缓存穿透是指查询一个一定不存在的数据,由于缓存不命中,并且出于容错考虑, 如果从存储层查不到数据则不写入缓存,这将导致这个不存在的数据每次请求都要到存储层去查询,失去了缓存的意义。
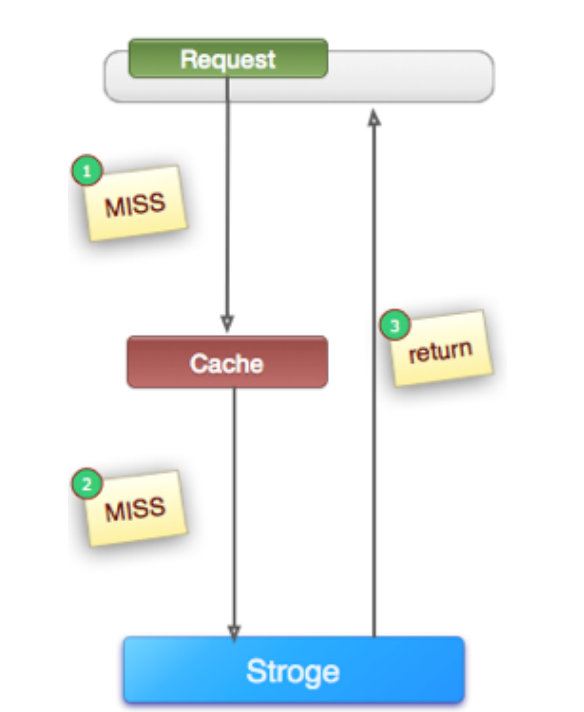
例如:下图是一个比较典型的cache-storage架构,cache(例如memcache, redis等等) + storage(例如mysql, hbase等等)架构,查一个压根就不存在的值, 如果不做兼容,永远会查询storage。
二. 危害:
对底层数据源(mysql, hbase, http接口, rpc调用等等)压力过大,有些底层数据源不具备高并发性。
例如mysql一般来说单台能够扛1000-QPS就已经很不错了(别说你的查询都是select * from table where id=xx 以及你的机器多么牛逼,那就有点矫情了)
例如他人提供的一个抗压性很差的http接口,可能穿透会击溃他的服务。
三. 如何发现:
我们可以分别记录cache命中数, storage命中数,以及总调用量,如果发现空命中(cache,storage都没有命中)较多,可能就会在缓存穿透问题。
注意:缓存本身的命中率(例如redis中的info提供了类似数字,只代表缓存本身)不代表storage和业务的命中率。
四. 产生原因以及业务是否允许?
产生原因有很多:可能是代码本身或者数据存在的问题造成的,也很有可能是一些恶意攻击、爬虫等等(因为http读接口都是开放的)
业务是否允许:这个要看做的项目或者业务是否允许这种情况发生,比如做一些非实时的推荐系统,假如新用户来了,确实没有他的推荐数据(推荐数据通常是根据历史行为算出),这种业务是会发生穿透现象的,至于业务允不允许要具体问题具体分析了。
五. 解决方法:
解决思路大致有两个,如下表。下面将分别说明
| 解决缓存穿透 |
适用场景 |
维护成本 |
| 缓存空对象 |
1. 数据命中不高 2. 数据频繁变化实时性高 |
1.代码维护简单 2.需要过多的缓存空间 3. 数据不一致 |
| bloomfilter或者压缩filter提前拦截 |
1. 数据命中不高 2. 数据相对固定实时性低 |
1.代码维护复杂 2.缓存空间占用少 |
1. 缓存空对象
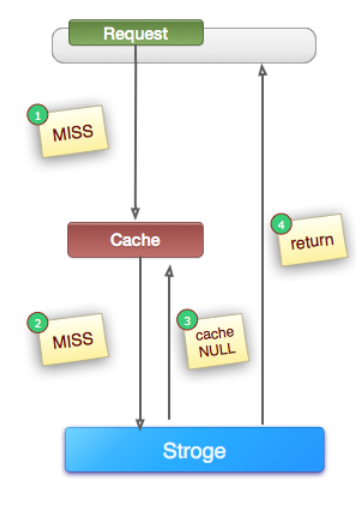
(1). 定义:如上图所示,当第②步MISS后,仍然将空对象保留到Cache中(可能是保留几分钟或者一段时间,具体问题具体分析),下次新的Request(同一个key)将会从Cache中获取到数据,保护了后端的Storage。
(2) 适用场景:数据命中不高,数据频繁变化实时性高(一些乱转业务)
(3) 维护成本:代码比较简单,但是有两个问题:
第一是空值做了缓存,意味着缓存系统中存了更多的key-value,也就是需要更多空间(有人说空值没多少,但是架不住多啊),解决方法是我们可以设置一个较短的过期时间。
第二是数据会有一段时间窗口的不一致,假如,Cache设置了5分钟过期,此时Storage确实有了这个数据的值,那此段时间就会出现数据不一致,解决方法是我们可以利用消息或者其他方式,清除掉Cache中的数据。
(4) 伪代码:
package com.carlosfu.service;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import com.carlosfu.cache.Cache;
import com.carlosfu.storage.Storage;
/**
* 某服务
*
* @author carlosfu
* @Date 2015-10-11
