本文首发于我的个人博客:尾尾部落
0. 基础概念
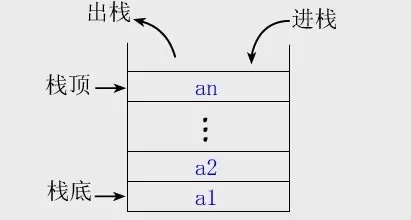
栈:后进先出(LIFO)
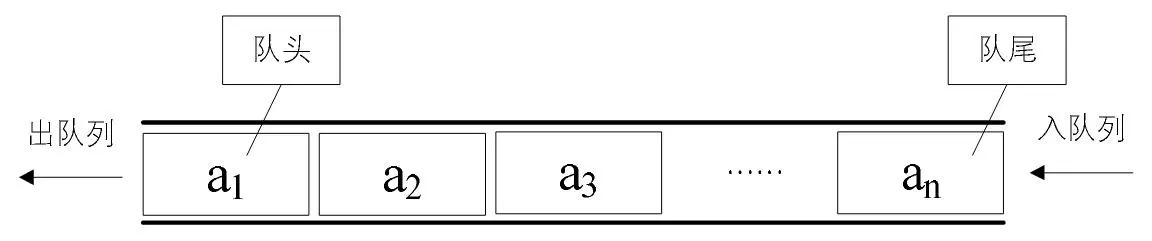
队列:先进先出(FIFO)
1. 栈的 java 实现
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Stack {
private int size = 0; //栈顶位置
private int[] array;
public Stack(){
this(10);
}
public Stack(int init) {
if(init <= 0){
init = 10;
}
array = new int[init];
}
/**
* 入栈操作
* @param item 入栈的元素
*/
public void push(int item){
if(size == array.length){
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, size*2); //扩容操作
}
array[size++] = item;
}
/**
* 获取栈顶元素,但栈顶元素不出栈
* @return 栈顶元素
*/
public int peek(){
if(size == 0){ //空栈
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("栈是空的");
}
return array[size-1];
}
/**
* 出栈,同时获取栈顶元素
* @return
*/
public int pop(){
int item = peek(); //获取栈顶元素
size--; //直接使元素个数减1,不用清除元素,下次入栈会覆盖旧元素的值
return item;
}
/**
* 判断栈是否已满
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull(){
return size == array.length;
}
/**
* 判断栈是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
}
2. 队列的 java 实现
public class ArrayQueue {
private final Object[] queue; //声明一个数组
private int head;
private int tail;
/**
* 初始化队列
* @param capacity 队列长度
*/
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
this.queue = new Object[capacity];
}
/**
* 入队
* @param o 入队元素
* @return 入队成功与否
*/
public boolean put(Object o){
if(head == (tail+1)%queue.length){
//说明队满
return false;
}
queue[tail] = o;
tail = (tail+1)%queue.length; //tail标记后移一位
return true;
}
/**
* 返回队首元素,但不出队
* @return
*/
public Object peak() {
if(head==tail){
//队空
return null;
}
return queue[head];
}
/**
* 出队
* @return 出队元素
*/
public Object pull(){
if(head==tail){
return null;
}
Object item = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
return item;
}
/**
* 判断是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return head == tail;
}
/**
* 判断是否为满
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull(){
return head == (tail+1)%queue.length;
}
/**
* 获取队列中的元素个数
* @return
*/
public int getsize(){
if(tail>=head){
return tail-head;
}else{
return (tail+queue.length)-head;
}
}
}
3. 用两个栈实现队列
剑指offer:用两个栈实现队列
LeetCode:Implement Queue using Stacks
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> input = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> output = new Stack<Integer>();
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
input.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
peek();
return output.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if(output.isEmpty()){
while(!input.isEmpty())
output.push(input.pop());
}
return output.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return input.isEmpty() && output.isEmpty();
}
}
4. 用队列实现栈
LeetCode:Implement Stack using Queues
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
if(q1.isEmpty()){
q1.add(x);
for(int i = 0; i < q2.size(); i++){
q1.add(q2.poll());
}
}else{
q2.add(x);
for(int i = 0; i < q1.size(); i++){
q2.add(q1.poll());
}
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return q1.isEmpty() ? q2.poll() : q1.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return q1.isEmpty() ? q2.peek() : q1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty() && q2.isEmpty();
}
}
5. 包含min函数的栈
剑指offer:包含min函数的栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈最小元素的min函数。
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> temp = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(temp.isEmpty() || temp.peek() >= x)
temp.push(x);
}
public void pop() {
int x = stack.pop();
int min = temp.peek();
if(x == min)
temp.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return temp.peek();
}
}
6. 栈的压入、弹出序列
剑指offer:栈的压入、弹出序列
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA, int [] popA) {
if(pushA.length != popA.length ||
pushA.length == 0 ||
popA.length == 0)
return false;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pushA.length; i++){
stack.push(pushA[i]);
while(!stack.empty() && stack.peek() == popA[index]){
stack.pop();
index++;
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
}