作者:刘乃杰
编辑整理:曾辉
引入
本系列文章是基于 Apache SeaTunnel 2.3.6版本,围绕Zeta引擎给大家介绍其任务是如何从提交到运行的全流程,希望通过这篇文档,对刚刚上手SeaTunnel的朋友提供一些帮助。
![file]()
我们整体的文章将会分成三篇,从以下方向给大家介绍:
- SeaTunnel Server端的初始化
- Client端的任务提交流程 3. Server端的接收到任务的执行流程
由于涉及源码解析,涉及篇幅较大,所以分成系列文章来记录下一个任务的整体流程。
参考
作者介绍
大家好,我是刘乃杰,一名大数据开发工程师,参与Apache SeaTunnel的开发也有一年多的时间了,不仅给SeaTunnel提交了一些PR,而且添加的一些功能也非常有意思,欢迎大家来找我交流,其中包括支持Avro格式文件,SQL Transform中支持嵌套结构查询,给节点添加Tag达到资源隔离等。
接之前的文章: Apache SeaTunnel Zeta引擎源码解析(一) Server端的初始化 Apache SeaTunnel Zeta引擎源码解析(二) Client端的任务提交流程
服务端提交任务相关
这篇是系列文章的最后一篇,我们再回顾一下当服务端启动后会执行的组件:
- coordinatorService 仅在master/standby节点启用,会监听集群状态,主备切换
- SlotService 在worker节点中启用,会定期上报自身信息到master中
- TaskExecutionSerive 在worker节点中启用,会定时更新执行的任务指标到IMAP中
在集群未接收到任何任务时,会运行这些组件,当Client发送一条SeaTunnelSubmitJobCodec信息到服务端后,服务端又是如何处理的呢?
接收消息
因为客户端与服务端在不同的机器上,所有这里无法使用方法调用,而是使用了消息传递,当服务端接收到一条消息后是如何进行相关的方法调用的呢 首先我们在上面的代码中,知道客户端向服务端发送的是一条类型为SeaTunnelSubmitJobCodec的消息
// 客户端相关代码
ClientMessage request =
SeaTunnelSubmitJobCodec.encodeRequest(
jobImmutableInformation.getJobId(),
seaTunnelHazelcastClient
.getSerializationService()
.toData(jobImmutableInformation),
jobImmutableInformation.isStartWithSavePoint());
PassiveCompletableFuture<Void> submitJobFuture =
seaTunnelHazelcastClient.requestOnMasterAndGetCompletableFuture(request);
我们进入SeaTunnelSubmitJobCodec这个类,查看他的相关调用类,可以找到一个SeaTunnelMessageTaskFactoryProvider的类,在这个里中维护了一个消息类型到MessageTask的映射关系,也可以理解为客户端消息到服务端调用类的映射关系,以SeaTunnelSubmitJobCodec为例,会返回SubmitJobTask这个类
private final Int2ObjectHashMap<MessageTaskFactory> factories = new Int2ObjectHashMap<>(60);
private void initFactories() {
factories.put(
SeaTunnelPrintMessageCodec.REQUEST_MESSAGE_TYPE,
(clientMessage, connection) ->
new PrintMessageTask(clientMessage, node, connection));
factories.put(
SeaTunnelSubmitJobCodec.REQUEST_MESSAGE_TYPE,
(clientMessage, connection) -> new SubmitJobTask(clientMessage, node, connection));
.....
}
当我们查看SubmitJobTask这个类时,又会发现继续调用了SubmitJobOperation这个类
@Override
protected Operation prepareOperation() {
return new SubmitJobOperation(
parameters.jobId,
parameters.jobImmutableInformation,
parameters.isStartWithSavePoint);
}
在SubmitJobOperation中我们可以看到真正调用的地方,将我们的信息交给了CoordinatorService组件,调用了其submitJob方法
@Override
protected PassiveCompletableFuture<?> doRun() throws Exception {
SeaTunnelServer seaTunnelServer = getService();
return seaTunnelServer
.getCoordinatorService()
.submitJob(jobId, jobImmutableInformation, isStartWithSavePoint);
}
这时一个客户端的消息就真正的被交给服务端来进行方法调用了,至于其他类型的操作也都可以类似找到相关的类,就不再赘述。
CoordinatorService
接下来看下在CoordinatorService是如何进行任务提交的
public PassiveCompletableFuture<Void> submitJob(
long jobId, Data jobImmutableInformation, boolean isStartWithSavePoint) {
CompletableFuture<Void> jobSubmitFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
// 首先会根据任务id来判断,当存在相同任务的id时,直接返回
if (getJobMaster(jobId) != null) {
logger.warning(
String.format(
"The job %s is currently running; no need to submit again.", jobId));
jobSubmitFuture.complete(null);
return new PassiveCompletableFuture<>(jobSubmitFuture);
}
// 初始化JobMaster对象
JobMaster jobMaster =
new JobMaster(
jobImmutableInformation,
this.nodeEngine,
executorService,
getResourceManager(),
getJobHistoryService(),
runningJobStateIMap,
runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
ownedSlotProfilesIMap,
runningJobInfoIMap,
metricsImap,
engineConfig,
seaTunnelServer);
//
executorService.submit(
() -> {
try {
// 由于2.3.6中任务id可以由用户传递,而在seatunnel中会根据任务id来做一些状态判断
// 所以这里的检查是保证在当前的状态中,不会存在相同id的任务
if (!isStartWithSavePoint
&& getJobHistoryService().getJobMetrics(jobId) != null) {
throw new JobException(
String.format(
"The job id %s has already been submitted and is not starting with a savepoint.",
jobId));
}
// 将当前任务的信息添加到IMAP中
runningJobInfoIMap.put(
jobId,
new JobInfo(System.currentTimeMillis(), jobImmutableInformation));
runningJobMasterMap.put(jobId, jobMaster);
// 对JobMaster做初始化操作
jobMaster.init(
runningJobInfoIMap.get(jobId).getInitializationTimestamp(), false);
// 当jobMaster初始化完成后,会认为任务创建成功
jobSubmitFuture.complete(null);
} catch (Throwable e) {
String errorMsg = ExceptionUtils.getMessage(e);
logger.severe(String.format("submit job %s error %s ", jobId, errorMsg));
jobSubmitFuture.completeExceptionally(new JobException(errorMsg));
}
if (!jobSubmitFuture.isCompletedExceptionally()) {
// 当任务正常提交后,调用jobMaster的run方法开始执行任务
// 以及最后会检查任务状态,从内部状态中将此次任务信息删除
try {
jobMaster.run();
} finally {
// voidCompletableFuture will be cancelled when zeta master node
// shutdown to simulate master failure,
// don't update runningJobMasterMap is this case.
