前言
本文将介绍在Spring MVC开发的web系统中,获取request对象的几种方法,并讨论其线程安全性。
目录
概述
如何测试线程安全性
方法1:Controller中加参数
方法2:自动注入
方法3:基类中自动注入
方法4:手动调用
方法5:@ModelAttribute方法
总结
概述
在使用Spring MVC开发Web系统时,经常需要在处理请求时使用request对象,比如获取客户端ip地址、请求的url、header中的属性(如cookie、授权信息)、body中的数据等。由于在Spring MVC中,处理请求的Controller、Service等对象都是单例的,因此获取request对象时最需要注意的问题,便是request对象是否是线程安全的:当有大量并发请求时,能否保证不同请求/线程中使用不同的request对象。
这里还有一个问题需要注意:前面所说的“在处理请求时”使用request对象,究竟是在哪里使用呢?考虑到获取request对象的方法有微小的不同,大体可以分为两类:
1) 在Spring的Bean中使用request对象:既包括Controller、Service、Repository等MVC的Bean,也包括了Component等普通的Spring Bean。为了方便说明,后文中Spring中的Bean一律简称为Bean。
2) 在非Bean中使用request对象:如普通的Java对象的方法中使用,或在类的静态方法中使用。
此外,本文讨论是围绕代表请求的request对象展开的,但所用方法同样适用于response对象、InputStream/Reader、OutputStream/ Writer等;其中InputStream/Reader可以读取请求中的数据,OutputStream/ Writer可以向响应写入数据。
最后,获取request对象的方法与Spring及MVC的版本也有关系;本文基于Spring4进行讨论,且所做的实验都是使用4.1.1版本。
如何测试线程安全性
既然request对象的线程安全问题需要特别关注,为了便于后面的讨论,下面先说明如何测试request对象是否是线程安全的。
测试的基本思路,是模拟客户端大量并发请求,然后在服务器判断这些请求是否使用了相同的request对象。
判断request对象是否相同,最直观的方式是打印出request对象的地址,如果相同则说明使用了相同的对象。然而,在几乎所有web服务器的实现中,都使用了线程池,这样就导致先后到达的两个请求,可能由同一个线程处理:在前一个请求处理完成后,线程池收回该线程,并将该线程重新分配给了后面的请求。而在同一线程中,使用的request对象很可能是同一个(地址相同,属性不同)。因此即便是对于线程安全的方法,不同的请求使用的request对象地址也可能相同。
为了避免这个问题,一种方法是在请求处理过程中使线程休眠几秒,这样可以让每个线程工作的时间足够长,从而避免同一个线程分配给不同的请求;另一种方法,是使用request的其他属性(如参数、header、body等)作为request是否线程安全的依据,因为即便不同的请求先后使用了同一个线程(request对象地址也相同),只要使用不同的属性分别构造了两次request对象,那么request对象的使用就是线程安全的。本文使用第二种方法进行测试。
客户端测试代码如下(创建1000个线程分别发送请求):
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String prefix = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "") + "::";
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
final String value = prefix + i;
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://localhost:8080/test?key=" + value);
httpClient.execute(httpGet);
httpClient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
}
}
}
服务器中Controller代码如下(暂时省略了获取request对象的代码):
@Controller
public class TestController {
// 存储已有参数,用于判断参数是否重复,从而判断线程是否安全
public static Set set = new HashSet<>();
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
// …………………………通过某种方式获得了request对象………………………………
// 判断线程安全
String value = request.getParameter("key");
if (set.contains(value)) {
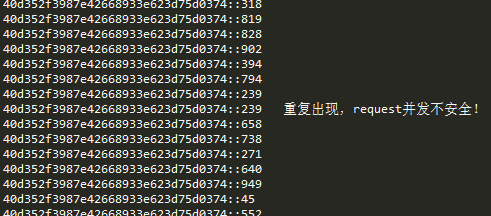
System.out.println(value + "\t重复出现,request并发不安全!");
} else {
System.out.println(value);
set.add(value);
}
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
如果request对象线程安全,服务器中打印结果如下所示:
![images/dnrnxFfK4HeRTPkJ6atzhRk8MhTsTfQk.png images/dnrnxFfK4HeRTPkJ6atzhRk8MhTsTfQk.png]()
如果存在线程安全问题,服务器中打印结果可能如下所示:
![images/hFZexjM3eCrX4EP2ZdzhHZcS8TsdFaJ3.png images/hFZexjM3eCrX4EP2ZdzhHZcS8TsdFaJ3.png]()
如无特殊说明,本文后面的代码中将省略掉测试代码。
方法1:Controller中加参数
代码示例