* @Time 下午6:28:46
*/
public class XXXService {
/**
* 缓存
*/
private Cache cache = new Cache();
/**
* 存储
*/
private Storage storage = new Storage();
/**
* 模拟正常模式
* @param key
* @return
*/
public String getNormal(String key) {
// 从缓存中获取数据
String cacheValue = cache.get(key);
// 缓存为空
if (StringUtils.isBlank(cacheValue)) {
// 从存储中获取
String storageValue = storage.get(key);
// 如果存储数据不为空,将存储的值设置到缓存
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(storageValue)) {
cache.set(key, storageValue);
}
return storageValue;
} else {
// 缓存非空
return cacheValue;
}
}
/**
* 模拟防穿透模式
* @param key
* @return
*/
public String getPassThrough(String key) {
// 从缓存中获取数据
String cacheValue = cache.get(key);
// 缓存为空
if (StringUtils.isBlank(cacheValue)) {
// 从存储中获取
String storageValue = storage.get(key);
cache.set(key, storageValue);
// 如果存储数据为空,需要设置一个过期时间(300秒)
if (StringUtils.isBlank(storageValue)) {
cache.expire(key, 60 * 5);
}
return storageValue;
} else {
// 缓存非空
return cacheValue;
}
}
}
2. bloomfilter或者压缩filter(bitmap等等)提前拦截
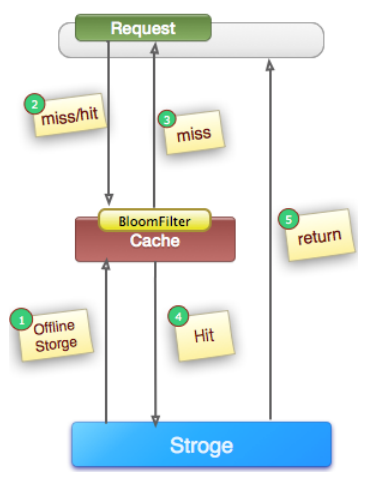
(1). 定义:如上图所示,在访问所有资源(cache, storage)之前,将存在的key用布隆过滤器提前保存起来,做第一层拦截, 例如: 我们的推荐服务有4亿个用户uid, 我们会根据用户的历史行为进行推荐(非实时),所有的用户推荐数据放到hbase中,但是每天有许多新用户来到网站,这些用户在当天的访问就会穿透到hbase。为此我们每天4点对所有uid做一份布隆过滤器。如果布隆过滤器认为uid不存在,那么就不会访问hbase,在一定程度保护了hbase(减少30%左右)。
注:有关布隆过滤器的相关知识,请自行查阅,有关guava中如何使用布隆过滤器,之后会系列文章给大家介绍。
(2) 适用场景:数据命中不高,数据相对固定实时性低(通常是数据集较大)
(3) 维护成本:代码维护复杂, 缓存空间占用少
第一是空值做了缓存,意味着缓存系统中存了更多的key-value,也就是需要更多空间(有人说空值没多少,但是架不住多啊),解决方法是我们可以设置一个较短的过期时间。
第二是数据会有一段时间窗口的不一致,假如,Cache设置了5分钟过期,此时Storage确实有了这个数据的值,那此段时间就会出现数据不一致,解决方法是我们可以利用消息或者其他方式,清除掉Cache中的数据。
六、参考资料:
附图一张,单机负载,哈哈: