重试机制与 CompletableFuture 拓展
禁止转载。
本文旨在讨论重试机制的特点和策略,分析常用重试类库的实现,讨论为 CompletableFuture 添加重试机制的方法。文章首发同名公众号,欢迎关注。
重试示例
以下是一个常见的使用异步重试的例子,当我们需要重试功能时,只需调用 retry 方法,传入相应的重试策略即可。这里的重试策略为重试 2 次,使用回退策略(backoff),重试间隔为 100ms,抖动因子为 0.75,同时指定了调度器。
// Project Reactor 提供的重试方法
public Mono<String> getUsername(String userId) {
// backoff 重试策略
var backoffRetry = Retry
.backoff(2, Duration.ofMillis(100))
.jitter(0.75)
.scheduler(Schedulers.newSingle("retry scheduler"));
return webClient.get()
.uri("localhost:8080/user/", userId)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
// 若为简单重试可改为调用 retry(n)
.retryWhen(backoffRetry);
}
以下图片摘自 Mono#retryWhen 文档注释:
![file]() Project Reactor 是基于发布-订阅模型的响应式组件。从图中可以看出,每次获取数据失败后,会等待一段时间,然后再次订阅发布者以获取数据,反复以上过程直到达到最终重试次数或者出现成功结果。
Project Reactor 是基于发布-订阅模型的响应式组件。从图中可以看出,每次获取数据失败后,会等待一段时间,然后再次订阅发布者以获取数据,反复以上过程直到达到最终重试次数或者出现成功结果。
Spring Retry 类库提供了重试模版:
RetryTemplate template = RetryTemplate.builder()
.maxAttempts(3)
.fixedBackoff(1000)
.retryOn(RemoteAccessException.class)
.build();
// 重试
template.execute(ctx -> {
// ... do something
});
重试模版需要传入任务,而 Project Reactor 中发布者-订阅者两者解耦,可以实现多次订阅,因此不影响链式调用。
若想为 CompletableFuture 增加重试功能,最好是使用类似 Spring-Retry 的模式,添加工具类方法 retry,参数包括任务、重试策略等。
重试策略
-
触发重试策略
特定异常(如支持黑白名单)、特定返回值、自定义
-
等待策略(backoff 算法)
无等待、固定时间(fixed)、等量增长时间(incremental)、指数增长时间(exponentail backoff)、随机时间(random)、斐波那契数列(fibnonacci) 、自定义
-
终止策略
尝试次数(maxAttempts)、超时终止、自定义
重试策略应该注意区分有状态重试和无状态重试:
有状态重试表示各个重试之间存在相互依赖,比如
-
每次访问网站信息时,返回错误信息包含了下一次可以正常访问的时间
-
输入密码多次错误后,需要等待若干时间再重试
-
共用相同的限流组件;
无状态重试表示每次重试不依赖其他重试的结果,实现容易,某些复杂的有状态重试可以使用无状态重试实现。
重试上下文信息
常见的重试上下文有:重试次数、每次返回结果、日志记录、回调。
回调方法包括每次返回结果时回调、最终返回结果时回调。
简易实现代码
手动实现最简单的方法是调用 exceptionally 或者 exceptionallyCompose 方法,多次传入重试任务。
1. 迭代实现 N 次重试
以下代码使用了迭代法,缺点是造成 CompletableFuture 内部维护的 stack 过深,增加不必要的内存开销;无法实现无限次重试。
public static <T> CompletableFuture<T> retry(Supplier<T> supplier, int attempts) {
var cf = supplyAsync(supplier);
for (int i = 0; i < attempts; i++) {
cf = cf.exceptionally(ex -> supplier.get());
}
return cf;
}
2. 递归实现 N 次重试
使用递归解决了以上问题:
@Slf4j
class RetryNAttemptsDemo {
// 演示用,忽略线程池配置
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 任务3次重试后返回正确结果
var times = new AtomicInteger();
Supplier<Integer> task = () -> {
if (times.getAndIncrement() < 3) {
throw new RuntimeException("异常结果");
} else {
return 42;
}
};
// 使用重试
retry(4, () -> supplyAsync(task))
.thenAcceptAsync(r -> log.info("获取结果: {}", r))
.whenComplete((__, ex) -> log.error("最终获取结果异常", ex))
.join();
}
public static <T> CompletableFuture<T> retry(int attempts, Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> supplier) {
// 使用CompletableFuture的写功能
var result = new CompletableFuture<T>();
retryNAttempts(result, attempts, supplier);
return result;
}
private static <T> void retryNAttempts(CompletableFuture<T> result, int attempts, Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> supplier) {
supplier.get()
.thenAccept(result::complete)
.whenComplete((__, throwable) -> {
if (attempts > 0L) {
log.warn("异常重试");
retryNAttempts(result, attempts - 1, supplier);
} else {
log.error("多次重试异常结果", throwable);
result.completeExceptionally(throwable);
}
});
}
}
执行结果如下,符合预期。
> Task :RetryNAttemptsDemo.main()
23:18:32.042 [main] WARN com.example.demo.futures.RetryNAttemptsDemo -- 异常重试
23:18:32.043 [main] WARN com.example.demo.futures.RetryNAttemptsDemo -- 异常重试
23:18:32.044 [main] WARN com.example.demo.futures.RetryNAttemptsDemo -- 异常重试
23:18:32.044 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1] INFO com.example.demo.futures.RetryNAttemptsDemo -- 获取结果: 42
3. 递归实现 backoff
思路:
- 正常结果和异常结果分别处理,若有最终结果则记录到 result
- 处理结果为重试等待时间
- 执行重试(使用 ScheduledExecutorService#schedule)
@Slf4j
class BackoffRetryDemo {
public static final long STOP_RETRY = -1L;
private final int maxAttempts;
private final AtomicInteger attempts = new AtomicInteger();
// 延迟时间(ms)
private final long delay;
BackoffRetryDemo(int maxAttempts, long delay) {
this.maxAttempts = maxAttempts;
this.delay = delay;
}
public <T> CompletableFuture<T> retry(Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> stageSupplier, ScheduledExecutorService delayer) {
CompletableFuture<T> result = new CompletableFuture<>();
retry(stageSupplier, delayer, result);
return result;
}
private <T> void retry(Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> stageSupplier, ScheduledExecutorService delayer, CompletableFuture<T> result) {
attempts.incrementAndGet();
stageSupplier.get()
.thenApply(r -> {
result.complete(r);
return STOP_RETRY;
})
.exceptionally(throwable -> {
if (attempts.get() >= maxAttempts) {
result.completeExceptionally(throwable);
return STOP_RETRY;
}
log.warn("异常重试");
return delay;
})
.thenAccept(delay -> {
if (delay == 0L)
delayer.execute(() -> retry(stageSupplier, delayer, result));
else if (delay > 0L)
delayer.schedule(() -> retry(stageSupplier, delayer, result), delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
var times = new AtomicInteger();
Supplier<Integer> task = () -> {
if (times.getAndIncrement() < 3) {
throw new RuntimeException("异常结果");
} else {
return 42;
}
};
var backoffRetry = new BackoffRetryDemo(4, 500);
backoffRetry.retry(() -> supplyAsync(task), Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor())
.thenAcceptAsync(r -> log.info("获取结果: {}", r))
.exceptionallyAsync(throwable -> {
log.error("最终获取结果异常", throwable);
return null;
})
.join();
}
}
执行日志如下:
> Task :BackoffRetryDemo.main()
23:54:12.099 [main] WARN com.example.demo.futures.BackoffRetryDemo -- 异常重试
23:54:12.610 [pool-1-thread-1] WARN com.example.demo.futures.BackoffRetryDemo -- 异常重试
23:54:13.113 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1] WARN com.example.demo.futures.BackoffRetryDemo -- 异常重试
23:54:13.621 [ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1] INFO com.example.demo.futures.BackoffRetryDemo -- 获取结果: 42
从结果可以看出,实现了延迟重试,重试等待时间为 500ms,三次尝试后获取到了正确结果。
不同类库的实现浅析
1. Resiliance4J
将 Retry 视为高阶函数装饰器,可以实现对任意方法的增强,如 Supplier, Consumer, CompletableFuture
CheckedFunction0<String> retryableSupplier = Retry
.decorateCheckedSupplier(retry, helloWorldService::sayHelloWorld);
// 线程安全类
public interface Retry {
// 装饰器方法,为 supplier 增加可重试功能
static <T> Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> decorateCompletionStage(
Retry retry,
ScheduledExecutorService scheduler,
Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> supplier
) {
return () -> {
// 这里使用 final 可能是为了兼容 JDK7
final CompletableFuture<T> promise = new CompletableFuture<>();
final Runnable block = new AsyncRetryBlock<>(scheduler, retry.asyncContext(), supplier,
promise);
block.run();
return promise;
};
}
// 全局管理 Retry 支持
String getName();
Map<String, String> getTags();
// 上下文支持回调
<T> Retry.Context<T> context();
<T> Retry.AsyncContext<T> asyncContext();
// 重试策略
RetryConfig getRetryConfig();
// 事件支持
EventPublisher getEventPublisher();