这种方法实现最简单,直接上Controller代码:
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test(HttpServletRequest request) throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
该方法实现的原理是,在Controller方法开始处理请求时,Spring会将request对象赋值到方法参数中。除了request对象,可以通过这种方法获取的参数还有很多,具体可以参见:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc-ann-methods
Controller中获取request对象后,如果要在其他方法中(如service方法、工具类方法等)使用request对象,需要在调用这些方法时将request对象作为参数传入。
线程安全性
测试结果:线程安全
分析:此时request对象是方法参数,相当于局部变量,毫无疑问是线程安全的。
优缺点
这种方法的主要缺点是request对象写起来冗余太多,主要体现在两点:
1) 如果多个controller方法中都需要request对象,那么在每个方法中都需要添加一遍request参数
2) request对象的获取只能从controller开始,如果使用request对象的地方在函数调用层级比较深的地方,那么整个调用链上的所有方法都需要添加request参数
实际上,在整个请求处理的过程中,request对象是贯穿始终的;也就是说,除了定时器等特殊情况,request对象相当于线程内部的一个全局变量。而该方法,相当于将这个全局变量,传来传去。
方法2:自动注入
代码示例
先上代码:
@Controller
public class TestController{
@Autowired
private HttpServletRequest request; //自动注入request
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException{
//模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
线程安全性
测试结果:线程安全
分析:在Spring中,Controller的scope是singleton(单例),也就是说在整个web系统中,只有一个TestController;但是其中注入的request却是线程安全的,原因在于:
使用这种方式,当Bean(本例的TestController)初始化时,Spring并没有注入一个request对象,而是注入了一个代理(proxy);当Bean中需要使用request对象时,通过该代理获取request对象。
下面通过具体的代码对这一实现进行说明。
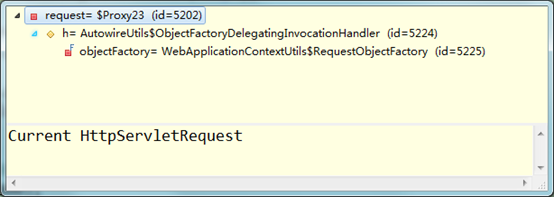
在上述代码中加入断点,查看request对象的属性,如下图所示:
![images/YDwMDwPY4Z2Qdf4raD3D2FrTnJyzBBcd.png images/YDwMDwPY4Z2Qdf4raD3D2FrTnJyzBBcd.png]()
在图中可以看出,request实际上是一个代理:代理的实现参见AutowireUtils的内部类ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler:
/**
* Reflective InvocationHandler for lazy access to the current target object.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
public ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory objectFactory) {
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// ……省略无关代码
try {
return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args); // 代理实现核心代码
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
也就是说,当我们调用request的方法method时,实际上是调用了由objectFactory.getObject()生成的对象的method方法;objectFactory.getObject()生成的对象才是真正的request对象。
继续观察上图,发现objectFactory的类型为WebApplicationContextUtils的内部类RequestObjectFactory;而RequestObjectFactory代码如下:
/**
* Factory that exposes the current request object on demand.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class RequestObjectFactory implements ObjectFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public ServletRequest getObject() {
return currentRequestAttributes().getRequest();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Current HttpServletRequest";
}
}
其中,要获得request对象需要先调用currentRequestAttributes()方法获得RequestAttributes对象,该方法的实现如下:
/**
* Return the current RequestAttributes instance as ServletRequestAttributes.
