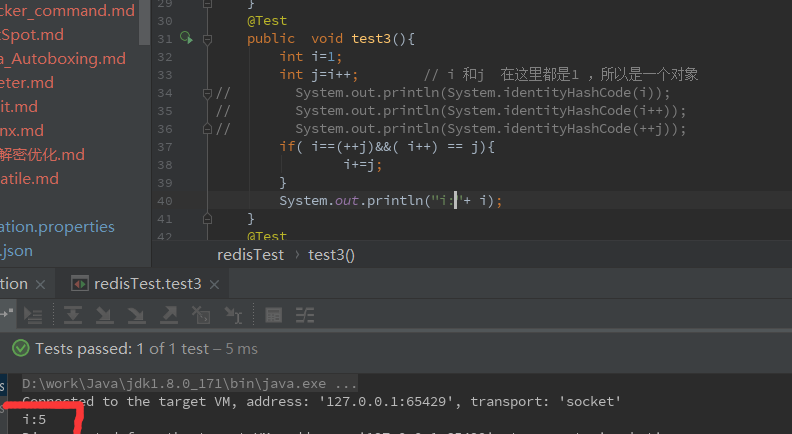
一、 示例代码
@Test
public void test3(){
int i=1;
int j=i++;
if( i==(++j)&&( i++) == j){
i+=j;
}
System.out.println("i'"+ i);
}
- 结果如下: 5
![java_autobox java_autobox]()
- 结果为什么会是这样呢? 仔细看来
二、 自动装箱、拆箱
-
定义
- 自动装箱,在编译之后被转化成了对应的包装方法,Integer.valueOf();
Integer i =1 ; 在编译中被执行: Integer i= Integer.valueOf(int i) ;
- 拆箱 ,在编译之后被转化成了对应的还原方法, Integer.intValue()方法。
int j = i++; 在编译中执行 拆箱 , int j = Integer.inValue(i);
- 示例,调用了拆箱,java虚拟机中常量池包括有Integer型常量池,用一个表存储,具体信息如下:
![33 33]()
存储的范围值默认是 -128~127, 故如果Interger指向的是这个范围内的数字在编译的时候会直接指向常量池中的对象;
三、 通过两种方法,比较地址是否相同:
-
第一种
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(i));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(i++));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(++j));
-
第二种
public class javaAuto {
static final Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
static final boolean is64bit = true;
public static void main(String... args) {
int i=1;
int j=i++;
System.out.println("-------------------------");
System.out.println("----");
printAddresses("i", i);
System.gc();
System.out.println("----");
printAddresses("j", ++j);
System.gc();
System.out.println("----");
printAddresses("i++", i++);
}
public static void printAddresses(String label, Object... objects) {
System.out.print(label + ": 0x");
long last = 0;
int offset = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(objects.getClass());
int scale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(objects.getClass());
switch (scale) {
case 4:
long factor = is64bit ? 8 : 1;
final long i1 = (unsafe.getInt(objects, offset) & 0xFFFFFFFFL) * factor;
System.out.print(Long.toHexString(i1));
last = i1;
for (int i = 1; i < objects.length; i++) {
final long i2 = (unsafe.getInt(objects, offset + i * 4) & 0xFFFFFFFFL) * factor;
if (i2 > last)
System.out.print(", +" + Long.toHexString(i2 - last));
else
System.out.print(", -" + Long.toHexString( last - i2));
last = i2;
}
break;
case 8:
throw new AssertionError("Not supported");
}
System.out.println();
}
private static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafe.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
}
- 通过这两种方式打印出的,i ,i++,++j 的地址都是一样的;他们的值呢?
四、值
- i 和 ++j 的值都是2,这个毋庸置疑;
- (i++)==j ,这个比较,楼主怀疑是先执行的比较,再执行的++操作,可是貌似又不符合运算符的运算规则。
- 待查...希望有人能告知答案,不胜感激
参考链接: https://blog.csdn.net/isscollege/article/details/78398968
欢迎关注公众号,查看更多内容 :
![XG54_9_WXMH_5X_HB_H_7V XG54_9_WXMH_5X_HB_H_7V]()