default <T> CompletionStage<T> executeCompletionStage(ScheduledExecutorService scheduler,
Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> supplier) {
return decorateCompletionStage(this, scheduler, supplier).get();
}
// 略去其他执行方法,如 executeSupplier,executeRunnable
// 监控信息
Metrics getMetrics();
interface Metrics {
long getNumberOfSuccessfulCallsWithoutRetryAttempt();
long getNumberOfFailedCallsWithoutRetryAttempt();
long getNumberOfSuccessfulCallsWithRetryAttempt();
long getNumberOfFailedCallsWithRetryAttempt();
}
// 回调支持
interface AsyncContext<T> {
void onComplete();
long onError(Throwable throwable);
long onResult(T result);
}
interface Context<T> {
void onComplete();
boolean onResult(T result);
void onError(Exception exception) throws Exception;
void onRuntimeError(RuntimeException runtimeException);
}
// 事件支持,发布订阅模式,实现回调或者异步的另一种机制,发布者和订阅者(消费者)解耦
interface EventPublisher extends io.github.resilience4j.core.EventPublisher<RetryEvent> {
EventPublisher onRetry(EventConsumer<RetryOnRetryEvent> eventConsumer);
EventPublisher onSuccess(EventConsumer<RetryOnSuccessEvent> eventConsumer);
EventPublisher onError(EventConsumer<RetryOnErrorEvent> eventConsumer);
EventPublisher onIgnoredError(EventConsumer<RetryOnIgnoredErrorEvent> eventConsumer);
}
// 这个类不知为何放在接口里面,实际上可以提出来
class AsyncRetryBlock<T> implements Runnable {
// 下一部分分析
}
}
不过异步增强的 CompletableFuture 不支持 Error 类型 fallback,封装了异步执行逻辑,实现逻辑和上一节 backoff 简易实现一致。
class AsyncRetryBlock<T> implements Runnable {
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
// 调用其回调方法 onResult, onError
private final Retry.AsyncContext<T> retryContext;
private final Supplier<CompletionStage<T>> supplier;
// 最终结果,使用 CompletableFuture 的写功能
private final CompletableFuture<T> promise;
// 略去构造器代码
@Override
public void run() {
final CompletionStage<T> stage = supplier.get();
stage.whenComplete((result, throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
// 支持 Exception 类型 fallback
if (throwable instanceof Exception) {
onError((Exception) throwable);
} else {
promise.completeExceptionally(throwable);
}
} else {
onResult(result);
}
});
}
// 重试或结束
private void onError(Exception t) {
final long delay = retryContext.onError(t);
if (delay < 1) {
promise.completeExceptionally(t);
} else {
scheduler.schedule(this, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
// 重试或结束
private void onResult(T result) {
final long delay = retryContext.onResult(result);
if (delay < 1) {
try {
retryContext.onComplete();
promise.complete(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
promise.completeExceptionally(e);
}
} else {
scheduler.schedule(this, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
}
再来看 Context 的具体实现,总结为以下几点:
- 记录执行统计信息(如 numOfAttempts, lastException, succeededWithoutRetryCounter)
- 发布相关事件(publishRetryEvent)
- 每次执行前后支持回调, 如 consumeResultBeforeRetryAttempt
- 代码执行时调用 RetryConfig 指定的策略(策略模式)
// RetryImpl 的内部类, RetryImpl 持有统计信息相关字段,重试策略相关字段
public final class AsyncContextImpl implements Retry.AsyncContext<T> {
private final AtomicInteger numOfAttempts = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final AtomicReference<Throwable> lastException = new AtomicReference<>();
@Override
public long onError(Throwable throwable) {
totalAttemptsCounter.increment();
// Handle the case if the completable future throw CompletionException wrapping the original exception
// where original exception is the one to retry not the CompletionException.
