epoll 是 Linux 下 IO多路复用的机制,可以监视多个描述符的读/写等事件,一旦某个描述符就绪(一般是读或者写事件发生了),就能够将发生的事件通知给关心的应用程序去处理该事件。
以前的网络编程方式
拿使用 socket 实现的聊天程序举例。
服务器端:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket server = null;
try {
server = new ServerSocket(PROT);
System.out.println(" server start .. ");
//进行阻塞
while (true) {//这里应该循环,使得可以接受多个客户端的请求。
Socket socket = server.accept();//会阻塞,直到有客户端来链接
//新建一个线程执行客户端的任务
new Thread(new ServerHandler(socket)).start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (server != null) {
try {
server.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
server = null;
}
}
每连接一个客户端,就新启动一个线程,如果有1万个客户端,就会产生一万个线程,会严重消耗掉 CPU 性能。
当然可以使用线程池,但是无法根本性地解决问题
使用 Nio
while (true) {
try {
//1 必须要让多路复用器开始监听
this.seletor.select();
//2 返回多路复用器已经选择的结果集
Iterator<SelectionKey> keys = this.seletor.selectedKeys().iterator();
//3 进行遍历
while (keys.hasNext()) {
//4 获取一个选择的元素
SelectionKey key = keys.next();
//5 直接从容器中移除就可以了
keys.remove();
//6 如果是有效的
if (key.isValid()) {
//7 如果为阻塞状态
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
this.accept(key);
}
//8 如果为可读状态
if (key.isReadable()) {
this.read(key);
}
//9 写数据
if (key.isWritable()) {
this.write(key); //ssc
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
如果有客户端连接成功:
private void accept(SelectionKey key) {
try {
//1 获取服务通道
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//2 执行阻塞方法
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
//3 设置阻塞模式
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//4 注册到多路复用器上,并设置读取标识
sc.register(this.seletor, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
我们看到 始终只有一个线程,不管有多少个客户端来连接。
注意:不是没有任何阻塞。
seletor.select()就会阻塞,但是其他的读写事件都不会,不像传统的
inputStream.read() 就会卡死在那里,直到有数据可读。
Nio和传统 io 的区别
传统 io
- 每连接一个客户端,就会产生一个 socket,有多少个 socket 就会建立多少个线程;
- 判断 socket 是否可读或可写,需要我们程序自己轮询;
- 读写操作可能会阻塞直到可处理;
- 传统 socket 是面向流的。
Nio
- 一个线程就可以处理 n 个 socket得读写;
- 不需要轮询所有的 socket,只需要轮询
this.seletor.select() ;
- 面向缓冲区的。
为什么 Nio 不需要轮询所有的 socket 就知道哪些 socket 就绪(可读或可写)呢?
因为在 Nio 中,任何 socket 就绪都会回调一个钩子方法,应用程序就会马上知道。
epoll
参考:
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/epoll.7.html
epoll 是对 poll 的增强
epoll 提供了三个系统调用:
epoll_create
创建一个 epoll 实例,也是一个文件描述符,所有后续调用
到的epoll接口都会使用此文件描述符。
epoll_ctl
epoll实例的操作接口
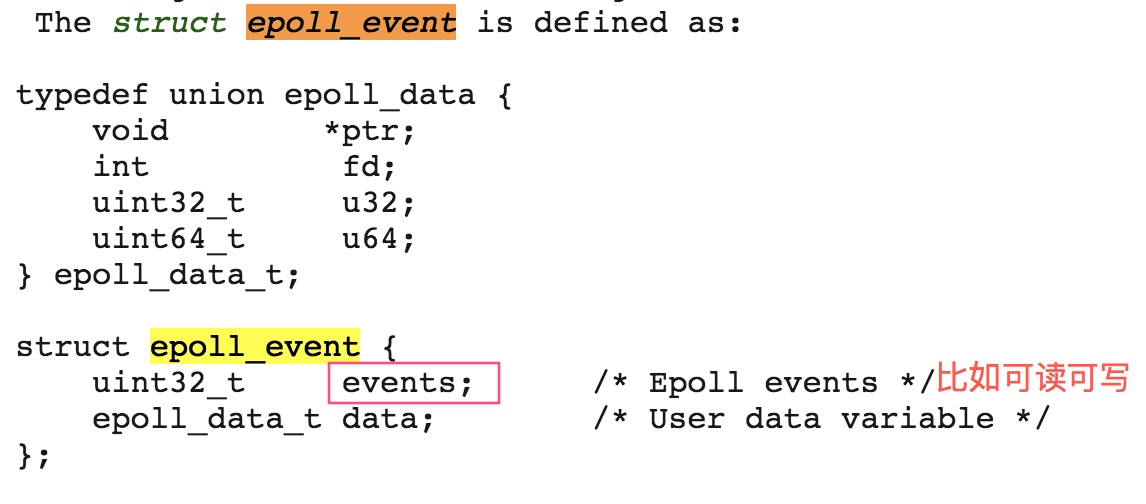
方法签名:int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
共有四个参数:
| 参数名 |
含义 |
| epfd |
epoll 实例 |
| op |
操作类型,枚举:EPOLL_CTL_ADD,EPOLL_CTL_MOD,EPOLL_CTL_DEL, op为EPOLL_CTL_ADD 表示注册一个目标文件描述符 到 epoll 实例 |
| fd |
目标文件描述符 |
| event |
目标文件描述符感兴趣的事件,比如可读,可写,event 结构如下 |
![2019-03-03_21-50-46.jpg 2019-03-03_21-50-46.jpg]()
events 是数字,可以是下面的枚举值由 or 组成的掩码:
EPOLLIN:可读;
EPOLLOUT:可写;
EPOLLERR:有异常发生;
等等,具体参考:http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/epoll.7.html
epoll_wait
等待 epoll 实例上的 io 事件发生。
方法签名如下:
