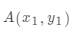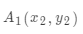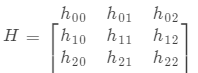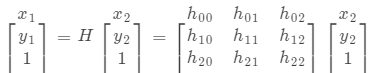现存在一个问题,就下面图片中的两本书而言,怎样快速让中间边的书本与左边书本对齐(最终效果能实现两张图片重叠(最终结果为右图)),进行的图像转变可旋转、平移、缩放、形变。
本文主要内容就是介绍利用 Opencv 来怎样解决上面的问题,解决这个问题需要三步
图片旋转、平移、缩放等操作的主要目的,就是要最终实现两图像中点对点一一映射关系,图像映射本质上就是像素点转换
图中标记了其中四组对应点,分别标为不同的颜色,分别标为红、橙、黄和绿四种颜色;比如这里的
涉及图片中点坐标变换,都需要借助于 矩阵 运算,这里探究的图像维度都属于二维,坐标只需要
面向此类转换问题,Homography 转换 ( 3 × 3 矩阵) 可用于解决此类转化问题,用来解决点对点映射问题,Homography 矩阵可写作下列方式:
下面用 Opencv + Python 来实现上面图片中的书籍的对齐,
import cv2import numpy as npif __name__ =='__main__' :#图片读取 "D:/book2.jpg" )141 ,131 ],[480 ,159 ],[493 ,630 ],[64 ,601 ]],dtype = float)"D:/book1.jpg" )318 ,256 ],[543 ,372 ],[316 ,670 ],[73 ,473 ]],dtype = float)#计算转换矩阵 #对图片进行仿射变换 1 ],img_dst.shape[0 ]))#Display images; "Source image" ,img_src)"Destination Image" ,img_dst)"Warped Source Image" ,out_img)0 )这里事先已经确定好对应的四个点的坐标,然后把这四个点的坐标带入 cv2.findHomography() 计算出转换矩阵,最后把矩阵应用到两图像中,得到最终的转换结果,
这里提醒一点,warpPerspective 函数进行对图像像素进行矩阵变换时,隐藏了一个参数 Interpolator ,默认为线性插值,功能是防止像素点像素值缺失
上面小案例不方便的一点需要确定对应四个点的坐标,这个步骤是比较繁琐的,下面案例将在程序中加入交互功能,实现某个图片的自动标记点收集、标记点点转换:
首先需要准备两张图片,其中一张为海报,一张为需要替换的海报;关于确定点的坐标时,被替换的图片的坐标非常好确定,只需知道图片的长宽即可;
但的海报图像区域四个点是不好确定的, 这里利用 Opencv 的鼠标回调函数,监视鼠标响应,根据用户点击来收集 PIck 得到的坐标;
def mouse_handler (event,x,y,flags,data) :if event ==cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:'im' ],(x,y),3 ,(0 ,0 ,255 ),5 ,16 )"Image" ,0 )"Image" ,data['im' ])if len(data['points' ]) <4 :'points' ].append([x,y])def get_four_points (im) :'im' ] = im.copy()'points' ] = []# Set the callback function for any mouse event "Image" , 0 )'Image' ,im)#请注意你标记点的数据,是顺时针,需要与pst_src 方向一致 "Image" ,mouse_handler,data)0 )# Convert array to np.array #竖直方向堆叠起来;;; 'points' ]).astype(float)return points坐标确定以后,接下来就很简单了,跟上个案例一样,计算变换矩阵,矩阵应用到图像旋转,最终更换海报内容也就轻松完成啦
需要注意一点,坐标 Pick 点的顺序须与记录替换图像顶点顺序一致,否则转换图会有偏差 ,案例完整代码如下:
if __name__ =='__main__' :"D:/first-image.jpg" )# 取得四个坐标 0 ,0 ],[size[1 ]-1 ,0 ],1 ]-1 ,size[0 ]-1 ],0 ,size[0 ]-1 ]#Read the destination image "D:/times-square.jpg" )"Click on four corners of bllboard and the press ENTER" )# Calculate Homography between source and destination points 1 ],img_dst.shape[0 ]))0 ,16 )#add wraped source image to destination image "Image" , 0 )"Image" ,img_dst)0 )