if (!jobMaster.getJobMasterCompleteFuture().isCancelled()) {
runningJobMasterMap.remove(jobId);
}
}
} else {
runningJobInfoIMap.remove(jobId);
runningJobMasterMap.remove(jobId);
}
});
return new PassiveCompletableFuture<>(jobSubmitFuture);
}
可以看到在服务端,会通过创建一个JobMaster对象,由这个对象来进行单个任务的管理。
在创建JobMaster对象时,会通过getResourceManager方法来获取资源管理对象,以及通过getJobHistoryService方法获取任务历史信息,jobHistoryService在启动时就会创建完成,ResourceManage则采用了懒加载的方式,在第一次有任务提交之后才会进行创建
/** Lazy load for resource manager */
public ResourceManager getResourceManager() {
if (resourceManager == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (resourceManager == null) {
ResourceManager manager =
new ResourceManagerFactory(nodeEngine, engineConfig)
.getResourceManager();
manager.init();
resourceManager = manager;
}
}
}
return resourceManager;
}
ResourceManager
目前seatunnel也仅支持standalone的部署方式,当初始化ResourceManager时,会获取到集群所有节点,然后向其发送SyncWorkerProfileOperation操作来获取节点的信息,然后更新到内部的registerWorker状态中
@Override
public void init() {
log.info("Init ResourceManager");
initWorker();
}
private void initWorker() {
log.info("initWorker... ");
List<Address> aliveNode =
nodeEngine.getClusterService().getMembers().stream()
.map(Member::getAddress)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
log.info("init live nodes: {}", aliveNode);
List<CompletableFuture<Void>> futures =
aliveNode.stream()
.map(
node ->
sendToMember(new SyncWorkerProfileOperation(), node)
.thenAccept(
p -> {
if (p != null) {
registerWorker.put(
node, (WorkerProfile) p);
log.info(
"received new worker register: "
+ ((WorkerProfile)
p)
.getAddress());
}
}))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
futures.forEach(CompletableFuture::join);
log.info("registerWorker: {}", registerWorker);
}
而我们之前在SlotService中注意到在每个节点会定时向master发送心跳信息,心跳信息里面包含了当前节点的状态,在ResourceManager中当接收到心跳信息后,也会在内部状态中更新每个节点的状态
@Override
public void heartbeat(WorkerProfile workerProfile) {
if (!registerWorker.containsKey(workerProfile.getAddress())) {
log.info("received new worker register: " + workerProfile.getAddress());
sendToMember(new ResetResourceOperation(), workerProfile.getAddress()).join();
} else {
log.debug("received worker heartbeat from: " + workerProfile.getAddress());
}
registerWorker.put(workerProfile.getAddress(), workerProfile);
}
JobMaster
在CoordinatorService中会创建JobMaster并调用其init方法,当init方法完成后会认为任务创建成功。然后再调用run方法来正式运行任务
我们看一下初始化以及init方法。
public JobMaster(
@NonNull Data jobImmutableInformationData,
@NonNull NodeEngine nodeEngine,
@NonNull ExecutorService executorService,
@NonNull ResourceManager resourceManager,
@NonNull JobHistoryService jobHistoryService,
@NonNull IMap runningJobStateIMap,
@NonNull IMap runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
@NonNull IMap ownedSlotProfilesIMap,
@NonNull IMap<Long, JobInfo> runningJobInfoIMap,
@NonNull IMap<Long, HashMap<TaskLocation, SeaTunnelMetricsContext>> metricsImap,
EngineConfig engineConfig,
SeaTunnelServer seaTunnelServer) {
this.jobImmutableInformationData = jobImmutableInformationData;
this.nodeEngine = nodeEngine;
this.executorService = executorService;
flakeIdGenerator =
this.nodeEngine
.getHazelcastInstance()
.getFlakeIdGenerator(Constant.SEATUNNEL_ID_GENERATOR_NAME);
this.ownedSlotProfilesIMap = ownedSlotProfilesIMap;
this.resourceManager = resourceManager;
this.jobHistoryService = jobHistoryService;
this.runningJobStateIMap = runningJobStateIMap;
this.runningJobStateTimestampsIMap = runningJobStateTimestampsIMap;
this.runningJobInfoIMap = runningJobInfoIMap;
this.engineConfig = engineConfig;
this.metricsImap = metricsImap;
this.seaTunnelServer = seaTunnelServer;
this.releasedSlotWhenTaskGroupFinished = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
在初始化时只是进行简单的变量赋值,并没有进行什么操作,我们需要着重看下init方法
public synchronized void init(long initializationTimestamp, boolean restart) throws Exception {
// 服务端接收到客户端传递过来的消息是一个二进制的对象
// 首先将其转换为JobImmutableInformation对象,而这个对象也正是客户端发送给服务端的对象
jobImmutableInformation =
nodeEngine.getSerializationService().toObject(jobImmutableInformationData);
// 获取checkpoint的相关配置,例如周期,超时时间等
jobCheckpointConfig =
createJobCheckpointConfig(
engineConfig.getCheckpointConfig(), jobImmutableInformation.getJobConfig());
LOGGER.info(
String.format(
"Init JobMaster for Job %s (%s) ",
jobImmutableInformation.getJobConfig().getName(),
jobImmutableInformation.getJobId()));
LOGGER.info(
String.format(
"Job %s (%s) needed jar urls %s",
jobImmutableInformation.getJobConfig().getName(),
jobImmutableInformation.getJobId(),
jobImmutableInformation.getPluginJarsUrls()));
ClassLoader appClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 获取ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader =
seaTunnelServer
.getClassLoaderService()
.getClassLoader(
jobImmutableInformation.getJobId(),
jobImmutableInformation.getPluginJarsUrls());
// 将客户端传递的信息反序列化为逻辑计划
logicalDag =
CustomClassLoadedObject.deserializeWithCustomClassLoader(
nodeEngine.getSerializationService(),
classLoader,
jobImmutableInformation.getLogicalDag());
try {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
// 在服务端会执行savemode的功能,例如对表进行创建,删除操作。
if (!restart
&& !logicalDag.isStartWithSavePoint()
&& ReadonlyConfig.fromMap(logicalDag.getJobConfig().getEnvOptions())
.get(EnvCommonOptions.SAVEMODE_EXECUTE_LOCATION)
.equals(SaveModeExecuteLocation.CLUSTER)) {
logicalDag.getLogicalVertexMap().values().stream()
.map(LogicalVertex::getAction)
.filter(action -> action instanceof SinkAction)
.map(sink -> ((SinkAction<?, ?, ?, ?>) sink).getSink())
.forEach(JobMaster::handleSaveMode);
}
// 逻辑计划到物理计划的解析
final Tuple2<PhysicalPlan, Map<Integer, CheckpointPlan>> planTuple =
PlanUtils.fromLogicalDAG(
logicalDag,
nodeEngine,
jobImmutableInformation,
initializationTimestamp,
executorService,
flakeIdGenerator,
runningJobStateIMap,
runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
engineConfig.getQueueType(),
engineConfig);
this.physicalPlan = planTuple.f0();
this.physicalPlan.setJobMaster(this);
this.checkpointPlanMap = planTuple.f1();
} finally {
// 重置当前线程的ClassLoader,并且释放上面创建的classLoader
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(appClassLoader);
seaTunnelServer
.getClassLoaderService()
.releaseClassLoader(
jobImmutableInformation.getJobId(),
jobImmutableInformation.getPluginJarsUrls());
}
Exception initException = null;
try {
// 初始化checkpointManager
this.initCheckPointManager(restart);
} catch (Exception e) {
initException = e;
}
// 添加一些回调函数做任务状态监听
this.initStateFuture();
if (initException != null) {
if (restart) {
cancelJob();
}
throw initException;
}
}
最后再看下run方法
public void run() {
try {
physicalPlan.startJob();
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.severe(
String.format(
"Job %s (%s) run error with: %s",
physicalPlan.getJobImmutableInformation().getJobConfig().getName(),
physicalPlan.getJobImmutableInformation().getJobId(),
ExceptionUtils.getMessage(e)));
} finally {
jobMasterCompleteFuture.join();
if (engineConfig.getConnectorJarStorageConfig().getEnable()) {
List<ConnectorJarIdentifier> pluginJarIdentifiers =
jobImmutableInformation.getPluginJarIdentifiers();
seaTunnelServer
.getConnectorPackageService()
.cleanUpWhenJobFinished(
jobImmutableInformation.getJobId(), pluginJarIdentifiers);
}
}
}
此方法比较简单,调用physicalPlan.startJob()对生成的物理计划调用run方法
通过以上代码可以看出,当服务端接收到客户端提交任务请求后,会初始化JobMaster类,在JobMaster中完成了从逻辑计划到物理计划的生成,最终执行生成的物理计划。
下面需要深入看下如何从逻辑计划生成物理计划
逻辑计划到物理计划
物理计划的生成是由JobMaster中调用生成的
final Tuple2<PhysicalPlan, Map<Integer, CheckpointPlan>> planTuple =
PlanUtils.fromLogicalDAG(
logicalDag,
nodeEngine,
jobImmutableInformation,
initializationTimestamp,
executorService,
flakeIdGenerator,
runningJobStateIMap,
runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
engineConfig.getQueueType(),
engineConfig);
在生成的方法中可以看到中间会先从逻辑计划生成执行计划,然后再由执行计划生成物理计划
public static Tuple2<PhysicalPlan, Map<Integer, CheckpointPlan>> fromLogicalDAG(
@NonNull LogicalDag logicalDag,
@NonNull NodeEngine nodeEngine,
@NonNull JobImmutableInformation jobImmutableInformation,
long initializationTimestamp,
@NonNull ExecutorService executorService,
@NonNull FlakeIdGenerator flakeIdGenerator,
@NonNull IMap runningJobStateIMap,
@NonNull IMap runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
@NonNull QueueType queueType,
@NonNull EngineConfig engineConfig) {
return new PhysicalPlanGenerator(
new ExecutionPlanGenerator(
logicalDag, jobImmutableInformation, engineConfig)
.generate(),
nodeEngine,
jobImmutableInformation,
initializationTimestamp,
executorService,
flakeIdGenerator,
runningJobStateIMap,
runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
queueType)
.generate();
}
执行计划的生成
public ExecutionPlanGenerator(
@NonNull LogicalDag logicalPlan,
@NonNull JobImmutableInformation jobImmutableInformation,
@NonNull EngineConfig engineConfig) {
checkArgument(
logicalPlan.getEdges().size() > 0, "ExecutionPlan Builder must have LogicalPlan.");
this.logicalPlan = logicalPlan;
this.jobImmutableInformation = jobImmutableInformation;
this.engineConfig = engineConfig;
}
public ExecutionPlan generate() {
log.debug("Generate execution plan using logical plan:");
Set<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges = generateExecutionEdges(logicalPlan.getEdges());
log.debug("Phase 1: generate execution edge list {}", executionEdges);
executionEdges = generateShuffleEdges(executionEdges);
log.debug("Phase 2: generate shuffle edge list {}", executionEdges);
executionEdges = generateTransformChainEdges(executionEdges);
log.debug("Phase 3: generate transform chain edge list {}", executionEdges);
List<Pipeline> pipelines = generatePipelines(executionEdges);
log.debug("Phase 4: generate pipeline list {}", pipelines);
ExecutionPlan executionPlan = new ExecutionPlan(pipelines, jobImmutableInformation);
log.debug("Phase 5: generate execution plan: {}", executionPlan);
return executionPlan;
}
首先看下执行计划这个类里面有什么内容:
public class ExecutionPlan {
private final List<Pipeline> pipelines;
private final JobImmutableInformation jobImmutableInformation;
}
public class Pipeline {
/** The ID of the pipeline. */
private final Integer id;
private final List<ExecutionEdge> edges;
private final Map<Long, ExecutionVertex> vertexes;
}
public class ExecutionEdge {
private ExecutionVertex leftVertex;
private ExecutionVertex rightVertex;
}
public class ExecutionVertex {
private Long vertexId;
private Action action;
private int parallelism;
}
我们再与逻辑计划比较一下
public class LogicalDag implements IdentifiedDataSerializable {
@Getter private JobConfig jobConfig;
private final Set<LogicalEdge> edges = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private final Map<Long, LogicalVertex> logicalVertexMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private IdGenerator idGenerator;
private boolean isStartWithSavePoint = false;
}
public class LogicalEdge implements IdentifiedDataSerializable {
private LogicalVertex inputVertex;
private LogicalVertex targetVertex;
private Long inputVertexId;
private Long targetVertexId;
}
public class LogicalVertex implements IdentifiedDataSerializable {
private Long vertexId;
private Action action;
private int parallelism;
}
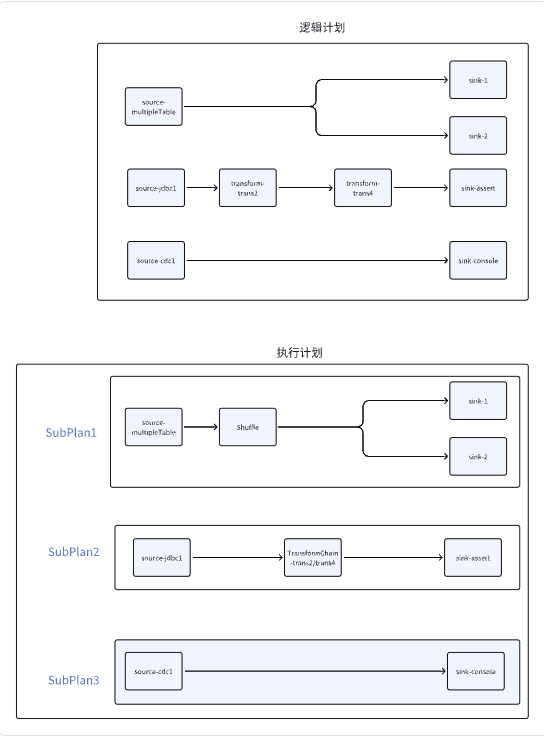
我们看这两个类的内容,感觉每个Pipeline都像一个逻辑计划,为什么需要这一步转换呢,我们来具体看下逻辑计划的生成过程。 在上面可以看到生成执行计划共有5步,我们逐步看下
// 入参是逻辑计划的边,每个边存储了上下游的节点
private Set<ExecutionEdge> generateExecutionEdges(Set<LogicalEdge> logicalEdges) {
Set<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Map<Long, ExecutionVertex> logicalVertexIdToExecutionVertexMap = new HashMap();
// 按照顺序进行排序,首先按照输入节点的顺序进行排序,当输入节点相同时,按照输出节点进行排序
List<LogicalEdge> sortedLogicalEdges = new ArrayList<>(logicalEdges);
Collections.sort(
sortedLogicalEdges,
(o1, o2) -> {
if (o1.getInputVertexId() != o2.getInputVertexId()) {
return o1.getInputVertexId() > o2.getInputVertexId() ? 1 : -1;
}
if (o1.getTargetVertexId() != o2.getTargetVertexId()) {
return o1.getTargetVertexId() > o2.getTargetVertexId() ? 1 : -1;
}
return 0;
});
// 循环将每个逻辑计划的边转换为执行计划的边
for (LogicalEdge logicalEdge : sortedLogicalEdges) {
LogicalVertex logicalInputVertex = logicalEdge.getInputVertex();
ExecutionVertex executionInputVertex =
logicalVertexIdToExecutionVertexMap.computeIfAbsent(
logicalInputVertex.getVertexId(),
vertexId -> {
long newId = idGenerator.getNextId();
// 对每个逻辑计划节点重新创建Action
Action newLogicalInputAction =
recreateAction(
logicalInputVertex.getAction(),
newId,
logicalInputVertex.getParallelism());
// 转换为执行计划节点
return new ExecutionVertex(
newId,
newLogicalInputAction,
logicalInputVertex.getParallelism());
});
// 与输入节点类似,重新创建执行计划节点
LogicalVertex logicalTargetVertex = logicalEdge.getTargetVertex();
ExecutionVertex executionTargetVertex =
logicalVertexIdToExecutionVertexMap.computeIfAbsent(
logicalTargetVertex.getVertexId(),
vertexId -> {
long newId = idGenerator.getNextId();
Action newLogicalTargetAction =
recreateAction(
logicalTargetVertex.getAction(),
newId,
logicalTargetVertex.getParallelism());
return new ExecutionVertex(
newId,
newLogicalTargetAction,
logicalTargetVertex.getParallelism());
});
// 生成执行计划的边
ExecutionEdge executionEdge =
new ExecutionEdge(executionInputVertex, executionTargetVertex);
executionEdges.add(executionEdge);
}
return executionEdges;
}
private Set<ExecutionEdge> generateShuffleEdges(Set<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges) {
// 以上游节点编号为key,list存储下游所有节点
Map<Long, List<ExecutionVertex>> targetVerticesMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 仅存储类型为Source的节点
Set<ExecutionVertex> sourceExecutionVertices = new HashSet<>();
executionEdges.forEach(
edge -> {
ExecutionVertex leftVertex = edge.getLeftVertex();
ExecutionVertex rightVertex = edge.getRightVertex();
if (leftVertex.getAction() instanceof SourceAction) {
sourceExecutionVertices.add(leftVertex);
}
targetVerticesMap
.computeIfAbsent(leftVertex.getVertexId(), id -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(rightVertex);
});
if (sourceExecutionVertices.size() != 1) {
return executionEdges;
}
ExecutionVertex sourceExecutionVertex = sourceExecutionVertices.stream().findFirst().get();
Action sourceAction = sourceExecutionVertex.getAction();
List<CatalogTable> producedCatalogTables = new ArrayList<>();
if (sourceAction instanceof SourceAction) {
try {
producedCatalogTables =
((SourceAction<?, ?, ?>) sourceAction)
.getSource()
.getProducedCatalogTables();
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
}
} else if (sourceAction instanceof TransformChainAction) {
return executionEdges;
} else {
throw new SeaTunnelException(
"source action must be SourceAction or TransformChainAction");
}
// 数据源仅产生单表或
// 数据源仅有一个下游输出时,直接返回
if (producedCatalogTables.size() <= 1
|| targetVerticesMap.get(sourceExecutionVertex.getVertexId()).size() <= 1) {
return executionEdges;
}
List<ExecutionVertex> sinkVertices =
targetVerticesMap.get(sourceExecutionVertex.getVertexId());
// 检查是否有其他类型的Action,在当前步骤下游节点尽可能有两种类型,Transform与Sink,这里是判断仅能有Sink类型
Optional<ExecutionVertex> hasOtherAction =
sinkVertices.stream()
.filter(vertex -> !(vertex.getAction() instanceof SinkAction))
.findFirst();
checkArgument(!hasOtherAction.isPresent());
// 当以上代码全部走完之后,当前的场景为:
// 仅有一个数据源,该数据源会产生多张表,下游还有多个sink节点依赖与产生的多表
// 也就是说当前任务仅有两类节点,一个会产生多张表的Source节点,一组依赖与该Source的Sink节点
// 那么会新生成一个shuffle节点,添加到两者之间
// 将依赖关系修改与source->shuffle->多个sink