// 异常解包
if (throwable instanceof CompletionException || throwable instanceof ExecutionException) {
Throwable cause = throwable.getCause();
return handleThrowable(cause);
} else {
return handleThrowable(throwable);
}
}
// handleThrowable 和 handleOnError 做了类似的逻辑,从名字上无法区分,还不如直接合并成一个方法
private long handleThrowable(Throwable throwable) {
// 自定义方法判断是否需要 retry,exceptionPredicate 来自 RetryConfig
if (!exceptionPredicate.test(throwable)) {
failedWithoutRetryCounter.increment();
publishRetryEvent(() -> new RetryOnIgnoredErrorEvent(getName(), throwable));
return -1;
}
return handleOnError(throwable);
}
private long handleOnError(Throwable throwable) {
lastException.set(throwable);
int attempt = numOfAttempts.incrementAndGet();
if (attempt >= maxAttempts) {
failedAfterRetryCounter.increment();
publishRetryEvent(() -> new RetryOnErrorEvent(name, attempt, throwable));
return -1;
}
// backoff 策略, 来自 RetryConfig
long interval = intervalBiFunction.apply(attempt, Either.left(throwable));
if (interval < 0) {
publishRetryEvent(() -> new RetryOnErrorEvent(getName(), attempt, throwable));
} else {
publishRetryEvent(() -> new RetryOnRetryEvent(getName(), attempt, throwable, interval));
}
return interval;
}
// 略去其他方法
}
2. Spring Retry
这里不讨论 AOP 实现的重试增强,仅讨论命令式代码实现。
Spring Retry 实现了有状态的重试,很多方法需要显式传参数 RetryContext,有多种 RetryContext 支持,RetrySynchronizationManager 提供了全局 RetryContext 上下文支持,底层使用 ThreadLocal,提供获取上下文、注册上下文等方法。
任务封装为 RetryCallback,不直接支持 CompletableFuture。
// 封装的重试任务
public interface RetryCallback<T, E extends Throwable> {
// 无状态重试不需要使用context
/**
* Execute an operation with retry semantics.
*/
T doWithRetry(RetryContext context) throws E;
/**
* A logical identifier for this callback to distinguish retries around business
* operations.
*/
default String getLabel() {
return null;
}
}
RetryOperation 定义了重试操作:
public interface RetryOperations {
<T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback) throws E;
<T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback, RecoveryCallback<T> recoveryCallback) throws E;
<T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback, RetryState retryState) throws E, ExhaustedRetryException;
<T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback, RecoveryCallback<T> recoveryCallback, RetryState retryState) throws E;
}
回调接口定义了回调操作:
public interface RetryListener {
// 开始重试时回调
/**
* Called before the first attempt in a retry. For instance, implementers can set up
* state that is needed by the policies in the {[@link](https://my.oschina.net/u/393) RetryOperations}. The whole
* retry can be vetoed by returning false from this method, in which case a
* {[@link](https://my.oschina.net/u/393) TerminatedRetryException} will be thrown.
*/
default <T, E extends Throwable> boolean open(RetryContext context, RetryCallback<T, E> callback) {
return true;
}
// 结束重试时回调
/**
* Called after the final attempt (successful or not). Allow the listener to clean up
* any resource it is holding before control returns to the retry caller.
*/
default <T, E extends Throwable> void close(RetryContext context, RetryCallback<T, E> callback,
Throwable throwable) {
}
// 成功时回调
/**
* Called after a successful attempt; allow the listener to throw a new exception to
* cause a retry (according to the retry policy), based on the result returned by the
* {[@link](https://my.oschina.net/u/393) RetryCallback#doWithRetry(RetryContext)}
*/
default <T, E extends Throwable> void onSuccess(RetryContext context, RetryCallback<T, E> callback, T result) {
}
// 失败时回调
/**
* Called after every unsuccessful attempt at a retry.
*/
default <T, E extends Throwable> void onError(RetryContext context, RetryCallback<T, E> callback,
Throwable throwable) {
}
}
这里仅讨论第一个 execute 方法的实现:
// 不可变类,线程安全类
public class RetryTemplate implements RetryOperations {
// 略去 execute 语义外方法,如对象创建与初始化
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private volatile BackOffPolicy backOffPolicy = new NoBackOffPolicy();
private volatile RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new SimpleRetryPolicy(3);
private volatile RetryListener[] listeners = new RetryListener[0];
private RetryContextCache retryContextCache = new MapRetryContextCache();
private boolean throwLastExceptionOnExhausted;
@Override
public final <T, E extends Throwable> T execute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback) throws E {
return doExecute(retryCallback, null, null);
}
// 方法比较长,模版方法模式
protected <T, E extends Throwable> T doExecute(RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback,
RecoveryCallback<T> recoveryCallback, RetryState state) throws E, ExhaustedRetryException {
RetryPolicy retryPolicy = this.retryPolicy;
BackOffPolicy backOffPolicy = this.backOffPolicy;
// Allow the retry policy to initialise itself...
