tf.train.Saver API说明
保存于恢复变量,对定义好完成训练或者完成部分训练的计算图所有OP操作的中间变量进行保存,保存为检查点文件(checkpoint file),检查点文件通过restore方法完成恢复,实现从变量到张量值(tensor value)得映射加载,可以进行调用或者继续训练。同时Saver支持全局步长参数,通过对不同的step自动保存为检查点
saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=0) ==> filename: 'my-model-0'
...
saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=1000) ==> filename: 'my-model-1000'
上述代码表示分别在step=0与step=1000的时候保存检查点。
Saver在保存检查点的时候默认保存计算图的全部变量,但是可以通过var_list来决定保存多少个变量到检查点文件中去。对保存的检查点进行恢复可以调用如下的方法:
restore(
sess,
save_path
)
从检查点恢复变量并映射到相关的tensor中去,要求必须有一个当前会话才可以重新加载计算图。当使用这种方式时候就无需再重复调用初始化方法来初始化变量了,restore方法本身就完成了变量初始化,然后就可以继续训练或者使用计算图进行预测。
预测图导出
使用tf.train.Saver会保存检测点文件,但是这些文件不是一个,是四个文件一组:
-checkpoint
-prefix-model-steps.data-00000-of-00001
-prefix-model-steps.index
-prefix-model-steps.meta
其中
prefix是前缀名称
steps是运行number of steps
当prefix=my_cnn_mnist,steps=10000时
![image image]()
通过读取checkpint文件与meta文件加载计算图,然后把所有的变量转换为常量形式通过GFile进行串行化写入生成预测图(PB文件),从检查点导出成为预测图(PB文件)的代码如下:
# We retrieve our checkpoint fullpath
checkpoint = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(model_dir)
input_checkpoint = checkpoint.model_checkpoint_path
# We precise the file fullname of our freezed graph
absolute_model_dir = "/".join(input_checkpoint.split('/')[:-1])
output_graph = absolute_model_dir + "/frozen_model.pb"
# We clear devices to allow TensorFlow to control on which device it will load operations
clear_devices = True
# We start a session using a temporary fresh Graph
with tf.Session(graph=tf.Graph()) as sess:
# We import the meta graph in the current default Graph
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph(input_checkpoint + '.meta', clear_devices=clear_devices)
# We restore the weights
saver.restore(sess, input_checkpoint)
# We use a built-in TF helper to export variables to constants
output_graph_def = tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(
sess, # The session is used to retrieve the weights
tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def(), # The graph_def is used to retrieve the nodes
output_node_names.split(",") # The output node names are used to select the usefull nodes
)
# Finally we serialize and dump the output graph to the filesystem
with tf.gfile.GFile(output_graph, "wb") as f:
f.write(output_graph_def.SerializeToString())
print("%d ops in the final graph." % len(output_graph_def.node))
return output_graph_def
这段代码我也是借鉴tensorflow中一个工具类copy过来的,发现很好用!
一个例子
首先定义个网络模型,对于输入与预测部分tensor的name属性我们都给予赋值。
定义输入-X
x = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 784], dtype=tf.float32, name="input_x")
y = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 10], dtype=tf.float32)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
定义预测输出
acc_mat = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
acc = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(acc_mat, tf.float32))
prediction = tf.argmax(logits, axis=1, name="prediction_out")
构建卷积神经网络的代码如下
def conv_net(x_dict, n_classes, dropout):
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(x_dict, 32, 5, activation=tf.nn.relu)
pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv1, pool_size=2, strides=2)
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(pool1, 64, 3, activation=tf.nn.relu)
pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv2, pool_size=2, strides=2)
fc1 = tf.layers.flatten(pool2, name="fc1")
fc2 = tf.layers.dense(fc1, 1024)
fc3 = tf.layers.dropout(fc2, rate=dropout)
out = tf.layers.dense(fc3, n_classes)
return out
logits = conv_net(x_image, num_classes, keep_prob)
cross_loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_loss)
step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
保存检查点的代码如下:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
......
saver.save(sess, "./my_cnn_mnist.model", global_step=10000)
导出预测图之后使用预测实现手写数字预测的代码如下
import argparse
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
print(tf.__version__)
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
def load_graph(frozen_graph_filename):
# 开始解析
with tf.gfile.GFile(frozen_graph_filename, "rb") as f:
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
# 加载图
with tf.Graph().as_default() as graph:
tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name="prefix")
return graph
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 传递参数,加载预测图
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--frozen_model_filename", default="./frozen_model.pb", type=str,
help="Frozen model file to import")
args = parser.parse_args()
# 加载
graph = load_graph(args.frozen_model_filename)
# 遍历所有
for op in graph.get_operations():
print(op.name)
# 获取张量
input_x = graph.get_tensor_by_name('prefix/input_x:0')
prediction = graph.get_tensor_by_name('prefix/prediction_out:0')
print(input_x, prediction)
# 运行预测图
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as sess:
for i in range(100):
test_img = np.expand_dims(mnist.test.images[i], 0)
predicted_ = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={input_x: test_img})[0]
label = np.argmax(mnist.test.labels[i])
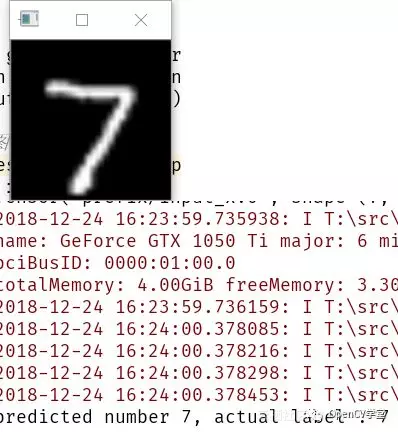
print("predicted number %s, actual label : %s" % (str(predicted_), str(label)))
ti = np.reshape(mnist.test.images[i], [28, 28])
ti = cv.resize( ti, (128, 128))
cv.imshow("actual image", ti)
cv.waitKey(0)
运行结果:
![image image]()
原文发布时间为:2018-12-24
本文作者: gloomyfish
本文来自云栖社区合作伙伴“ OpenCV学堂”,了解相关信息可以关注“CVSCHOOL”微信公众号