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events,
int maxevents, int timeout);
| 参数名 |
含义 |
| epfd |
epoll 实例 |
| maxevents |
返回的最大的可处理的事件数量,必须大于0 |
| timeout |
epoll_wait 方法阻塞的超时时间 |
| event |
目标文件描述符待处理的事件,比如可读,可写 |
超时什么时候结束呢
- 任何一个文件描述符回调了事件(前面通过epoll_ctl 注册的事件);
- 被signal handler 中断;
- 超时
epoll 和 poll 的最大的区别(优点)
- 能监控更多的文件描述符;
- 不需要每次监控都要把所有的文件描述符 从用户态拷贝到内核态;
- 不需要每次遍历所有的文件描述符。
epoll为什么判断是否有可处理的事件时不用遍历所有的文件描述符
说白了,epoll 采用了事件回调机制(类似 [观察者模式]()),其实后面有很多框架都采用了这种事件回调机制,比如 Nodejs 等。
epoll 监听 fd 事件时,有一个就绪队列,一旦某个 fd 就绪(即有待处理的事件,例如可读,可写),就会放在这个就绪队列,应用程序调用.select() 时,不用重新遍历所有的 fd,只需要查询这个就绪队列就行。
Nio select 源码分析
注册 channel(套接字)
see /Users/xxx/Downloads/jdk_src2/sun/nio/ch/SelectorImpl.java
protected final SelectionKey register(AbstractSelectableChannel ch,
int ops,
Object attachment)
{
if (!(ch instanceof SelChImpl))
throw new IllegalSelectorException();
SelectionKeyImpl k = new SelectionKeyImpl((SelChImpl)ch, this);
k.attach(attachment);
synchronized (publicKeys) {
implRegister(k);
}
k.interestOps(ops);
return k;
}
其中,
- implRegister(k) 是为了写入 channel 文件描述符的位置;
- k.interestOps(ops) 为了写入监听的channel 可处理的操作
ops 的取值
- SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
- SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
- SelectionKey.OP_READ
implRegister的实现
见/Users/whuanghkl/Downloads/rt.jar.source/classes/sun/nio/ch/AbstractPollSelectorImpl.java
protected void implRegister(SelectionKeyImpl ski) {
synchronized (closeLock) {
if (closed)
throw new ClosedSelectorException();
// Check to see if the array is large enough
if (channelArray.length == totalChannels) {
// Make a larger array
int newSize = pollWrapper.totalChannels * 2;
SelectionKeyImpl temp[] = new SelectionKeyImpl[newSize];
// Copy over
for (int i=channelOffset; i<totalChannels; i++)
temp[i] = channelArray[i];
channelArray = temp;
// Grow the NativeObject poll array
pollWrapper.grow(newSize);
}
channelArray[totalChannels] = ski;
ski.setIndex(totalChannels);
pollWrapper.addEntry(ski.channel);
totalChannels++;
keys.add(ski);
}
}
void addEntry(SelChImpl var1) {
this.putDescriptor(this.totalChannels, IOUtil.fdVal(var1.getFD()));
this.putEventOps(this.totalChannels, 0);
this.putReventOps(this.totalChannels, 0);
++this.totalChannels;
}
Windows系统 实现
见 /Users/xxx/Downloads/openjdk-8u40-src-b25-10_feb_2015/openjdk/jdk/src/windows/classes/sun/nio/ch/WindowsSelectorImpl.java
protected void implRegister(SelectionKeyImpl ski) {
synchronized (closeLock) {
if (pollWrapper == null)
throw new ClosedSelectorException();
growIfNeeded();
channelArray[totalChannels] = ski;
ski.setIndex(totalChannels);
fdMap.put(ski);
keys.add(ski);
pollWrapper.addEntry(totalChannels, ski);
totalChannels++;
}
}
重点方法: pollWrapper.addEntry(totalChannels, ski);
void addEntry(SelChImpl var1) {
this.putDescriptor(this.totalChannels, IOUtil.fdVal(var1.getFD()));
