Spark源码分析之ResultTask处理
更多资源
视频
概述
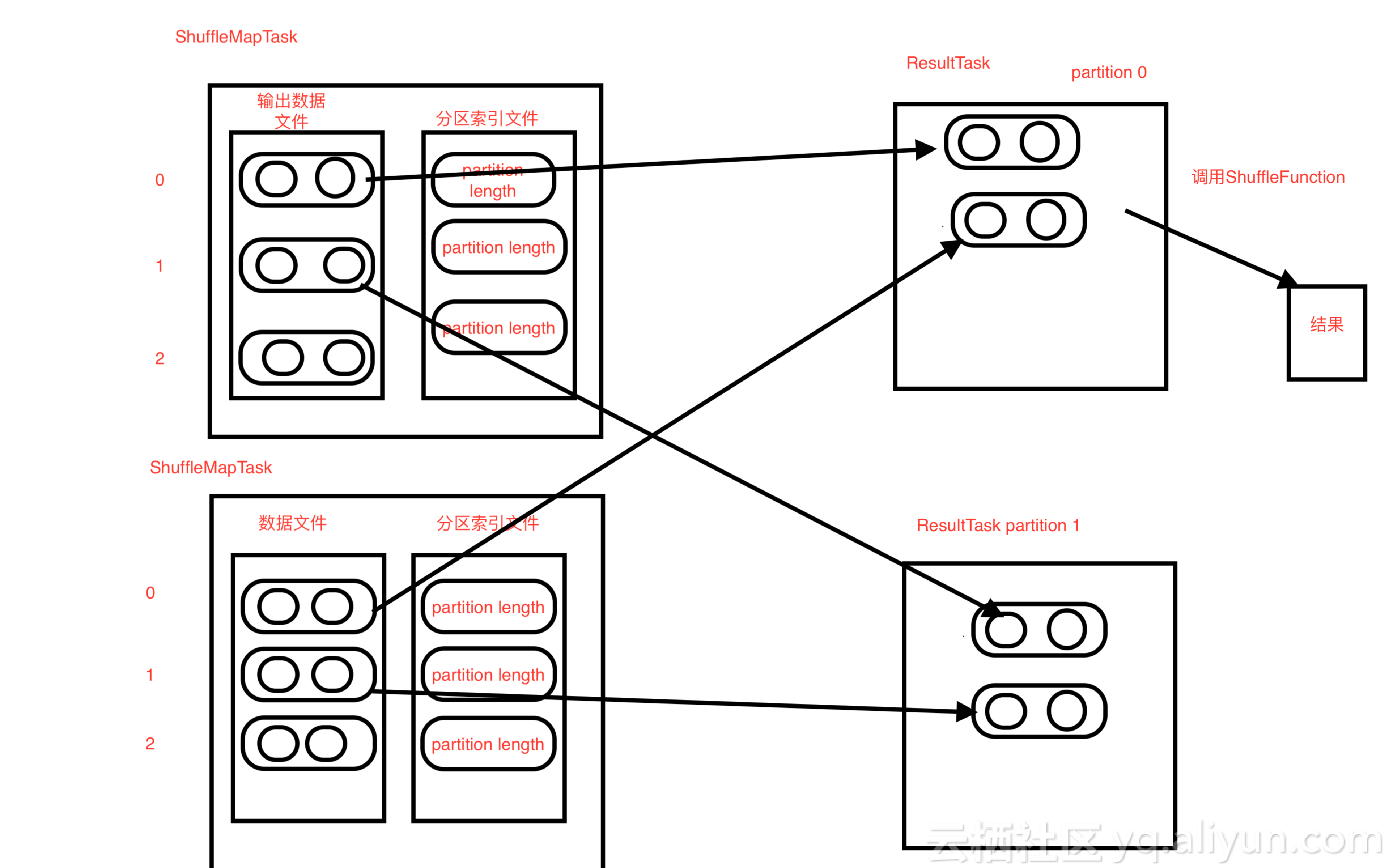
- ResultTask 执行当前分区的计算,首先从ShuffleMapTask拿到当前分区的数据,会从所有的ShuffleMapTask都拿一遍当前的分区数据,然后调用reduceByKey自定义的函数进行计算
- 最后合并所有的ResultTask输出结果,进行输出
图解
![ResultTask_ ResultTask_]()
ResultTask.scala 类
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.spark.scheduler
import java.nio.ByteBuffer
import java.io._
import org.apache.spark._
import org.apache.spark.broadcast.Broadcast
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
/**
* A task that sends back the output to the driver application.
*
* See [[Task]] for more information.
*
* @param stageId id of the stage this task belongs to
* @param taskBinary broadcasted version of the serialized RDD and the function to apply on each
* partition of the given RDD. Once deserialized, the type should be
* (RDD[T], (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U).