*/
private static ServletRequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes requestAttr = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
if (!(requestAttr instanceof ServletRequestAttributes)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Current request is not a servlet request");
}
return (ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttr;
}
生成RequestAttributes对象的核心代码在类RequestContextHolder中,其中相关代码如下(省略了该类中的无关代码):
public abstract class RequestContextHolder {
public static RequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() throws IllegalStateException {
RequestAttributes attributes = getRequestAttributes();
// 此处省略不相关逻辑…………
return attributes;
}
public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get();
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get();
}
return attributes;
}
private static final ThreadLocal requestAttributesHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal("Request attributes");
private static final ThreadLocal inheritableRequestAttributesHolder =
new NamedInheritableThreadLocal("Request context");
}
通过这段代码可以看出,生成的RequestAttributes对象是线程局部变量(ThreadLocal),因此request对象也是线程局部变量;这就保证了request对象的线程安全性。
优缺点
该方法的主要优点:
1) 注入不局限于Controller中:在方法1中,只能在Controller中加入request参数。而对于方法2,不仅可以在Controller中注入,还可以在任何Bean中注入,包括Service、Repository及普通的Bean。
2) 注入的对象不限于request:除了注入request对象,该方法还可以注入其他scope为request或session的对象,如response对象、session对象等;并保证线程安全。
3) 减少代码冗余:只需要在需要request对象的Bean中注入request对象,便可以在该Bean的各个方法中使用,与方法1相比大大减少了代码冗余。
但是,该方法也会存在代码冗余。考虑这样的场景:web系统中有很多controller,每个controller中都会使用request对象(这种场景实际上非常频繁),这时就需要写很多次注入request的代码;如果还需要注入response,代码就更繁琐了。下面说明自动注入方法的改进方法,并分析其线程安全性及优缺点。
方法3:基类中自动注入
代码示例
与方法2相比,将注入部分代码放入到了基类中。
基类代码:
public class BaseController {
@Autowired
protected HttpServletRequest request;
}
Controller代码如下;这里列举了BaseController的两个派生类,由于此时测试代码会有所不同,因此服务端测试代码没有省略;客户端也需要进行相应的修改(同时向2个url发送大量并发请求)。
@Controller
public class TestController extends BaseController {
// 存储已有参数,用于判断参数value是否重复,从而判断线程是否安全
public static Set set = new HashSet<>();
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
String value = request.getParameter("key");
// 判断线程安全
if (set.contains(value)) {
System.out.println(value + "\t重复出现,request并发不安全!");
} else {
System.out.println(value);
set.add(value);
}
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
@Controller
public class Test2Controller extends BaseController {
@RequestMapping("/test2")
public void test2() throws InterruptedException {
String value = request.getParameter("key");
// 判断线程安全(与TestController使用一个set进行判断)
if (TestController.set.contains(value)) {
System.out.println(value + "\t重复出现,request并发不安全!");
} else {
System.out.println(value);
TestController.set.add(value);
}
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
线程安全性
测试结果:线程安全
分析:在理解了方法2的线程安全性的基础上,很容易理解方法3是线程安全的:当创建不同的派生类对象时,基类中的域(这里是注入的request)在不同的派生类对象中会占据不同的内存空间,也就是说将注入request的代码放在基类中对线程安全性没有任何影响;测试结果也证明了这一点。
优缺点
与方法2相比,避免了在不同的Controller中重复注入request;但是考虑到java只允许继承一个基类,所以如果Controller需要继承其他类时,该方法便不再好用。
无论是方法2和方法3,都只能在Bean中注入request;如果其他方法(如工具类中static方法)需要使用request对象,则需要在调用这些方法时将request参数传递进去。下面介绍的方法4,则可以直接在诸如工具类中的static方法中使用request对象(当然在各种Bean中也可以使用)。
方法4:手动调用
代码示例
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
线程安全性
测试结果:线程安全
分析:该方法与方法2(自动注入)类似,只不过方法2中通过自动注入实现,本方法通过手动方法调用实现。因此本方法也是线程安全的。
优缺点
优点:可以在非Bean中直接获取。缺点:如果使用的地方较多,代码非常繁琐;因此可以与其他方法配合使用。
方法5:@ModelAttribute方法
代码示例
下面这种方法及其变种(变种:将request和bindRequest放在子类中)在网上经常见到:
@Controller
public class TestController {
private HttpServletRequest request;
@ModelAttribute
public void bindRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
this.request = request;
}
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟程序执行了一段时间
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
线程安全性
测试结果:线程不安全
分析:@ModelAttribute注解用在Controller中修饰方法时,其作用是Controller中的每个@RequestMapping方法执行前,该方法都会执行。因此在本例中,bindRequest()的作用是在test()执行前为request对象赋值。虽然bindRequest()中的参数request本身是线程安全的,但由于TestController是单例的,request作为TestController的一个域,无法保证线程安全。
总结
综上所述,Controller中加参数(方法1)、自动注入(方法2和方法3)、手动调用(方法4)都是线程安全的,都可以用来获取request对象。如果系统中request对象使用较少,则使用哪种方式均可;如果使用较多,建议使用自动注入(方法2 和方法3)来减少代码冗余。如果需要在非Bean中使用request对象,既可以在上层调用时通过参数传入,也可以直接在方法中通过手动调用(方法4)获得。
更多参考内容:http://www.roncoo.com/course/list.html?courseName=spring