![]()
本文包含以下内容:
新、旧方法指定初始化和销毁方法
InitializingBean、DisposableBean指定生命周期方法
@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy调用Bean 创建前后的方法
BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器,进行初始化 前后的工作
上述3种的联合调试
1.新、旧方法指定初始化和销毁方法
在之前,指定一个Bean 的初始化方法和销毁方法可以在 bean.xml 文件中<bean> 标签中指定 init-method和 destroy-method 进行初始函数、 销毁函数的指定。要求没有任何参数、可以报任何异常
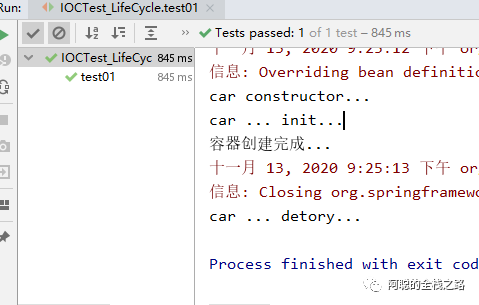
在注解中也可以通过在 @Bean (initMethod= "init" ,destroyMethod= "detory" ) 注解中指定 ,初始化方法和销毁方法。下面开始测试
@Componentpublic class Car {
public Car(){ System.out.println("car constructor..."); }
public void init(){ System.out.println("car ... init..."); }
public void detory(){ System.out.println("car ... detory..."); }
}
@Bean(initMethod="init",destroyMethod="detory") public Car car(){ return new Car(); }
@Test public void test01(){ //1、创建ioc容器 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class); System.out.println("容器创建完成...");
//applicationContext.getBean("car"); //关闭容器 applicationContext.close(); }
![]()
5.测试, 非单例的情况加上 @Scope ( "prototype" ) 注解,获得结果,表示,非单例的组件在容器创建后就不在进行管理,不再进行销毁操作了
![]()
2.InitializingBean、DisposableBean指定生命周期方法
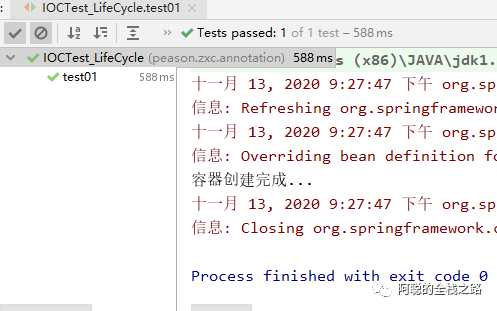
除了通过指定指定初始化方法、销毁方法外,还可以通过继承 InitializingBean 、 DisposableBean 接口分别实现其afterPropertiesSet 、destroy 方法实现,在Bean创建前后执行函数操作,下面进行测试:
@Componentpublic class Cat implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean {
public Cat(){ System.out.println("cat constructor..."); }
@Override public void destroy() throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("cat...destroy..."); }
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("cat...afterPropertiesSet..."); }
}
![]()
3.@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy调用Bean 创建前后的方法
在springboot中可以通过@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy,分别制定在Bean装配前后 执行的函数。下面开始测试:
@Componentpublic class Dog implements ApplicationContextAware {
//@Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public Dog(){ System.out.println("dog constructor..."); }
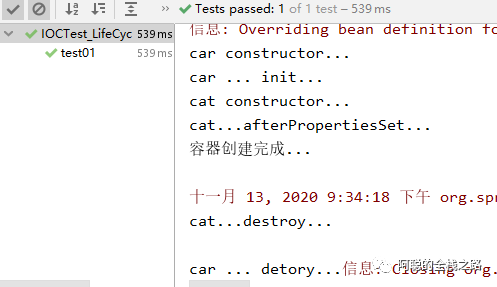
//对象创建并赋值之后调用 @PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("Dog....@PostConstruct..."); }
//容器移除对象之前 @PreDestroy public void detory(){ System.out.println("Dog....@PreDestroy..."); }}
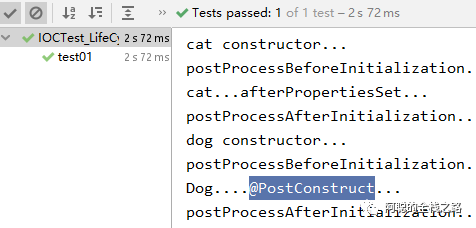
2)运行测试方法,在Bean 创建完成之后、容器创建完成前 调用的 @PostConstruct 在Bean 销毁前 调用了 @PreDestroy 的方法
![]()
4.BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器,进行初始化 前后的工作
可以通过建立BeanPostProcessor 实现类,通过其 postProcessBeforeInitialization 、postProcessAfterInitialization 方法可以在Bean 完成创建之后、Bean 销毁之前,执行指定方法。下面开始测试:
1.创建自定义 BeanPostProcessor 实现类
/** * 后置处理器:初始化前后进行处理工作 * 将后置处理器加入到容器中 * @author lfy */@Componentpublic class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean); return bean; }
@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean); return bean; }
}
2.运行测试,得到结果,在Bean 创建完成之后,调用了 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法 ,在创建Bean 完成之后调用 postProcessAfterInitialization 。结果如下:
![]()
5.上述3种的联合调试
综合上述内容,同时加入(1)InitializingBean、DisposableBean (2)@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy (3)BeanPostProcessor 查看执行方法的先后顺序
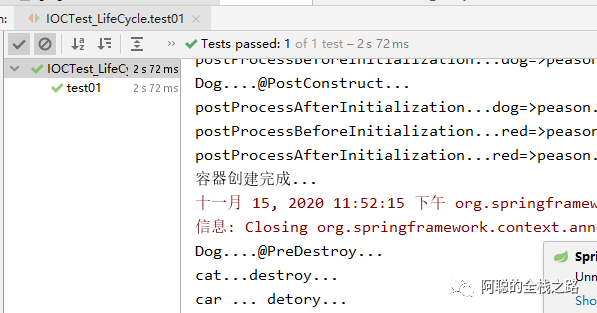
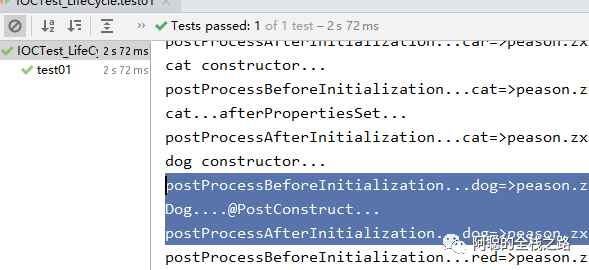
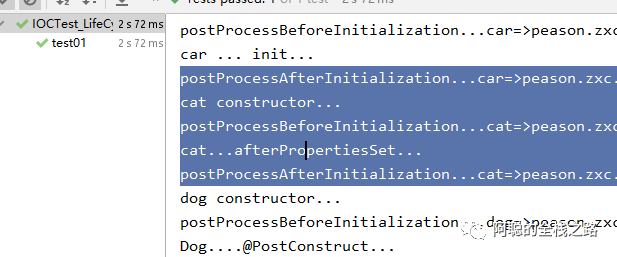
1.)首先是创建,测试结果如下图所示:执行顺序是,现执行 postProcessBeforeInitialization 而后是 构造方法 、而后是 postProcessAfterInitialization 而后是 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet
![]()
![]()
-END-
![]()
可以关注我的公众号,免费获取价值1980元学习资料