// 重试过程中,context 不断变化,每次重试需要初始化
RetryContext context = open(retryPolicy, state);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("RetryContext retrieved: " + context);
}
// Make sure the context is available globally for clients who need
// it...
// 保证重试执行时可以随时获得 context,使用了 ThreadLocal, context 和线程绑定
RetrySynchronizationManager.register(context);
Throwable lastException = null;
boolean exhausted = false;
try {
// 一些准备工作
// 回调,可提前终止重试
// Give clients a chance to enhance the context...
boolean running = doOpenInterceptors(retryCallback, context);
if (!running) {
throw new TerminatedRetryException("Retry terminated abnormally by interceptor before first attempt");
}
// 设置 context 最大重试数
if (!context.hasAttribute(RetryContext.MAX_ATTEMPTS)) {
context.setAttribute(RetryContext.MAX_ATTEMPTS, retryPolicy.getMaxAttempts());
}
// Get or Start the backoff context...
BackOffContext backOffContext = null;
Object resource = context.getAttribute("backOffContext");
if (resource instanceof BackOffContext) {
backOffContext = (BackOffContext) resource;
}
if (backOffContext == null) {
backOffContext = backOffPolicy.start(context);
if (backOffContext != null) {
context.setAttribute("backOffContext", backOffContext);
}
}
Object label = retryCallback.getLabel();
String labelMessage = (label != null) ? "; for: '" + label + "'" : "";
// 准备工作结束,开始执行 retry 核心代码
// 循环内部为任务执行的完整 try-catch 过程,基本思想和函数式基于轨道编程(Railway-Oriented-Programming)的 CompletableFuture 不同
/*
* We allow the whole loop to be skipped if the policy or context already
* forbid the first try. This is used in the case of external retry to allow a
* recovery in handleRetryExhausted without the callback processing (which
* would throw an exception).
*/
while (canRetry(retryPolicy, context) && !context.isExhaustedOnly()) {
try {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Retry: count=" + context.getRetryCount() + labelMessage);
}
// Reset the last exception, so if we are successful
// the close interceptors will not think we failed...
lastException = null;
// 任务执行
T result = retryCallback.doWithRetry(context);
// 成功回调
doOnSuccessInterceptors(retryCallback, context, result);
return result;
}
catch (Throwable e) {
lastException = e;
try {
// 每次异常回调
// 进行的操作一般有:失败次数 + 1, 记录 lastException
registerThrowable(retryPolicy, state, context, e);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new TerminatedRetryException("Could not register throwable", ex);
}
finally {
// RetryListener 失败回调
doOnErrorInterceptors(retryCallback, context, e);
}
// 执行 backoff 策略
if (canRetry(retryPolicy, context) && !context.isExhaustedOnly()) {
try {
backOffPolicy.backOff(backOffContext);
}
catch (BackOffInterruptedException ex) {
// back off was prevented by another thread - fail the retry
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Abort retry because interrupted: count=" + context.getRetryCount()
+ labelMessage);
}
throw ex;
}
}
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Checking for rethrow: count=" + context.getRetryCount() + labelMessage);
}
if (shouldRethrow(retryPolicy, context, state)) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger
.debug("Rethrow in retry for policy: count=" + context.getRetryCount() + labelMessage);
}
throw RetryTemplate.<E>wrapIfNecessary(e);
}
} // while 循环内 try-catch 结束
// 仅考虑无状态重试(state is null),可以忽略这段代码
/*
* A stateful attempt that can retry may rethrow the exception before now,
* but if we get this far in a stateful retry there's a reason for it,
* like a circuit breaker or a rollback classifier.