this.putEventOps(this.totalChannels, 0);
this.putReventOps(this.totalChannels, 0);
++this.totalChannels;
}
注册(监听)channel感兴趣的操作
k.interestOps(ops)
public SelectionKey interestOps(int ops) {
ensureValid();
return nioInterestOps(ops);
}
public SelectionKey nioInterestOps(int ops) {
if ((ops & ~channel().validOps()) != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
channel.translateAndSetInterestOps(ops, this);
interestOps = ops;
return this;
}
方法channel.translateAndSetInterestOps(ops, this)中调用了 void translateAndSetInterestOps(int ops, SelectionKeyImpl sk);
translateAndSetInterestOps 见/Users/xxx/Downloads/jdk_src2/sun/nio/ch/SocketChannelImpl.java
/**
* Translates an interest operation set into a native poll event set
*/
public void translateAndSetInterestOps(int ops, SelectionKeyImpl sk) {
int newOps = 0;
if ((ops & SelectionKey.OP_READ) != 0)
newOps |= Net.POLLIN;
if ((ops & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0)
newOps |= Net.POLLOUT;
if ((ops & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0)
newOps |= Net.POLLCONN;
sk.selector.putEventOps(sk, newOps);
}
/Users/xxx/Downloads/jdk_src2/sun/nio/ch/AbstractPollSelectorImpl.java 中
public void putEventOps(SelectionKeyImpl sk, int ops) {
synchronized (closeLock) {
if (closed)
throw new ClosedSelectorException();
pollWrapper.putEventOps(sk.getIndex(), ops);
}
}
void putEventOps(int i, int event) {
int offset = SIZE_POLLFD * i + EVENT_OFFSET;
pollArray.putShort(offset, (short)event);
}
unsafe 常用操作解析
putInt 表示在指定位置写入一个 int类型数据
/**
* Writes an int at the specified offset from this native object's
* base address.
*
* @param offset
* The offset at which to write the int
*
* @param value
* The int value to be written
*/
final void putInt(int offset, int value) {
unsafe.putInt(offset + address, value);
}
poll
见 /Users/xxx/Downloads/openjdk-8u40-src-b25-10_feb_2015/openjdk/jdk/src/windows/classes/sun/nio/ch/WindowsSelectorImpl.java
private int poll() throws IOException{ // poll for the main thread
return poll0(pollWrapper.pollArrayAddress,
Math.min(totalChannels, MAX_SELECTABLE_FDS),
readFds, writeFds, exceptFds, timeout);
}
private int poll(int index) throws IOException {
// poll for helper threads
return poll0(pollWrapper.pollArrayAddress +
(pollArrayIndex * PollArrayWrapper.SIZE_POLLFD),
Math.min(MAX_SELECTABLE_FDS,
totalChannels - (index + 1) * MAX_SELECTABLE_FDS),
readFds, writeFds, exceptFds, timeout);
}
调用操作系统的能力来监听socket
select
select做了哪些事?
- poll,阻塞,获取channel 列表中可操作的channel;
- 如果有可以操作的channel,则poll 会返回;
- 根据操作系统调用的返回readFds, writeFds, exceptFds,来更新selectedKeys
见 /Users/xxx/Downloads/jdk_src2/sun/nio/ch/AbstractPollSelectorImpl.java
/**
* Copy the information in the pollfd structs into the opss
* of the corresponding Channels. Add the ready keys to the
* ready queue.
