堆排序介绍
堆排序,顾名思义,就是基于堆。因此先来介绍一下堆的概念。
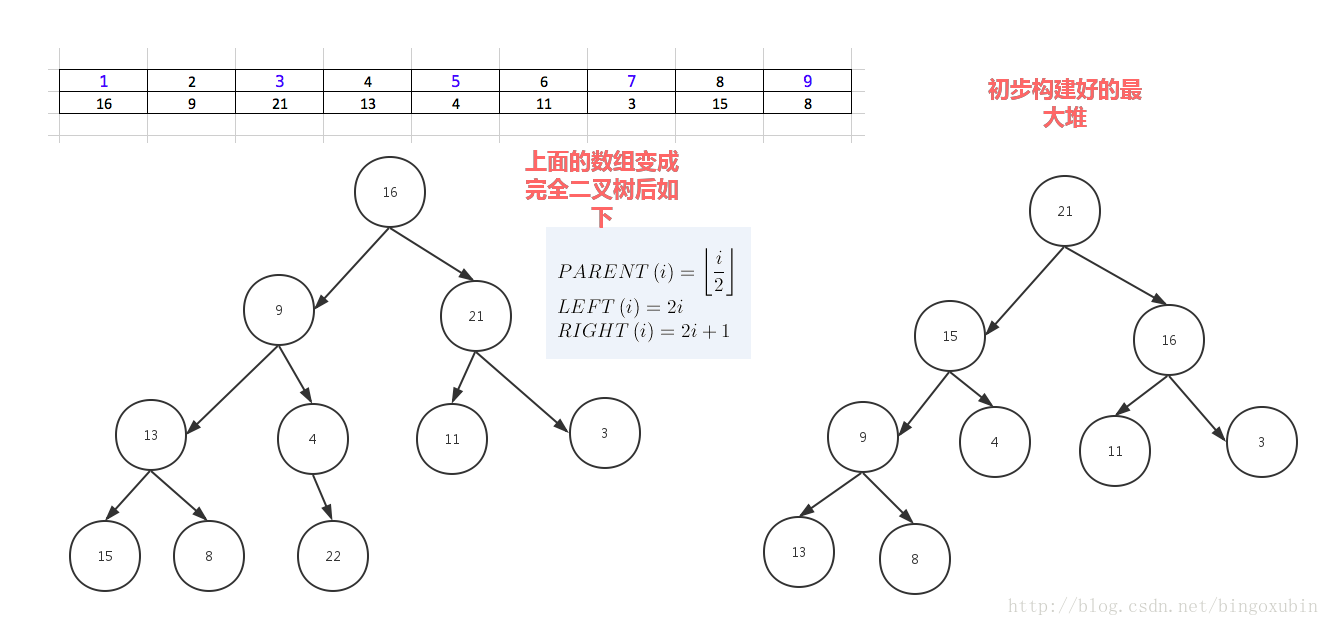
堆分为最大堆和最小堆,其实就是完全二叉树。最大堆要求节点的元素都要大于其孩子,最小堆要求节点元素都小于其左右孩子,两者对左右孩子的大小关系不做任何要求,其实很好理解。有了上面的定义,我们可以得知,处于最大堆的根节点的元素一定是这个堆中的最大值。其实我们的堆排序算法就是抓住了堆的这一特点,每次都取堆顶的元素,将其放在序列最后面,然后将剩余的元素重新调整为最大堆,依次类推,最终得到排序的序列。
![这里写图片描述]()
-
步骤:
-
堆排序就是把堆顶的最大数取出,
将剩余的堆继续调整为最大堆,具体过程在第二块有介绍,以递归实现
剩余部分调整为最大堆后,再次将堆顶的最大数取出,再将剩余部分调整为最大堆,这个过程持续到剩余数只有一个时结束
__author__ = 'Alex Li'
import time,random
def sift_down(arr, node, end):
root = node
while True:
child = 2 * root +1
if child > end:
break
print("v:",root,arr[root],child,arr[child])
print(arr)
if child + 1 <= end and arr[child] < arr[child + 1]:
child += 1
if arr[root] < arr[child]:
tmp = arr[root]
arr[root] = arr[child]
arr[child]= tmp
root = child
else:
break
print('-------------')
def heap_sort(arr):
first = len(arr) // 2 -1
for i in range(first, -1, -1):
sift_down(arr, i, len(arr) - 1)
print('--------end---',arr)
for end in range(len(arr) -1, 0, -1):
arr[0], arr[end] = arr[end], arr[0]
sift_down(arr, 0, end - 1)
def main():
array = [16,9,21,13,4,11,3,22,8,7,15,29]
print(array)
start_t = time.time()
heap_sort(array)
end_t = time.time()
print("cost:",end_t -start_t)
print(array)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
dataset = [16,9,21,3,13,14,23,6,4,11,3,15,99,8,22]
for i in range(len(dataset)-1,0,-1):
print("-------",dataset[0:i+1],len(dataset),i)
for index in range(int((i+1)/2),0,-1):
print(index)
p_index = index
l_child_index = p_index *2 - 1
r_child_index = p_index *2
print("l index",l_child_index,'r index',r_child_index)
p_node = dataset[p_index-1]
left_child = dataset[l_child_index]
if p_node < left_child:
dataset[p_index - 1], dataset[l_child_index] = left_child, p_node
p_node = dataset[p_index - 1]
if r_child_index < len(dataset[0:i+1]):
right_child = dataset[r_child_index]
print(p_index,p_node,left_child,right_child)
if p_node < right_child:
dataset[p_index - 1] , dataset[r_child_index] = right_child,p_node
p_node = dataset[p_index - 1]
else:
print("p node [%s] has no right child" % p_node)
print("switch i index", i, dataset[0], dataset[i] )
print("before switch",dataset[0:i+1])
dataset[0],dataset[i] = dataset[i],dataset[0]
print(dataset)