开篇
ArrayBlockingQueue是数组实现的线程安全的有界的阻塞队列。
- 线程安全是指ArrayBlockingQueue内部通过“互斥锁”保护竞争资源,实现了多线程对竞争资源的互斥访问。
- 有界是指ArrayBlockingQueue对应的数组是有界限的。
- 阻塞队列是指多线程访问竞争资源时,当竞争资源已被某线程获取时,其它要获取该资源的线程需要阻塞等待;而且,ArrayBlockingQueue是按 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序,元素都是从尾部插入到队列,从头部开始返回。
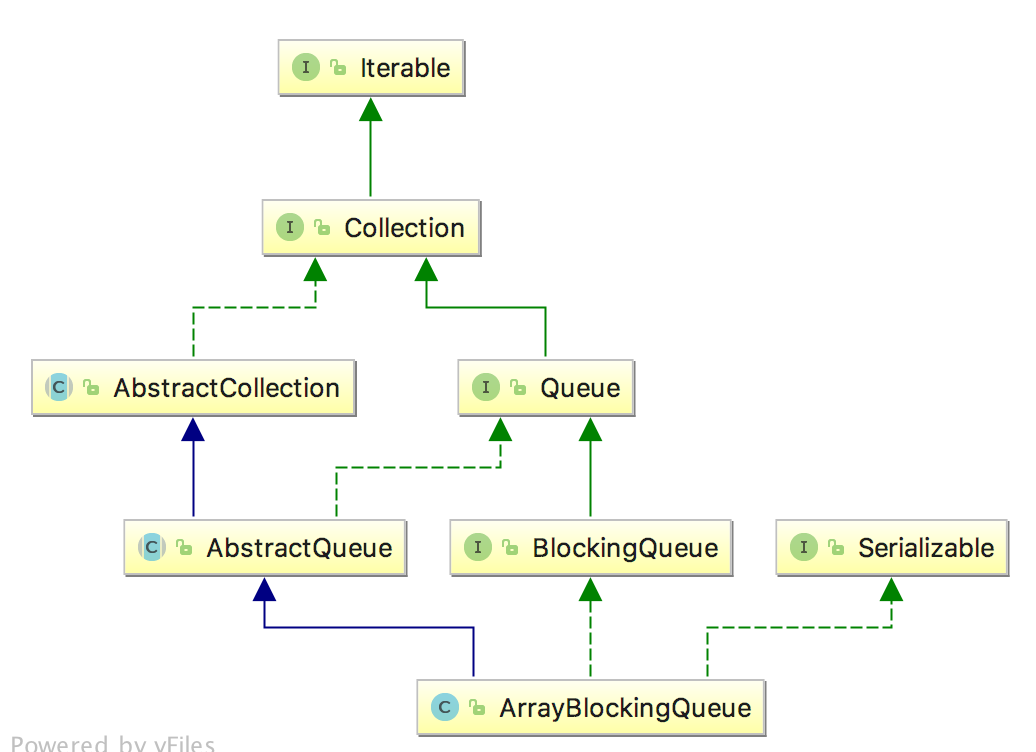
ArrayBlockingQueue类图
ArrayBlockingQueue构造函数
ArrayBlockingQueue的构造函数信息表明以下几个信息:
- 线程安全 ReentrantLock lock
- 容量有界 this.items = new Object[capacity];
- 状态同步 Condition notEmpty、Condition notFull
public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
final Object[] items;
int takeIndex;
int putIndex;
int count;
// 通过lock来保证线程安全,通过lock下的Condition来实现状态同步
final ReentrantLock lock;
private final Condition notEmpty;
private final Condition notFull;
transient Itrs itrs = null;
// 构造函数必须指定数组大小,所以是有界的
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(capacity, fair);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); // Lock only for visibility, not mutual exclusion
try {
int i = 0;
try {
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
items[i++] = e;
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
count = i;
putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
ArrayBlockingQueue常用操作
ArrayBlockingQueue的add/put/offer方法
ArrayBlockingQueue的所有add()方法其实执行的就是offer()方法,其他核心的逻辑在enqueue方法中。当然所有操作都是执行加锁操作lock.lock()。
- add/offer方法是非阻塞的,如果队列满就直接返回异常
- put()方法是阻塞的,如果队列满就等待,等待notFull的信号量,notFull.await()在take等方法执行的时候会触发notFull.signal()。
- enqueue()方法内部就是往item数组中添加元素、计算元素个数count++、重置putIndex、通知非空信号量notEmpty.signal()。
public boolean add(E e) {
return super.add(e);
}
// 将指定的元素插入到此队列的尾部(如果立即可行且不会超过该队列的容量),在成功时返回 true,如果此队列已满,则抛出 IllegalStateException。
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == items.length)
return false;
else {
enqueue(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 将指定的元素插入此队列的尾部,如果该队列已满,则等待可用的空间。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[putIndex] == null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
count++;
notEmpty.signal();
}
ArrayBlockingQueue的poll/take/peek方法
ArrayBlockingQueue的所有take相关操作最终都是执行dequeue操作的。
- 所有删除元素操作都是先进行加锁保证线程安全
- poll()和take()方法是阻塞的
- take()和poll()带时间参数是阻塞
- dequeue()内部通过takeIndex参数获取待返回的参数,重置元素个数count,移动下一个元素位置takeIndex等。
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return itemAt(takeIndex); // null when queue is empty
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
ArrayBlockingQueue的内部的锁
在ArrayBlockingQueue函数内部的加锁动作,我们发现有lock和lockInterruptibly两种,lock 与 lockInterruptibly比较区别在于:
- lock 优先考虑获取锁,待获取锁成功后,才响应中断。
- lockInterruptibly 优先考虑响应中断,而不是响应锁的普通获取或重入获取。
详细区别:
- ReentrantLock.lockInterruptibly允许在等待时由其它线程调用等待线程的Thread.interrupt方法来中断等待线程的等待而直接返回,这时不用获取锁,而会抛出一个InterruptedException。
- ReentrantLock.lock方法不允许Thread.interrupt中断,即使检测到Thread.isInterrupted,一样会继续尝试获取锁,失败则继续休眠。只是在最后获取锁成功后再把当前线程置为interrupted状态,然后再中断线程。
ArrayBlockingQueue的内部的信号量
ArrayBlockingQueue由于数组的容量是固定的,所以需要信号量协调put和take动作。
- 在put的时候遇到数组满的时候通过notFull.await()实现等待,直到dequeue()方法消费一个元素后执行notFull.signal()通知可以put新元素。
- 在take的时候遇到数组空的时候通过notEmpty.await()实现等待,直到enqueue()方法新增一个元素后执行notEmpty.signal()通知可以take新元素。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[putIndex] == null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
count++;
notEmpty.signal();
}
----------------------------------------------------
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
ArrayBlockingQueue迭代器
ArrayBlockingQueue迭代器的迭代器比较简单,hasNext()判断下一个元素是否为null,next()通过移动下标获取下一个元素,中间涉及到一些下标到末尾重新从头开始。当然有一些细节代码我直接省略了不影响理解迭代过程。
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
private int cursor;
private E nextItem;
private int nextIndex;
private E lastItem;
private int lastRet;
private int prevTakeIndex;
private int prevCycles;
private static final int NONE = -1;
private static final int REMOVED = -2;
private static final int DETACHED = -3;
Itr() {
lastRet = NONE;
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == 0) {
// assert itrs == null;
cursor = NONE;
nextIndex = NONE;
prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
} else {
final int takeIndex = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.takeIndex;
prevTakeIndex = takeIndex;
nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = takeIndex);
cursor = incCursor(takeIndex);
if (itrs == null) {
itrs = new Itrs(this);
} else {
itrs.register(this); // in this order
itrs.doSomeSweeping(false);
}
prevCycles = itrs.cycles;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private int incCursor(int index) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
if (++index == items.length)
index = 0;
if (index == putIndex)
index = NONE;
return index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;
if (nextItem != null)
return true;
noNext();
return false;
}
public E next() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;
final E x = nextItem;
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (!isDetached())
incorporateDequeues();
// assert nextIndex != NONE;
// assert lastItem == null;
lastRet = nextIndex;
final int cursor = this.cursor;
if (cursor >= 0) {
nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = cursor);
// assert nextItem != null;
this.cursor = incCursor(cursor);
} else {
nextIndex = NONE;
nextItem = null;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return x;
}
}