开篇
Deque 接口继承自 Queue接口,但 Deque 支持同时从两端添加或移除元素,因此又被成为双端队列。鉴于此,Deque 接口的实现可以被当作 FIFO队列使用,也可以当作LIFO队列(栈)来使用。官方也是推荐使用 Deque 的实现来替代 Stack。
ArrayDeque 是 Deque 接口的一种具体实现,是依赖于可变数组来实现的。ArrayDeque 没有容量限制,可根据需求自动进行扩容。ArrayDeque不支持值为 null 的元素。
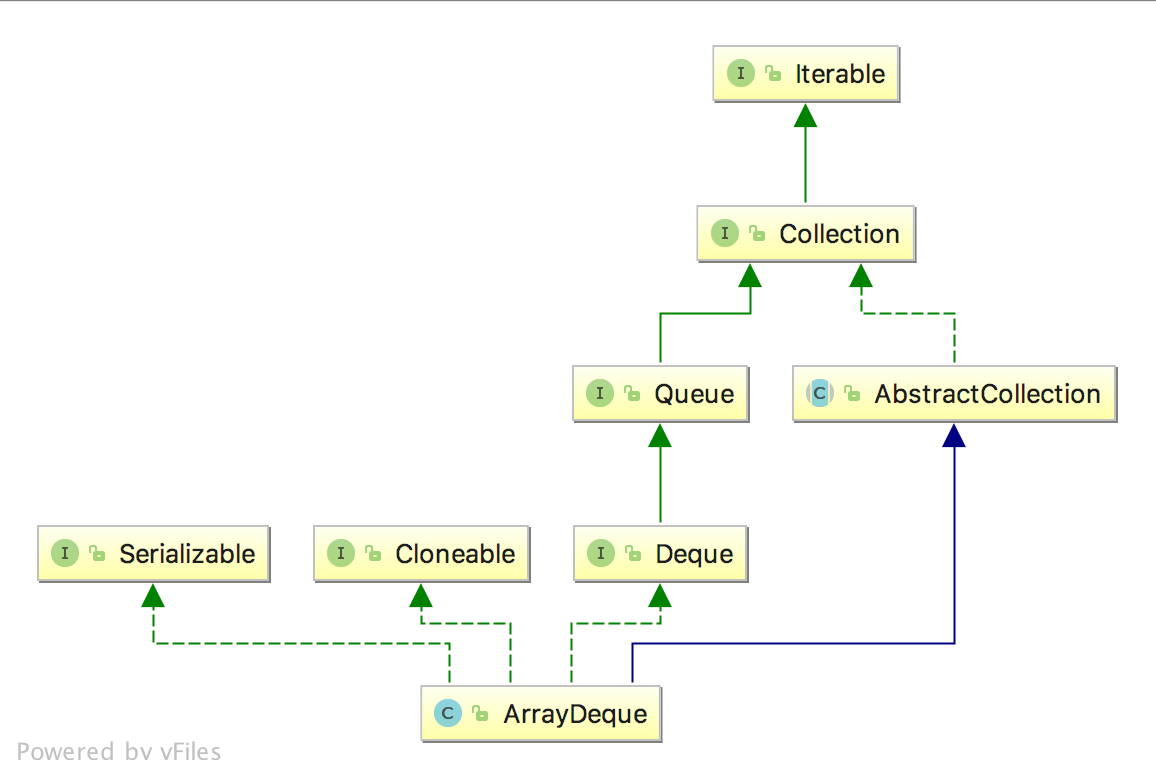
ArrayDeque类图
ArrayDeque的类变量和构造函数
ArrayDeque的类变量当中数组elements用来保存队列元素,head指针指向第一个存储元素,tail指向最后一个元素的下一个位置。
ArrayDeque的calculateSize的逻辑非常巧妙,用于计算大于numElements的最小的2*n次方的值。
public class ArrayDeque<E> extends AbstractCollection<E>
implements Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
// ArrayDeque采用数组来保存元素,通过头尾指针实现循环数组
transient Object[] elements; // non-private to simplify nested class access
// 第一个元素和最后一个元素的位置
transient int head;
transient int tail;
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
// 计算数组大小的方式,实现大于numElements的最小的2*n次方的数字
private static int calculateSize(int numElements) {
int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
initialCapacity++;
if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
}
return initialCapacity;
}
// 分配数组的大小,calculateSize计算大小
private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
elements = new Object[calculateSize(numElements)];
}
ArrayDeque的add相关操作
ArrayDeque的add操作支持head端插入和tail端插入,head端插入是先计算位置后插入元素,tail端的插入是先保存元素后计算位置,所以会造成head的指针指向第一个元素的位置,tail指向最后一个元素的下一个位置。
ArrayDeque的扩容时机是在head和tail相等的时候,根据上面分析我们可以得出ArrayDeque的容量达到(旧容量-1)的时候进行扩容。
ArrayDeque的头部插入过程是回退head指针后添加元素。
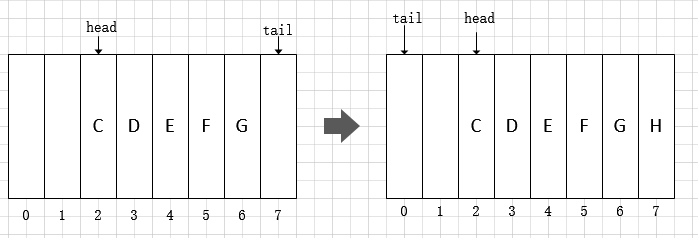
ArrayDeque的尾部插入过程是添加元素后前进tail指针。
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//head往后移动一个位置放置新插入的元素
//head指向第一个元素的下标
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