Set<ExecutionEdge> newExecutionEdges = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 这里的Shuffle策略此次不深入了解了
ShuffleStrategy shuffleStrategy =
ShuffleMultipleRowStrategy.builder()
.jobId(jobImmutableInformation.getJobId())
.inputPartitions(sourceAction.getParallelism())
.catalogTables(producedCatalogTables)
.queueEmptyQueueTtl(
(int)
(engineConfig.getCheckpointConfig().getCheckpointInterval()
* 3))
.build();
ShuffleConfig shuffleConfig =
ShuffleConfig.builder().shuffleStrategy(shuffleStrategy).build();
long shuffleVertexId = idGenerator.getNextId();
String shuffleActionName = String.format("Shuffle [%s]", sourceAction.getName());
ShuffleAction shuffleAction =
new ShuffleAction(shuffleVertexId, shuffleActionName, shuffleConfig);
shuffleAction.setParallelism(sourceAction.getParallelism());
ExecutionVertex shuffleVertex =
new ExecutionVertex(shuffleVertexId, shuffleAction, shuffleAction.getParallelism());
ExecutionEdge sourceToShuffleEdge = new ExecutionEdge(sourceExecutionVertex, shuffleVertex);
newExecutionEdges.add(sourceToShuffleEdge);
// 将多个sink节点的并行度修改为1
for (ExecutionVertex sinkVertex : sinkVertices) {
sinkVertex.setParallelism(1);
sinkVertex.getAction().setParallelism(1);
ExecutionEdge shuffleToSinkEdge = new ExecutionEdge(shuffleVertex, sinkVertex);
newExecutionEdges.add(shuffleToSinkEdge);
}
return newExecutionEdges;
}
这一步Shuffle是针对某些特殊场景,source支持多表读取,并且有多个sink节点依赖与该source节点时会在中间添加一个shuffle节点
private Set<ExecutionEdge> generateTransformChainEdges(Set<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges) {
// 使用了三个结构,存储所有的Source节点,以及每个输入,输出节点
// inputVerticesMap中以下游节点id为key,存储了所有的上游输入节点
// targetVerticesMap则以上游节点id为key,存储了所有的下游输出节点
Map<Long, List<ExecutionVertex>> inputVerticesMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Long, List<ExecutionVertex>> targetVerticesMap = new HashMap<>();
Set<ExecutionVertex> sourceExecutionVertices = new HashSet<>();
executionEdges.forEach(
edge -> {
ExecutionVertex leftVertex = edge.getLeftVertex();
ExecutionVertex rightVertex = edge.getRightVertex();
if (leftVertex.getAction() instanceof SourceAction) {
sourceExecutionVertices.add(leftVertex);
}
inputVerticesMap
.computeIfAbsent(rightVertex.getVertexId(), id -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(leftVertex);
targetVerticesMap
.computeIfAbsent(leftVertex.getVertexId(), id -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(rightVertex);
});
Map<Long, ExecutionVertex> transformChainVertexMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<Long, Long> chainedTransformVerticesMapping = new HashMap<>();
// 对每个source进行循环,即从DAG中所有的头节点开始变量
for (ExecutionVertex sourceVertex : sourceExecutionVertices) {
List<ExecutionVertex> vertices = new ArrayList<>();
vertices.add(sourceVertex);
for (int index = 0; index < vertices.size(); index++) {
ExecutionVertex vertex = vertices.get(index);
fillChainedTransformExecutionVertex(
vertex,
chainedTransformVerticesMapping,
transformChainVertexMap,
executionEdges,
Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputVerticesMap),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(targetVerticesMap));
// 当当前节点存在下游节点时,将所有下游节点放入list中,二层循环会重新计算刚刚加入进去的下游节点,可能是Transform节点也可能是Sink节点
if (targetVerticesMap.containsKey(vertex.getVertexId())) {
vertices.addAll(targetVerticesMap.get(vertex.getVertexId()));
}
}
}
// 循环完成,会将可以链化的Transform节点进行链化,在链化过程中会将可以链化的关系边从执行计划中删除
// 所以此时的逻辑计划已经无法构成图的关系,需要重新构建
Set<ExecutionEdge> transformChainEdges = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 对现存关系进行循环
for (ExecutionEdge executionEdge : executionEdges) {
ExecutionVertex leftVertex = executionEdge.getLeftVertex();
ExecutionVertex rightVertex = executionEdge.getRightVertex();
boolean needRebuild = false;
// 会从链化的map中查询当前边的输入,输出节点
// 如果在链化的map中存在,则表明该节点已经被链化,需要从映射关系中找到链化之后的节点
// 重新修正DAG
if (chainedTransformVerticesMapping.containsKey(leftVertex.getVertexId())) {
needRebuild = true;
leftVertex =
transformChainVertexMap.get(
chainedTransformVerticesMapping.get(leftVertex.getVertexId()));
}
if (chainedTransformVerticesMapping.containsKey(rightVertex.getVertexId())) {
needRebuild = true;
rightVertex =
transformChainVertexMap.get(
chainedTransformVerticesMapping.get(rightVertex.getVertexId()));
}
if (needRebuild) {
executionEdge = new ExecutionEdge(leftVertex, rightVertex);
}
transformChainEdges.add(executionEdge);
}
return transformChainEdges;
}
private void fillChainedTransformExecutionVertex(
ExecutionVertex currentVertex,
Map<Long, Long> chainedTransformVerticesMapping,
Map<Long, ExecutionVertex> transformChainVertexMap,
Set<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges,
Map<Long, List<ExecutionVertex>> inputVerticesMap,
Map<Long, List<ExecutionVertex>> targetVerticesMap) {
// 当map中以及包含当前节点则退出
if (chainedTransformVerticesMapping.containsKey(currentVertex.getVertexId())) {
return;
}
List<ExecutionVertex> transformChainedVertices = new ArrayList<>();
collectChainedVertices(
currentVertex,
transformChainedVertices,
executionEdges,
inputVerticesMap,
targetVerticesMap);
// 当list不为空时,表示list里面的transform节点可以被合并成一个
if (transformChainedVertices.size() > 0) {
long newVertexId = idGenerator.getNextId();
List<SeaTunnelTransform> transforms = new ArrayList<>(transformChainedVertices.size());
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(transformChainedVertices.size());
Set<URL> jars = new HashSet<>();
Set<ConnectorJarIdentifier> identifiers = new HashSet<>();
transformChainedVertices.stream()
.peek(
// 在mapping中添加所有历史节点编号与新节点编号的映射
vertex ->
chainedTransformVerticesMapping.put(
vertex.getVertexId(), newVertexId))
.map(ExecutionVertex::getAction)
.map(action -> (TransformAction) action)
.forEach(
action -> {
transforms.add(action.getTransform());
jars.addAll(action.getJarUrls());
identifiers.addAll(action.getConnectorJarIdentifiers());
names.add(action.getName());
});
String transformChainActionName =
String.format("TransformChain[%s]", String.join("->", names));
// 将多个TransformAction合并成一个TransformChainAction
TransformChainAction transformChainAction =
new TransformChainAction(
newVertexId, transformChainActionName, jars, identifiers, transforms);
transformChainAction.setParallelism(currentVertex.getAction().getParallelism());
ExecutionVertex executionVertex =
new ExecutionVertex(
newVertexId, transformChainAction, currentVertex.getParallelism());
// 在状态中将修改完成的节点信息放入
transformChainVertexMap.put(newVertexId, executionVertex);
chainedTransformVerticesMapping.put(
currentVertex.getVertexId(), executionVertex.getVertexId());
}
}
private void collectChainedVertices(
ExecutionVertex currentVertex,
List<ExecutionVertex> chainedVertices,
Set<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges,
Map<Long, List<ExecutionVertex>> inputVerticesMap,
Map<Long, List<ExecutionVertex>> targetVerticesMap) {
Action action = currentVertex.getAction();
// 仅对TransformAction进行合并
if (action instanceof TransformAction) {
if (chainedVertices.size() == 0) {
// 需要进行合并的节点list为空时,将自身添加到list中
// 进入该分支的条件为当前节点为TransformAction并且所需链化列表为空
// 此时可能有几种场景:第一个Transform节点进入,该Transform节点无任何限制
chainedVertices.add(currentVertex);
} else if (inputVerticesMap.get(currentVertex.getVertexId()).size() == 1) {
// 当进入该条件分支则表明:
// 所需链化的列表chainedVertices已经至少有一个TransformAction了
// 此时的场景为:上游的Transform节点仅有一个下游节点,即当前节点。此限制是由下方的判断保证
// 将当前TransformAction节点与上一个TransformAction节点进行链化
// 在执行计划中将该关系删除
executionEdges.remove(
new ExecutionEdge(
chainedVertices.get(chainedVertices.size() - 1), currentVertex));
// 将自身加入需要链化的list中
chainedVertices.add(currentVertex);
} else {
return;
}
} else {
return;
}
// It cannot chain to any target vertex if it has multiple target vertices.