*/
if (state != null && context.hasAttribute(GLOBAL_STATE)) {
break;
}
} // while 循环末尾
if (state == null && this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Retry failed last attempt: count=" + context.getRetryCount() + labelMessage);
}
exhausted = true;
return handleRetryExhausted(recoveryCallback, context, state);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
// 重试代码抛出异常,无法处理,rethrow
throw RetryTemplate.<E>wrapIfNecessary(e);
}
finally {
close(retryPolicy, context, state, lastException == null || exhausted);
// RetryListener 关闭回调
doCloseInterceptors(retryCallback, context, lastException);
RetrySynchronizationManager.clear();
}
}
}
总结一下 Spring-Retry 的特点
-
支持回调(RetryListener) 和有状态上下文(RetryContext、backoffContext、RetryState)
-
缺点:不支持异步 backoff,backoff 在同一线程内。
-
上下文和线程绑定,底层使用 ThreadLocal,代码中会有隐式传参问题。
CompletableFuture 和重试机制有关的特点
-
若想实现特定返回值触发重试策略,CompletableFuture 存在成功运算管道和异常管道,推荐的做法是:thenCompose 转化某些错误值到特定异常,配置特定异常触发重试策略。
-
ComletableFuture 中的结果为异常时,需要解包才能获取真实的代码执行时异常。
-
CompletableFuture 提供了限时获取值方法,可以轻松实现超时终止策略。
-
取消机制,上文中的简易实现没有考虑 retry 方法返回结果被取消的情况,此时运行中的任务应该主动 cancel。
-
可以天然地支持异步重试(重试任务执行不限于同一线程中)
-
在单线程中sleep一段时间,再重试也是一种能接受的解决方案
CFFU
CFFU(CompletableFuture Fu )是一个小小的 CompletableFuture(CF)辅助增强库,提升 CF 使用体验并减少误用,在业务中更方便高效安全地使用 CF。 CFFU 并不支持重试,如果你想实现 CompletableFuture 的重试功能,可以使用 Resilience4J。
本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布!
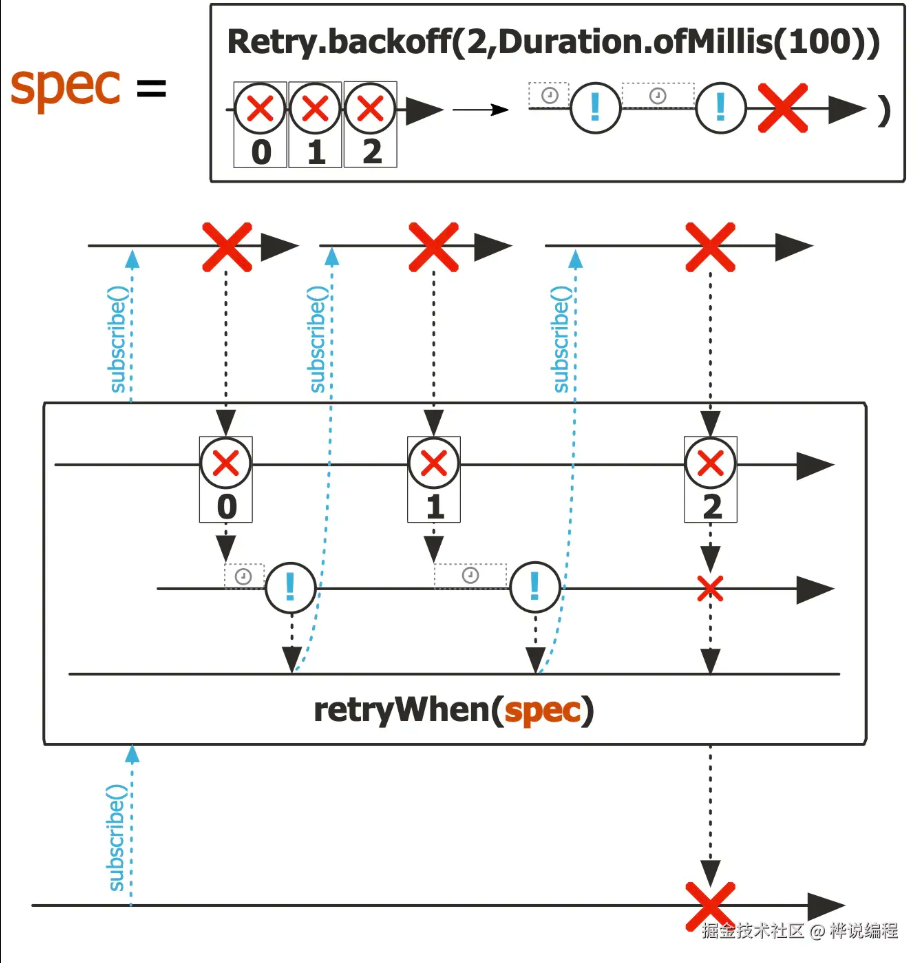 Project Reactor 是基于发布-订阅模型的响应式组件。从图中可以看出,每次获取数据失败后,会等待一段时间,然后再次订阅发布者以获取数据,反复以上过程直到达到最终重试次数或者出现成功结果。
Project Reactor 是基于发布-订阅模型的响应式组件。从图中可以看出,每次获取数据失败后,会等待一段时间,然后再次订阅发布者以获取数据,反复以上过程直到达到最终重试次数或者出现成功结果。



