节中,我们使用的User就是在这个时候被赋值的 |
需要注意
① 谁进行的验证
Identity的实现比较复杂,兜兜转转最终的验证时由 cookie authentication handler 的 HandleAuthenticateAsync完成的,如果你在看Identity源代码的话,那么直接跳转到这里可以节省时间
怎么验证的
事实上,说的简单一点,就是在登陆的时候,把票据加密写到cookie里,验证的时候
获取cookie >解密 >还原成票据 >把票据塞到http context中
即使是认证失败了,也是这4个步骤,最终 负责授权的组件会检查 http context 中的票据,还会结合其它情况来确定是否允许当前的请求继续进行下去,而我们的逻辑代码中也可以查看票据,根据不同的 认证结果 返回不同的数据
全文完