*/
protected int updateSelectedKeys() {
int numKeysUpdated = 0;
// Skip zeroth entry; it is for interrupts only
for (int i=channelOffset; i<totalChannels; i++) {
int rOps = pollWrapper.getReventOps(i);
if (rOps != 0) {
SelectionKeyImpl sk = channelArray[i];
pollWrapper.putReventOps(i, 0);
if (selectedKeys.contains(sk)) {
if (sk.channel.translateAndSetReadyOps(rOps, sk)) {
numKeysUpdated++;
}
} else {
sk.channel.translateAndSetReadyOps(rOps, sk);
if ((sk.nioReadyOps() & sk.nioInterestOps()) != 0) {
selectedKeys.add(sk);
numKeysUpdated++;
}
}
}
}
return numKeysUpdated;
}
处理监听结果
见 /Users/xxx/Downloads/openjdk-8u40-src-b25-10_feb_2015/openjdk/jdk/src/windows/classes/sun/nio/ch/WindowsSelectorImpl.java
private int processSelectedKeys(long updateCount) {
int numKeysUpdated = 0;
numKeysUpdated += processFDSet(updateCount, readFds,
Net.POLLIN,
false);
numKeysUpdated += processFDSet(updateCount, writeFds,
Net.POLLCONN |
Net.POLLOUT,
false);
numKeysUpdated += processFDSet(updateCount, exceptFds,
Net.POLLIN |
Net.POLLCONN |
Net.POLLOUT,
true);
return numKeysUpdated;
}
![]()
AbstractPollArrayWrapper 源码
/**
* Manipulates a native array of pollfd structs.
*
* @author Mike McCloskey
* @since 1.4
*/
public abstract class AbstractPollArrayWrapper {
// Miscellaneous constants
static final short SIZE_POLLFD = 8;
static final short FD_OFFSET = 0;
static final short EVENT_OFFSET = 4;
static final short REVENT_OFFSET = 6;
// The poll fd array
protected AllocatedNativeObject pollArray;
// Number of valid entries in the pollArray
protected int totalChannels = 0;
// Base address of the native pollArray
protected long pollArrayAddress;
// Access methods for fd structures
int getEventOps(int i) {
int offset = SIZE_POLLFD * i + EVENT_OFFSET;
return pollArray.getShort(offset);
}
int getReventOps(int i) {
int offset = SIZE_POLLFD * i + REVENT_OFFSET;
return pollArray.getShort(offset);
}
int getDescriptor(int i) {
int offset = SIZE_POLLFD * i + FD_OFFSET;
return pollArray.getInt(offset);
}
void putEventOps(int i, int event) {
int offset = SIZE_POLLFD * i + EVENT_OFFSET;
pollArray.putShort(offset, (short)event);
}
void putReventOps(int i, int revent) {
int offset = SIZE_POLLFD * i + REVENT_OFFSET;
pollArray.putShort(offset, (short)revent);
}
void putDescriptor(int i, int fd) {
int offset = SIZE_POLLFD * i + FD_OFFSET;
pollArray.putInt(offset, fd);
}
}
int 是四个字节
见/Users/xxx/Downloads/jdk_src2/sun/nio/ch/NativeObject.java
/**
* Reads an address from this native object at the given offset and
* constructs a native object using that address.
*
* @param offset
* The offset of the address to be read. Note that the size of an
* address is implementation-dependent.
*
* @return The native object created using the address read from the
* given offset
*/
NativeObject getObject(int offset) {
long newAddress = 0L;
switch (addressSize()) {
case 8:
newAddress = unsafe.getLong(offset + address);
break;
case 4:
newAddress = unsafe.getInt(offset + address) & 0x00000000FFFFFFFF;
break;
default:
throw new InternalError("Address size not supported");
}
return new NativeObject(newAddress);
}
poll file description 的结构
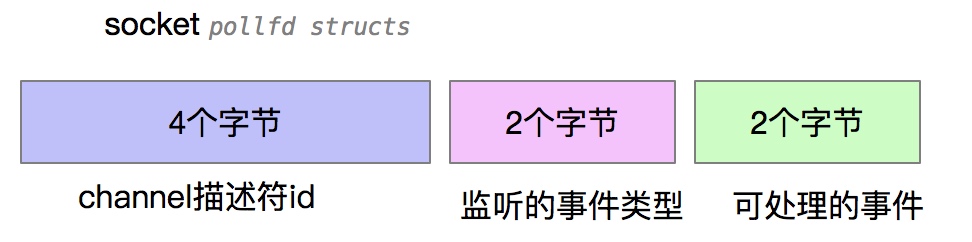
见 /Users/xxx/Downloads/jdk_src2/sun/nio/ch/PollArrayWrapper.java
Manipulates a native array of pollfd structs on Solaris:
typedef struct pollfd {
int fd;
short events;
short revents;
} pollfd_t;
一个描述符占用8个字节
![]()
jdk源码
https://yddmax.github.io/2017/06/05/openjdk%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E7%9B%AE%E5%BD%95/
后记
epoll 属于偏底层的,不太好理解。
为了加深理解,可以了解下 JavaScript 的 Event Loop 或 NodeJs 的 Event Loop
参考:
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/epoll.7.html
https://juejin.im/entry/5b6058fde51d45348a2ffc65)
https://linux.die.net/man/2/epoll_wait
https://juejin.im/post/5b0524f8518825428a2631ee