if (targetVerticesMap.get(currentVertex.getVertexId()).size() == 1) {
// 当当前节点仅有一个下游节点时,再次尝试链化
// 如果当前节点存在多个下游节点,则不会将下游的节点进行链化,所以能保证上面的链化时两个节点是一对一的关系
// 这里会调用的场景为Transform节点仅有一个下游节点
collectChainedVertices(
targetVerticesMap.get(currentVertex.getVertexId()).get(0),
chainedVertices,
executionEdges,
inputVerticesMap,
targetVerticesMap);
}
}
private List<Pipeline> generatePipelines(Set<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges) {
// 存储每个执行计划节点
Set<ExecutionVertex> executionVertices = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (ExecutionEdge edge : executionEdges) {
executionVertices.add(edge.getLeftVertex());
executionVertices.add(edge.getRightVertex());
}
// 调用Pipeline执行器将执行计划转换为Pipeline
PipelineGenerator pipelineGenerator =
new PipelineGenerator(executionVertices, new ArrayList<>(executionEdges));
List<Pipeline> pipelines = pipelineGenerator.generatePipelines();
Set<String> duplicatedActionNames = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> actionNames = new HashSet<>();
for (Pipeline pipeline : pipelines) {
Integer pipelineId = pipeline.getId();
for (ExecutionVertex vertex : pipeline.getVertexes().values()) {
// 获取当前Pipeline的每个执行节点,重新设置Action的名称,添加了pipeline的名称
Action action = vertex.getAction();
String actionName = String.format("pipeline-%s [%s]", pipelineId, action.getName());
action.setName(actionName);
if (actionNames.contains(actionName)) {
duplicatedActionNames.add(actionName);
}
actionNames.add(actionName);
}
}
// 检查,不能存在重复的Action Name
checkArgument(
duplicatedActionNames.isEmpty(),
"Action name is duplicated: " + duplicatedActionNames);
return pipelines;
}
public PipelineGenerator(Collection<ExecutionVertex> vertices, List<ExecutionEdge> edges) {
this.vertices = vertices;
this.edges = edges;
}
public List<Pipeline> generatePipelines() {
List<ExecutionEdge> executionEdges = expandEdgeByParallelism(edges);
// 将执行计划进行拆分,按照关联关系,将执行计划进行拆分
// 拆分为几个不相关的执行计划
List<List<ExecutionEdge>> edgesList = splitUnrelatedEdges(executionEdges);
edgesList =
edgesList.stream()
.flatMap(e -> this.splitUnionEdge(e).stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// just convert execution plan to pipeline at now. We should split it to multi pipeline with
// cache in the future
IdGenerator idGenerator = new IdGenerator();
// 将执行计划图转换为Pipeline
return edgesList.stream()
.map(
e -> {
Map<Long, ExecutionVertex> vertexes = new HashMap<>();
List<ExecutionEdge> pipelineEdges =
e.stream()
.map(
edge -> {
if (!vertexes.containsKey(
edge.getLeftVertexId())) {
vertexes.put(
edge.getLeftVertexId(),
edge.getLeftVertex());
}
ExecutionVertex source =
vertexes.get(
edge.getLeftVertexId());
if (!vertexes.containsKey(
edge.getRightVertexId())) {
vertexes.put(
edge.getRightVertexId(),
edge.getRightVertex());
}
ExecutionVertex destination =
vertexes.get(
edge.getRightVertexId());
return new ExecutionEdge(
source, destination);
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new Pipeline(
(int) idGenerator.getNextId(), pipelineEdges, vertexes);
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
第五步则是生成执行计划实例,传递了第四步生成的Pipeline参数
小结一下: 执行计划会将逻辑计划做这几件事情
- 当source会生成多张表,并且有多个sink节点依赖于此source时,会在中间添加一个shuffle节点
- 尝试对transform节点进行链化合并,将多个transform节点合并为一个节点
- 将任务进行拆分,将一个
配置文件/LogicalDag拆分为几个不相关的任务List<Pipeline>
![]()
物理计划的生成
在看物理计划生成之前,先看下生成的物理计划中包含了什么信息, 我们对物理计划以及内部相关的内都拿出来看一下相关信息
public class PhysicalPlan {
private final List<SubPlan> pipelineList;
private final AtomicInteger finishedPipelineNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final AtomicInteger canceledPipelineNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final AtomicInteger failedPipelineNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final JobImmutableInformation jobImmutableInformation;
private final IMap<Object, Object> runningJobStateIMap;
private final IMap<Object, Long[]> runningJobStateTimestampsIMap;
private CompletableFuture<JobResult> jobEndFuture;
private final AtomicReference<String> errorBySubPlan = new AtomicReference<>();
private final String jobFullName;
private final long jobId;
private JobMaster jobMaster;
private boolean makeJobEndWhenPipelineEnded = true;
private volatile boolean isRunning = false;
}
这个类中有一个关键字段pipelineList,是一个SubPlan的列表
public class SubPlan {
private final int pipelineMaxRestoreNum;
private final int pipelineRestoreIntervalSeconds;
private final List<PhysicalVertex> physicalVertexList;
private final List<PhysicalVertex> coordinatorVertexList;
private final int pipelineId;
private final AtomicInteger finishedTaskNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final AtomicInteger canceledTaskNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final AtomicInteger failedTaskNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final String pipelineFullName;
private final IMap<Object, Object> runningJobStateIMap;
private final Map<String, String> tags;
private final IMap<Object, Long[]> runningJobStateTimestampsIMap;
private CompletableFuture<PipelineExecutionState> pipelineFuture;
private final PipelineLocation pipelineLocation;
private AtomicReference<String> errorByPhysicalVertex = new AtomicReference<>();
private final ExecutorService executorService;
private JobMaster jobMaster;
private PassiveCompletableFuture<Void> reSchedulerPipelineFuture;
private Integer pipelineRestoreNum;
private final Object restoreLock = new Object();
private volatile PipelineStatus currPipelineStatus;
public volatile boolean isRunning = false;
private Map<TaskGroupLocation, SlotProfile> slotProfiles;
}
在SubPlan中,又维护了PhysicalVertex物理节点的一个列表,并且拆分成了物理计划节点和协调器节点。
public class PhysicalVertex {
private final TaskGroupLocation taskGroupLocation;
private final String taskFullName;
private final TaskGroupDefaultImpl taskGroup;
private final ExecutorService executorService;
private final FlakeIdGenerator flakeIdGenerator;
private final Set<URL> pluginJarsUrls;
private final Set<ConnectorJarIdentifier> connectorJarIdentifiers;
private final IMap<Object, Object> runningJobStateIMap;
private CompletableFuture<TaskExecutionState> taskFuture;
private final IMap<Object, Long[]> runningJobStateTimestampsIMap;
private final NodeEngine nodeEngine;
private JobMaster jobMaster;
private volatile ExecutionState currExecutionState = ExecutionState.CREATED;
public volatile boolean isRunning = false;
private AtomicReference<String> errorByPhysicalVertex = new AtomicReference<>();
}
public class TaskGroupDefaultImpl implements TaskGroup {
private final TaskGroupLocation taskGroupLocation;
private final String taskGroupName;
// 存储了当前物理节点所需要执行的task
// 这里的每个task可能是一个读取数据的任务,也可能是一个写入数据的任务
// 或者是数据拆分,checkpoint的任务等等
private final Map<Long, Task> tasks;
public PhysicalPlanGenerator(
@NonNull ExecutionPlan executionPlan,
@NonNull NodeEngine nodeEngine,
@NonNull JobImmutableInformation jobImmutableInformation,
long initializationTimestamp,
@NonNull ExecutorService executorService,
@NonNull FlakeIdGenerator flakeIdGenerator,
@NonNull IMap runningJobStateIMap,
@NonNull IMap runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
@NonNull QueueType queueType) {
this.pipelines = executionPlan.getPipelines();
this.nodeEngine = nodeEngine;
this.jobImmutableInformation = jobImmutableInformation;
this.initializationTimestamp = initializationTimestamp;
this.executorService = executorService;
this.flakeIdGenerator = flakeIdGenerator;
// the checkpoint of a pipeline
this.pipelineTasks = new HashSet<>();
this.startingTasks = new HashSet<>();
this.subtaskActions = new HashMap<>();
this.runningJobStateIMap = runningJobStateIMap;
this.runningJobStateTimestampsIMap = runningJobStateTimestampsIMap;
this.queueType = queueType;
}
public Tuple2<PhysicalPlan, Map<Integer, CheckpointPlan>> generate() {
// 获取用户配置中的节点过滤条件,用于选择任务将要运行的节点
Map<String, String> tagFilter =
(Map<String, String>)
jobImmutableInformation
.getJobConfig()
.getEnvOptions()
.get(EnvCommonOptions.NODE_TAG_FILTER.key());
// TODO Determine which tasks do not need to be restored according to state
CopyOnWriteArrayList<PassiveCompletableFuture<PipelineStatus>>
waitForCompleteBySubPlanList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
Map<Integer, CheckpointPlan> checkpointPlans = new HashMap<>();
final int totalPipelineNum = pipelines.size();
Stream<SubPlan> subPlanStream =
pipelines.stream()
.map(
pipeline -> {
// 每次都将状态清空
this.pipelineTasks.clear();
this.startingTasks.clear();
this.subtaskActions.clear();
final int pipelineId = pipeline.getId();
// 获取当前任务的信息
final List<ExecutionEdge> edges = pipeline.getEdges();
// 获取所有的SourceAction
List<SourceAction<?, ?, ?>> sources = findSourceAction(edges);
// 生成Source数据切片任务,即SourceSplitEnumeratorTask,
// 这个任务会调用连接器中的SourceSplitEnumerator类,如果该连接器支持的话
List<PhysicalVertex> coordinatorVertexList =
getEnumeratorTask(
sources, pipelineId, totalPipelineNum);
// 生成Sink提交任务,即SinkAggregatedCommitterTask
// 这个任务会调用连接器中的SinkAggregatedCommitter类,如果该连接器支持的话
// 这两个任务是作为协调任务来执行的
coordinatorVertexList.addAll(
getCommitterTask(edges, pipelineId, totalPipelineNum));
List<PhysicalVertex> physicalVertexList =
getSourceTask(
edges, sources, pipelineId, totalPipelineNum);
//
physicalVertexList.addAll(
getShuffleTask(edges, pipelineId, totalPipelineNum));
CompletableFuture<PipelineStatus> pipelineFuture =
new CompletableFuture<>();
waitForCompleteBySubPlanList.add(
new PassiveCompletableFuture<>(pipelineFuture));
// 添加checkpoint的任务
checkpointPlans.put(
pipelineId,
CheckpointPlan.builder()
.pipelineId(pipelineId)
.pipelineSubtasks(pipelineTasks)
.startingSubtasks(startingTasks)
.pipelineActions(pipeline.getActions())
.subtaskActions(subtaskActions)
.build());
return new SubPlan(
pipelineId,
totalPipelineNum,
initializationTimestamp,
physicalVertexList,
coordinatorVertexList,
jobImmutableInformation,
executorService,
runningJobStateIMap,
runningJobStateTimestampsIMap,
tagFilter);
});
PhysicalPlan physicalPlan =
new PhysicalPlan(
subPlanStream.collect(Collectors.toList()),
executorService,
jobImmutableInformation,
initializationTimestamp,
runningJobStateIMap,
runningJobStateTimestampsIMap);
return Tuple2.tuple2(physicalPlan, checkpointPlans);
}
生成物理计划的过程就是去将执行计划转换成SeaTunnelTask,并且在执行过程中添加各种协调任务,例如数据切分任务,数据提交任务,checkpoint任务。
在SeaTunnelTask中,会将任务转换成SourceFlowLifeCycle,SinkFlowLifeCycle,TransformFlowLifeCycle,ShuffleSinkFlowLifeCycle,ShuffleSourceFlowLifeCycle。
我们以SourceFlowLifeCycle, SinkFlowLifeCycle为例
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
this.splitSerializer = sourceAction.getSource().getSplitSerializer();
this.reader =
sourceAction
.getSource()
.createReader(
new SourceReaderContext(
indexID,
sourceAction.getSource().getBoundedness(),
this,
metricsContext,
eventListener));
this.enumeratorTaskAddress = getEnumeratorTaskAddress();
}
@Override
public void open() throws Exception {
reader.open();
register();
}
public void collect() throws Exception {
if (!prepareClose) {
if (schemaChanging()) {
log.debug("schema is changing, stop reader collect records");
Thread.sleep(200);
return;
}
reader.pollNext(collector);
if (collector.isEmptyThisPollNext()) {
Thread.sleep(100);
} else {
collector.resetEmptyThisPollNext();
/**
* The current thread obtain a checkpoint lock in the method {@link
* SourceReader#pollNext(Collector)}. When trigger the checkpoint or savepoint,
* other threads try to obtain the lock in the method {@link
* SourceFlowLifeCycle#triggerBarrier(Barrier)}. When high CPU load, checkpoint
* process may be blocked as long time. So we need sleep to free the CPU.
*/
Thread.sleep(0L);
}
if (collector.captureSchemaChangeBeforeCheckpointSignal()) {
if (schemaChangePhase.get() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"previous schema changes in progress, schemaChangePhase: "
+ schemaChangePhase.get());
}
schemaChangePhase.set(SchemaChangePhase.createBeforePhase());
runningTask.triggerSchemaChangeBeforeCheckpoint().get();
log.info("triggered schema-change-before checkpoint, stopping collect data");
} else if (collector.captureSchemaChangeAfterCheckpointSignal()) {
if (schemaChangePhase.get() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"previous schema changes in progress, schemaChangePhase: "
+ schemaChangePhase.get());
}
schemaChangePhase.set(SchemaChangePhase.createAfterPhase());
runningTask.triggerSchemaChangeAfterCheckpoint().get();
log.info("triggered schema-change-after checkpoint, stopping collect data");
}
} else {
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
可以看到Source的数据读取,是在SourceFlowLifeCycle的collect方法中被真正的调用,
数据读取到之后,会放入SeaTunnelSourceCollector中,在这个collector中,当接收到数据时,会进行指标的更新,并将数据发送给相关的下游
@Override
public void collect(T row) {
try {
if (row instanceof SeaTunnelRow) {
String tableId = ((SeaTunnelRow) row).getTableId();
int size;
if (rowType instanceof SeaTunnelRowType) {
size = ((SeaTunnelRow) row).getBytesSize((SeaTunnelRowType) rowType);
} else if (rowType instanceof MultipleRowType) {
size = ((SeaTunnelRow) row).getBytesSize(rowTypeMap.get(tableId));
} else {
throw new SeaTunnelEngineException(
"Unsupported row type: " + rowType.getClass().getName());
}
sourceReceivedBytes.inc(size);
sourceReceivedBytesPerSeconds.markEvent(size);
flowControlGate.audit((SeaTunnelRow) row);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(tableId)) {
String tableName = getFullName(TablePath.of(tableId));
Counter sourceTableCounter = sourceReceivedCountPerTable.get(tableName);
if (Objects.nonNull(sourceTableCounter)) {
sourceTableCounter.inc();
} else {
Counter counter =
metricsContext.counter(SOURCE_RECEIVED_COUNT + "#" + tableName);
counter.inc();
sourceReceivedCountPerTable.put(tableName, counter);
}
}
}
sendRecordToNext(new Record<>(row));
emptyThisPollNext = false;
sourceReceivedCount.inc();
sourceReceivedQPS.markEvent();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void sendRecordToNext(Record<?> record) throws IOException {
synchronized (checkpointLock) {
for (OneInputFlowLifeCycle<Record<?>> output : outputs) {
output.received(record);
}
}
}
@Override
public void received(Record<?> record) {
try {
if (record.getData() instanceof Barrier) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Barrier barrier = (Barrier) record.getData();
if (barrier.prepareClose(this.taskLocation)) {
prepareClose = true;
}
if (barrier.snapshot()) {
try {
lastCommitInfo = writer.prepareCommit();
} catch (Exception e) {
writer.abortPrepare();
throw e;
}
List<StateT> states = writer.snapshotState(barrier.getId());
if (!writerStateSerializer.isPresent()) {
runningTask.addState(
barrier, ActionStateKey.of(sinkAction), Collections.emptyList());
} else {
runningTask.addState(
barrier,
ActionStateKey.of(sinkAction),
serializeStates(writerStateSerializer.get(), states));
}
if (containAggCommitter) {
CommitInfoT commitInfoT = null;
if (lastCommitInfo.isPresent()) {
commitInfoT = lastCommitInfo.get();
}
runningTask
.getExecutionContext()
.sendToMember(
new SinkPrepareCommitOperation<CommitInfoT>(
barrier,
committerTaskLocation,
commitInfoSerializer.isPresent()
? commitInfoSerializer
.get()
.serialize(commitInfoT)
: null),
committerTaskAddress)
.join();
}
} else {
if (containAggCommitter) {
runningTask
.getExecutionContext()
.sendToMember(
new BarrierFlowOperation(barrier, committerTaskLocation),
committerTaskAddress)
.join();
}
}
runningTask.ack(barrier);
log.debug(
"trigger barrier [{}] finished, cost {}ms. taskLocation [{}]",
barrier.getId(),
System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime,
taskLocation);
} else if (record.getData() instanceof SchemaChangeEvent) {
if (prepareClose) {
return;
}
SchemaChangeEvent event = (SchemaChangeEvent) record.getData();
writer.applySchemaChange(event);
} else {
if (prepareClose) {
return;
}
writer.write((T) record.getData());
sinkWriteCount.inc();
sinkWriteQPS.markEvent();
if (record.getData() instanceof SeaTunnelRow) {
long size = ((SeaTunnelRow) record.getData()).getBytesSize();
sinkWriteBytes.inc(size);
sinkWriteBytesPerSeconds.markEvent(size);
String tableId = ((SeaTunnelRow) record.getData()).getTableId();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tableId)) {
String tableName = getFullName(TablePath.of(tableId));
Counter sinkTableCounter = sinkWriteCountPerTable.get(tableName);
if (Objects.nonNull(sinkTableCounter)) {
sinkTableCounter.inc();
} else {
Counter counter =
metricsContext.counter(SINK_WRITE_COUNT + "#" + tableName);
counter.inc();
sinkWriteCountPerTable.put(tableName, counter);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
同样,在这个类中是真正调用Sink的Writer方法,将数据写入到下游中。
任务执行
在CoordinatorService中通过init方法生成了物理计划,然后会再调用run来真正的将任务运行起来。
CoordinatorService {
jobMaster.init(
runningJobInfoIMap.get(jobId).getInitializationTimestamp(), false);
...
jobMaster.run();
}
JobMaster {
public void run() {
...
physicalPlan.startJob();
...
}
}
在JobMaster中启动任务,会调用PhysicalPlan的startJob方法
public void startJob() {
isRunning = true;
log.info("{} state process is start", getJobFullName());
stateProcess();
}
private synchronized void stateProcess() {
if (!isRunning) {
log.warn(String.format("%s state process is stopped", jobFullName));
return;
}
switch (getJobStatus()) {
case CREATED:
updateJobState(JobStatus.SCHEDULED);
break;
case SCHEDULED:
getPipelineList()
.forEach(
subPlan -> {
if (PipelineStatus.CREATED.equals(
subPlan.getCurrPipelineStatus())) {
subPlan.startSubPlanStateProcess();
}
});
updateJobState(JobStatus.RUNNING);
break;
case RUNNING:
case DOING_SAVEPOINT:
break;
case FAILING:
case CANCELING:
jobMaster.neverNeedRestore();
getPipelineList().forEach(SubPlan::cancelPipeline);
break;
case FAILED:
case CANCELED:
case SAVEPOINT_DONE:
case FINISHED:
stopJobStateProcess();
jobEndFuture.complete(new JobResult(getJobStatus(), errorBySubPlan.get()));
return;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown Job State: " + getJobStatus());
}
}
在PhysicalPlan中,启动任务会将任务的状态更新为SCHEDULED状态,然后会继续调用SubPlan的启动方法。
public void startSubPlanStateProcess() {
isRunning = true;
log.info("{} state process is start", getPipelineFullName());
stateProcess();
}
private synchronized void stateProcess() {
if (!isRunning) {
log.warn(String.format("%s state process not start", pipelineFullName));
return;
}
PipelineStatus state = getCurrPipelineStatus();
switch (state) {
case CREATED:
updatePipelineState(PipelineStatus.SCHEDULED);
break;
case SCHEDULED:
try {
ResourceUtils.applyResourceForPipeline(jobMaster.getResourceManager(), this);
log.debug(
"slotProfiles: {}, PipelineLocation: {}",
slotProfiles,
this.getPipelineLocation());
updatePipelineState(PipelineStatus.DEPLOYING);
} catch (Exception e) {
makePipelineFailing(e);
}
break;
case DEPLOYING:
coordinatorVertexList.forEach(
task -> {
if (task.getExecutionState().equals(ExecutionState.CREATED)) {
task.startPhysicalVertex();
task.makeTaskGroupDeploy();
}
});
physicalVertexList.forEach(
task -> {
if (task.getExecutionState().equals(ExecutionState.CREATED)) {
task.startPhysicalVertex();
task.makeTaskGroupDeploy();
}
});
updatePipelineState(PipelineStatus.RUNNING);
break;
case RUNNING:
break;
case FAILING:
case CANCELING:
coordinatorVertexList.forEach(
task -> {
task.startPhysicalVertex();
task.cancel();
});
physicalVertexList.forEach(
task -> {
task.startPhysicalVertex();
task.cancel();
});
break;
case FAILED:
case CANCELED:
if (checkNeedRestore(state) && prepareRestorePipeline()) {
jobMaster.releasePipelineResource(this);
restorePipeline();
return;
}
subPlanDone(state);
stopSubPlanStateProcess();
pipelineFuture.complete(
new PipelineExecutionState(pipelineId, state, errorByPhysicalVertex.get()));
return;
case FINISHED:
subPlanDone(state);
stopSubPlanStateProcess();
pipelineFuture.complete(
new PipelineExecutionState(
pipelineId, getPipelineState(), errorByPhysicalVertex.get()));
return;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown Pipeline State: " + getPipelineState());
}
}
在SubPlan中,当状态为SCHEDULED时,会进行资源的申请,
public static void applyResourceForPipeline(
@NonNull ResourceManager resourceManager, @NonNull SubPlan subPlan) {
Map<TaskGroupLocation, CompletableFuture<SlotProfile>> futures = new HashMap<>();
Map<TaskGroupLocation, SlotProfile> slotProfiles = new HashMap<>();
// TODO If there is no enough resources for tasks, we need add some wait profile
subPlan.getCoordinatorVertexList()
.forEach(
coordinator ->
futures.put(
coordinator.getTaskGroupLocation(),
applyResourceForTask(
resourceManager, coordinator, subPlan.getTags())));
subPlan.getPhysicalVertexList()
.forEach(
task ->
futures.put(
task.getTaskGroupLocation(),
applyResourceForTask(
resourceManager, task, subPlan.getTags())));
futures.forEach(
(key, value) -> {
try {
slotProfiles.put(key, value == null ? null : value.join());
} catch (CompletionException e) {
// do nothing
}
});
// set it first, avoid can't get it when get resource not enough exception and need release
// applied resource
subPlan.getJobMaster().setOwnedSlotProfiles(subPlan.getPipelineLocation(), slotProfiles);
if (futures.size() != slotProfiles.size()) {
throw new NoEnoughResourceException();
}
}
public static CompletableFuture<SlotProfile> applyResourceForTask(
ResourceManager resourceManager, PhysicalVertex task, Map<String, String> tags) {
// TODO custom resource size
return resourceManager.applyResource(
task.getTaskGroupLocation().getJobId(), new ResourceProfile(), tags);
}
public CompletableFuture<List<SlotProfile>> applyResources(
long jobId, List<ResourceProfile> resourceProfile, Map<String, String> tagFilter)
throws NoEnoughResourceException {
waitingWorkerRegister();
ConcurrentMap<Address, WorkerProfile> matchedWorker = filterWorkerByTag(tagFilter);
if (matchedWorker.isEmpty()) {
log.error("No matched worker with tag filter {}.", tagFilter);
throw new NoEnoughResourceException();
}
return new ResourceRequestHandler(jobId, resourceProfile, matchedWorker, this)
.request(tagFilter);
}
在一个SubPlan中会将所有的任务进行资源的申请,申请资源是通过ResourceManager进行的。申请时首先会按照用户任务中设置的tag来选择将要运行任务的节点,这样就可以将任务运行在我们指定的节点上,达到资源隔离的目的。
public Optional<WorkerProfile> preCheckWorkerResource(ResourceProfile r) {
// Shuffle the order to ensure random selection of workers
List<WorkerProfile> workerProfiles =
Arrays.asList(registerWorker.values().toArray(new WorkerProfile[0]));
Collections.shuffle(workerProfiles);
// Check if there are still unassigned slots
Optional<WorkerProfile> workerProfile =
workerProfiles.stream()
.filter(
worker ->
Arrays.stream(worker.getUnassignedSlots())
.anyMatch(
slot ->
slot.getResourceProfile()
.enoughThan(r)))
.findAny();
if (!workerProfile.isPresent()) {
// Check if there are still unassigned resources
workerProfile =
workerProfiles.stream()
.filter(WorkerProfile::isDynamicSlot)
.filter(worker -> worker.getUnassignedResource().enoughThan(r))
.findAny();
}
return workerProfile;
}
private CompletableFuture<SlotAndWorkerProfile> singleResourceRequestToMember(
int i, ResourceProfile r, WorkerProfile workerProfile) {
CompletableFuture<SlotAndWorkerProfile> future =
resourceManager.sendToMember(
new RequestSlotOperation(jobId, r), workerProfile.getAddress());
return future.whenComplete(
withTryCatch(
LOGGER,
(slotAndWorkerProfile, error) -> {
if (error != null) {
throw new RuntimeException(error);
} else {
resourceManager.heartbeat(slotAndWorkerProfile.getWorkerProfile());
addSlotToCacheMap(i, slotAndWorkerProfile.getSlotProfile());
}
}));
}
当拿到全部可用节点后,会将节点先打乱,然后再随机查找一个可用资源比所需资源大的节点,随即与该节点通信,发送RequestSlotOperation给该节点
@Override
public synchronized SlotAndWorkerProfile requestSlot(
long jobId, ResourceProfile resourceProfile) {
initStatus = false;
SlotProfile profile = selectBestMatchSlot(resourceProfile);
if (profile != null) {
profile.assign(jobId);
assignedResource.accumulateAndGet(profile.getResourceProfile(), ResourceProfile::merge);
unassignedResource.accumulateAndGet(
profile.getResourceProfile(), ResourceProfile::subtract);
unassignedSlots.remove(profile.getSlotID());
assignedSlots.put(profile.getSlotID(), profile);
contexts.computeIfAbsent(
profile.getSlotID(),
p -> new SlotContext(profile.getSlotID(), taskExecutionService));
}
LOGGER.fine(
String.format(
"received slot request, jobID: %d, resource profile: %s, return: %s",
jobId, resourceProfile, profile));
return new SlotAndWorkerProfile(getWorkerProfile(), profile);
}
该节点的SlotService中接收到requestSlot请求后,会将自身信息进行更新,然后返回给master节点信息。 在请求资源的过程中,如果最终请求的资源没有达到预期结果,会得到NoEnoughResourceException异常,任务运行失败。 当资源请求成功后,会开始进行任务的部署,task.makeTaskGroupDeploy()将任务发送到worker节点上来运行任务
TaskDeployState deployState =
deploy(jobMaster.getOwnedSlotProfiles(taskGroupLocation));
public TaskDeployState deploy(@NonNull SlotProfile slotProfile) {
try {
if (slotProfile.getWorker().equals(nodeEngine.getThisAddress())) {
return deployOnLocal(slotProfile);
} else {
return deployOnRemote(slotProfile);
}
} catch (Throwable th) {
return TaskDeployState.failed(th);
}
}
private TaskDeployState deployOnRemote(@NonNull SlotProfile slotProfile) {
return deployInternal(
taskGroupImmutableInformation -> {
try {
return (TaskDeployState)
NodeEngineUtil.sendOperationToMemberNode(
nodeEngine,
new DeployTaskOperation(
slotProfile,
nodeEngine
.getSerializationService()
.toData(
taskGroupImmutableInformation)),
slotProfile.getWorker())
.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (getExecutionState().isEndState()) {
log.warn(ExceptionUtils.getMessage(e));
log.warn(
String.format(
"%s deploy error, but the state is already in end state %s, skip this error",
getTaskFullName(), currExecutionState));
return TaskDeployState.success();
} else {
return TaskDeployState.failed(e);
}
}
});
}
部署任务时,会将任务信息发送到刚刚在资源分配时获取到的节点上
public TaskDeployState deployTask(@NonNull Data taskImmutableInformation) {
TaskGroupImmutableInformation taskImmutableInfo =
nodeEngine.getSerializationService().toObject(taskImmutableInformation);
return deployTask(taskImmutableInfo);
}
public TaskDeployState deployTask(@NonNull TaskGroupImmutableInformation taskImmutableInfo) {
logger.info(
String.format(
"received deploying task executionId [%s]",
taskImmutableInfo.getExecutionId()));
TaskGroup taskGroup = null;
try {
Set<ConnectorJarIdentifier> connectorJarIdentifiers =
taskImmutableInfo.getConnectorJarIdentifiers();
Set<URL> jars = new HashSet<>();
ClassLoader classLoader;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(connectorJarIdentifiers)) {
// Prioritize obtaining the jar package file required for the current task execution
// from the local, if it does not exist locally, it will be downloaded from the
// master node.