* @param partition partition of the RDD this task is associated with
* @param locs preferred task execution locations for locality scheduling
* @param outputId index of the task in this job (a job can launch tasks on only a subset of the
* input RDD's partitions).
*/
private[spark] class ResultTask[T, U](
stageId: Int,
stageAttemptId: Int,
taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]],
partition: Partition,
locs: Seq[TaskLocation],
val outputId: Int,
internalAccumulators: Seq[Accumulator[Long]])
extends Task[U](stageId, stageAttemptId, partition.index, internalAccumulators)
with Serializable {
@transient private[this] val preferredLocs: Seq[TaskLocation] = {
if (locs == null) Nil else locs.toSet.toSeq
}
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): U = {
// Deserialize the RDD and the func using the broadcast variables.
val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, func) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[T], (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U)](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
_executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime
metrics = Some(context.taskMetrics)
func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context))
}
// This is only callable on the driver side.
override def preferredLocations: Seq[TaskLocation] = preferredLocs
override def toString: String = "ResultTask(" + stageId + ", " + partitionId + ")"
}
- 反序列化ResultTask,结果为rdd,和func函数
- taskBinary的值是在DAGScheduler.submitMissingTasks()方法中进行序列化的
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, func) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[T], (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U)](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
- DAGScheduler中序列化taskBinary:Broadcast参数
var taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]] = null
try {
// For ShuffleMapTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, shuffleDep).
// For ResultTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, func).
val taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef).array()
case stage: ResultStage =>
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef).array()
}
taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes)
- ResultTask.runTask()方法
- func 函数将Iterator转换为数组: RDD.collect()方法中的 (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.toArray
- 整个ResultTask计算在 rdd.iterator(partition, context) 中完成
- 此时的RDD为:ShuffleRDD,所以rdd.iterator()方法调用的是ShuffleRDD.iterator()方法,会调用ShuffleRDD.compute()方法
func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context))
/**
* Return an array that contains all of the elements in this RDD.
*/
def collect(): Array[T] = withScope {
val results = sc.runJob(this, (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.toArray)
Array.concat(results: _*)
}
- ShuffleRDD.compute()方法
- 通过依赖找到 dep.shuffleHandle()函数,也就是reduceByKey()中自定义的函数
- SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager得到默认的SortShuffleManager
- 调用SortShuffleManager.getReader()方法
- read()方法,调用 BlockStoreShuffleReader.read()方法
override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[(K, C)] = {
val dep = dependencies.head.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]]
SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.getReader(dep.shuffleHandle, split.index, split.index + 1, context)
.read()
.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]]
}
- SortShuffleManager.getReader()方法
- 返回 BlockStoreShuffleReader()对象
/**
* Get a reader for a range of reduce partitions (startPartition to endPartition-1, inclusive).
* Called on executors by reduce tasks.
*/
override def getReader[K, C](
handle: ShuffleHandle,
startPartition: Int,
endPartition: Int,
context: TaskContext): ShuffleReader[K, C] = {
new BlockStoreShuffleReader(
handle.asInstanceOf[BaseShuffleHandle[K, _, C]], startPartition, endPartition, context)
}
- BlockStoreShuffleReader.read()方法
- 该方法会拿到ShuffleMapTask输出的数据,通过ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator()可以拿到所有ShuffleMapTask输出的文件数据(并且是当前partition的数据),把这些数据反序列化放到可迭代变量recordIter中
/** Read the combined key-values for this reduce task */
override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = {
val streamWrapper: (BlockId, InputStream) => InputStream = { (blockId, in) =>
blockManager.wrapForCompression(blockId,
CryptoStreamUtils.wrapForEncryption(in, blockManager.conf))
}
val wrappedStreams = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator(
context,
blockManager.shuffleClient,
blockManager,
mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition),
streamWrapper,
// Note: we use getSizeAsMb when no suffix is provided for backwards compatibility
SparkEnv.get.conf.getSizeAsMb("spark.reducer.maxSizeInFlight", "48m") * 1024 * 1024,
SparkEnv.get.conf.getBoolean("spark.shuffle.detectCorrupt", true))
val ser = Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer)
val serializerInstance = ser.newInstance()
// Create a key/value iterator for each stream
val recordIter = wrappedStreams.flatMap { case (blockId, wrappedStream) =>
// Note: the asKeyValueIterator below wraps a key/value iterator inside of a
// NextIterator. The NextIterator makes sure that close() is called on the
// underlying InputStream when all records have been read.
serializerInstance.deserializeStream(wrappedStream).asKeyValueIterator
}
// Update the context task metrics for each record read.
val readMetrics = context.taskMetrics.createShuffleReadMetricsForDependency()
val metricIter = CompletionIterator[(Any, Any), Iterator[(Any, Any)]](
recordIter.map(record => {
readMetrics.incRecordsRead(1)
record
}),
context.taskMetrics().updateShuffleReadMetrics())
// An interruptible iterator must be used here in order to support task cancellation
val interruptibleIter = new InterruptibleIterator[(Any, Any)](context, metricIter)
val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
// We are reading values that are already combined
val combinedKeyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(combinedKeyValuesIterator, context)
} else {
// We don't know the value type, but also don't care -- the dependency *should*
// have made sure its compatible w/ this aggregator, which will convert the value
// type to the combined type C
val keyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, Nothing)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(keyValuesIterator, context)
}
} else {
require(!dep.mapSideCombine, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]]
}
// Sort the output if there is a sort ordering defined.
dep.keyOrdering match {
case Some(keyOrd: Ordering[K]) =>
// Create an ExternalSorter to sort the data. Note that if spark.shuffle.spill is disabled,
// the ExternalSorter won't spill to disk.
val sorter =
new ExternalSorter[K, C, C](context, ordering = Some(keyOrd), serializer = Some(ser))
sorter.insertAll(aggregatedIter)
context.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(sorter.memoryBytesSpilled)
context.taskMetrics().incDiskBytesSpilled(sorter.diskBytesSpilled)
context.internalMetricsToAccumulators(
InternalAccumulator.PEAK_EXECUTION_MEMORY).add(sorter.peakMemoryUsedBytes)
CompletionIterator[Product2[K, C], Iterator[Product2[K, C]]](sorter.iterator, sorter.stop())
case None =>
aggregatedIter
}
}
- BlockStoreShuffleReader.read()方法 详解
- 该方法会拿到ShuffleMapTask输出的数据,通过ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator()可以拿到所有ShuffleMapTask输出的文件数据(并且是当前partition的数据),把这些数据反序列化放到可迭代变量recordIter中
val streamWrapper: (BlockId, InputStream) => InputStream = { (blockId, in) =>
blockManager.wrapForCompression(blockId,
CryptoStreamUtils.wrapForEncryption(in, blockManager.conf))
}
val wrappedStreams = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator(
context,
blockManager.shuffleClient,
blockManager,
mapOutputTracker.getMapSizesByExecutorId(handle.shuffleId, startPartition, endPartition),
streamWrapper,
// Note: we use getSizeAsMb when no suffix is provided for backwards compatibility
SparkEnv.get.conf.getSizeAsMb("spark.reducer.maxSizeInFlight", "48m") * 1024 * 1024,
SparkEnv.get.conf.getBoolean("spark.shuffle.detectCorrupt", true))
val ser = Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer)
val serializerInstance = ser.newInstance()
// Create a key/value iterator for each stream
val recordIter = wrappedStreams.flatMap { case (blockId, wrappedStream) =>
// Note: the asKeyValueIterator below wraps a key/value iterator inside of a
// NextIterator. The NextIterator makes sure that close() is called on the
// underlying InputStream when all records have been read.
serializerInstance.deserializeStream(wrappedStream).asKeyValueIterator
}
- BlockStoreShuffleReader.read()方法 详解
- 把recordIter 放到 metricIter中(ShuffleMapTask中的输出数据文件都在这里边)
- 把metricIter作为实例化参数传给InterruptibleIterator,赋值给变量interruptibleIter
- 把interruptibleIter转化为可迭代的变量 combinedKeyValuesIterator
- 把迭代变量传给 dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(combinedKeyValuesIterator, context),赋值给可迭代变量: aggregatedIter
- 判断 dep.keyOrdering 有没有排序,如果没有,直接返回 aggregatedIter
- 如果dep.keyOrdering 有有排序,则通过ExternalSorter 算法进行排序处理,再返回结果
// Create a key/value iterator for each stream
val recordIter = wrappedStreams.flatMap { case (blockId, wrappedStream) =>
// Note: the asKeyValueIterator below wraps a key/value iterator inside of a
// NextIterator. The NextIterator makes sure that close() is called on the
// underlying InputStream when all records have been read.
serializerInstance.deserializeStream(wrappedStream).asKeyValueIterator
}
// Update the context task metrics for each record read.
val readMetrics = context.taskMetrics.createShuffleReadMetricsForDependency()
val metricIter = CompletionIterator[(Any, Any), Iterator[(Any, Any)]](
recordIter.map(record => {
readMetrics.incRecordsRead(1)
record
}),
context.taskMetrics().updateShuffleReadMetrics())
// An interruptible iterator must be used here in order to support task cancellation
val interruptibleIter = new InterruptibleIterator[(Any, Any)](context, metricIter)
val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
// We are reading values that are already combined
val combinedKeyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(combinedKeyValuesIterator, context)
} else {
// We don't know the value type, but also don't care -- the dependency *should*
// have made sure its compatible w/ this aggregator, which will convert the value
// type to the combined type C
val keyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, Nothing)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(keyValuesIterator, context)
}
} else {
require(!dep.mapSideCombine, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]]
}