//tail往前移动一个位置放置新插入的元素
//tail指向末尾元素的下一个位置,注意是末尾元素的下一个位置
public void addLast(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[tail] = e;
//tail循环以后和head保持一个空余位置,也就是说head=tail+1的时候进行扩容
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
ArrayDeque的remove相关操作
ArrayDeque的remove操作包括从head开始删除和从tail开始删除。
- 头部删除pollFirst()方法返回head指针指向的元素同时向后移动一个位置
- 尾部删除pollLast()方法返回tail指针指向位置的前一个位置的元素后tail指针往前移动一个位置
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[h];
// Element is null if deque empty
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
public E pollLast() {
int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[t];
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[t] = null;
tail = t;
return result;
}
public E getFirst() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[head];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
public E getLast() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekFirst() {
// elements[head] is null if deque empty
return (E) elements[head];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekLast() {
return (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
}
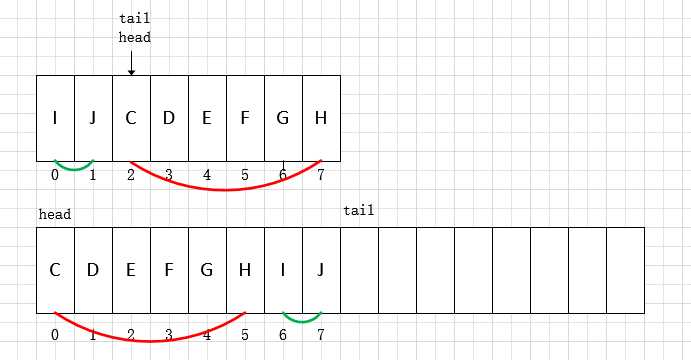
ArrayDeque的扩容过程
ArrayDeque的扩容过程如下:
- 以2倍速率进行扩容(int newCapacity = n << 1)
- 拷贝下标head到数组末尾的元素到新数组
- 拷贝下标0到tail指针的元素到新数组
private void doubleCapacity() {
assert head == tail;
int p = head;
int n = elements.length;
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
int newCapacity = n << 1;
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
elements = a;
head = 0;
tail = n;
}
ArrayDeque的操作图解过程
参考文章
Java 容器源码分析之 Deque 与 ArrayDeque