jars =
serverConnectorPackageClient.getConnectorJarFromLocal(
connectorJarIdentifiers);
} else if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(taskImmutableInfo.getJars())) {
jars = taskImmutableInfo.getJars();
}
classLoader =
classLoaderService.getClassLoader(
taskImmutableInfo.getJobId(), Lists.newArrayList(jars));
if (jars.isEmpty()) {
taskGroup =
nodeEngine.getSerializationService().toObject(taskImmutableInfo.getGroup());
} else {
taskGroup =
CustomClassLoadedObject.deserializeWithCustomClassLoader(
nodeEngine.getSerializationService(),
classLoader,
taskImmutableInfo.getGroup());
}
logger.info(
String.format(
"deploying task %s, executionId [%s]",
taskGroup.getTaskGroupLocation(), taskImmutableInfo.getExecutionId()));
synchronized (this) {
if (executionContexts.containsKey(taskGroup.getTaskGroupLocation())) {
throw new RuntimeException(
String.format(
"TaskGroupLocation: %s already exists",
taskGroup.getTaskGroupLocation()));
}
deployLocalTask(taskGroup, classLoader, jars);
return TaskDeployState.success();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.severe(
String.format(
"TaskGroupID : %s deploy error with Exception: %s",
taskGroup != null && taskGroup.getTaskGroupLocation() != null
? taskGroup.getTaskGroupLocation().toString()
: "taskGroupLocation is null",
ExceptionUtils.getMessage(t)));
return TaskDeployState.failed(t);
}
}
当worker节点接收到任务后,会调用TaskExecutionService的deployTask方法将任务提交到启动时创建的线程池中。
当任务提交到线程池中
private final class BlockingWorker implements Runnable {
private final TaskTracker tracker;
private final CountDownLatch startedLatch;
private BlockingWorker(TaskTracker tracker, CountDownLatch startedLatch) {
this.tracker = tracker;
this.startedLatch = startedLatch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
TaskExecutionService.TaskGroupExecutionTracker taskGroupExecutionTracker =
tracker.taskGroupExecutionTracker;
ClassLoader classLoader =
executionContexts
.get(taskGroupExecutionTracker.taskGroup.getTaskGroupLocation())
.getClassLoader();
ClassLoader oldClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
final Task t = tracker.task;
ProgressState result = null;
try {
startedLatch.countDown();
t.init();
do {
result = t.call();
} while (!result.isDone()
&& isRunning
&& !taskGroupExecutionTracker.executionCompletedExceptionally());
...
}
}
会调用Task.call 方法,从而数据同步的任务会真正的被调用起来。
ClassLoader
在SeaTunnel中,修改了默认的ClassLoader的类,修改为子类优先,从而避免了与其他组件类冲突的问题
@Override
public synchronized ClassLoader getClassLoader(long jobId, Collection<URL> jars) {
log.debug("Get classloader for job {} with jars {}", jobId, jars);
if (cacheMode) {
// with cache mode, all jobs share the same classloader if the jars are the same
jobId = 1L;
}
if (!classLoaderCache.containsKey(jobId)) {
classLoaderCache.put(jobId, new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
classLoaderReferenceCount.put(jobId, new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
}
Map<String, ClassLoader> classLoaderMap = classLoaderCache.get(jobId);
String key = covertJarsToKey(jars);
if (classLoaderMap.containsKey(key)) {
classLoaderReferenceCount.get(jobId).get(key).incrementAndGet();
return classLoaderMap.get(key);
} else {
ClassLoader classLoader = new SeaTunnelChildFirstClassLoader(jars);
log.info("Create classloader for job {} with jars {}", jobId, jars);
classLoaderMap.put(key, classLoader);
classLoaderReferenceCount.get(jobId).put(key, new AtomicInteger(1));
return classLoader;
}
}
RestAPI任务提交
SeaTunnel也支持RestAPI的提交方式,当需要此功能时,首先需要在hazelcast.yaml文件中添加这样一段配置
network:
rest-api:
enabled: true
endpoint-groups:
CLUSTER_WRITE:
enabled: true
DATA:
enabled: true
当添加这样一段配置后,hazelcast节点启动后就可以接收http请求了
我们同样以提交任务为例,看下执行流程。
当我们使用RestAPI来提交任务时,客户端的就变成了我们发送http请求的节点,服务端就是seatunnel集群。
当服务端接收到请求后,会根据请求的链接,调用相应的方法
public void handle(HttpPostCommand httpPostCommand) {
String uri = httpPostCommand.getURI();
try {
if (uri.startsWith(SUBMIT_JOB_URL)) {
handleSubmitJob(httpPostCommand, uri);
} else if (uri.startsWith(STOP_JOB_URL)) {
handleStopJob(httpPostCommand, uri);
} else if (uri.startsWith(ENCRYPT_CONFIG)) {
handleEncrypt(httpPostCommand);
} else {
original.handle(httpPostCommand);
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
prepareResponse(SC_400, httpPostCommand, exceptionResponse(e));
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warning("An error occurred while handling request " + httpPostCommand, e);
prepareResponse(SC_500, httpPostCommand, exceptionResponse(e));
}
this.textCommandService.sendResponse(httpPostCommand);
}
会根据路径来查找相应的方法
private void handleSubmitJob(HttpPostCommand httpPostCommand, String uri)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
Map<String, String> requestParams = new HashMap<>();
RestUtil.buildRequestParams(requestParams, uri);
Config config = RestUtil.buildConfig(requestHandle(httpPostCommand), false);
ReadonlyConfig envOptions = ReadonlyConfig.fromConfig(config.getConfig("env"));
String jobName = envOptions.get(EnvCommonOptions.JOB_NAME);
JobConfig jobConfig = new JobConfig();
jobConfig.setName(
StringUtils.isEmpty(requestParams.get(RestConstant.JOB_NAME))
? jobName
: requestParams.get(RestConstant.JOB_NAME));
boolean startWithSavePoint =
Boolean.parseBoolean(requestParams.get(RestConstant.IS_START_WITH_SAVE_POINT));
String jobIdStr = requestParams.get(RestConstant.JOB_ID);
Long finalJobId = StringUtils.isNotBlank(jobIdStr) ? Long.parseLong(jobIdStr) : null;
SeaTunnelServer seaTunnelServer = getSeaTunnelServer();
RestJobExecutionEnvironment restJobExecutionEnvironment =
new RestJobExecutionEnvironment(
seaTunnelServer,
jobConfig,
config,
textCommandService.getNode(),
startWithSavePoint,
finalJobId);
JobImmutableInformation jobImmutableInformation = restJobExecutionEnvironment.build();
long jobId = jobImmutableInformation.getJobId();
if (!seaTunnelServer.isMasterNode()) {
NodeEngineUtil.sendOperationToMasterNode(
getNode().nodeEngine,
new SubmitJobOperation(
jobId,
getNode().nodeEngine.toData(jobImmutableInformation),
jobImmutableInformation.isStartWithSavePoint()))
.join();
} else {
submitJob(seaTunnelServer, jobImmutableInformation, jobConfig);
}
this.prepareResponse(
httpPostCommand,
new JsonObject()
.add(RestConstant.JOB_ID, String.valueOf(jobId))
.add(RestConstant.JOB_NAME, jobConfig.getName()));
}
这里的逻辑与客户端差不多,由于没有local模式,那么就不需要去创建本地服务了。
在客户端我们会通过ClientJobExecutionEnvironment这个类来进行逻辑计划解析等操作,同样这样也有一个RestJobExecutionEnvironment来做同样的事情。
最终提交任务时,如果当前节点非master节点,那么就会向master节点发送信息,master节点接收到信息后与从命令行客户端接收信息的处理逻辑就一致了。
如果当前节点是master节点,会直接调用submitJob方法,这里直接调用了coordinatorService.submitJob方法进行后续的处理。
private void submitJob(
SeaTunnelServer seaTunnelServer,
JobImmutableInformation jobImmutableInformation,
JobConfig jobConfig) {
CoordinatorService coordinatorService = seaTunnelServer.getCoordinatorService();
Data data =
textCommandService
.getNode()
.nodeEngine
.getSerializationService()
.toData(jobImmutableInformation);
PassiveCompletableFuture<Void> voidPassiveCompletableFuture =
coordinatorService.submitJob(
Long.parseLong(jobConfig.getJobContext().getJobId()),
data,
jobImmutableInformation.isStartWithSavePoint());
voidPassiveCompletableFuture.join();
}
可以看出,两种提交方式,都是会在提交任务的一端做逻辑计划解析,然后将信息发送给master节点,再由master节点做任务的物理计划解析,分配等操作。
本文由 白鲸开源科技 提供发布支持!