CRI 简介
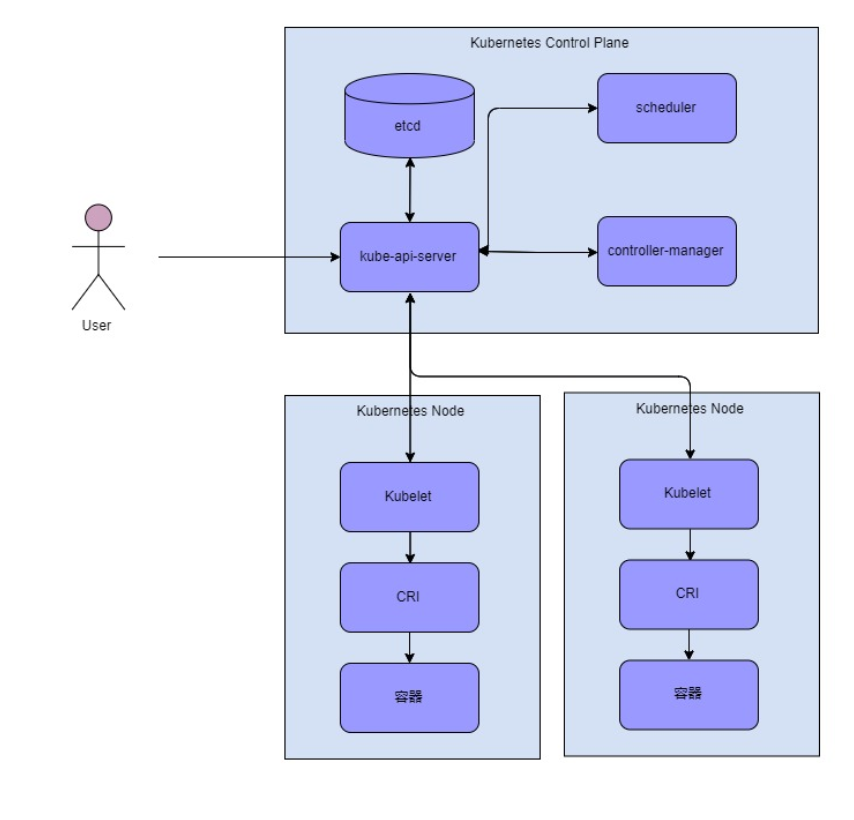
在 Kubernetes1.5 之前 Docker 作为第一个容器运行时,Kubelet 通过内嵌 dockershim 操作容器API,但随着越来越多的容器运行时的希望加入kubelet,社区开始有人提出通过加入一个client/server接口来抽象容器运行时。在 v1.6.0 后, Kubernetes 开始默认启用 CRI(容器运行时接口),下图是容器运行时在 kubernets 中得作用。
![cri-simple-architecture.png cri-simple-architecture.png]()
CRI 架构介绍
以下主要介绍Kubernetes1.18版的CRI
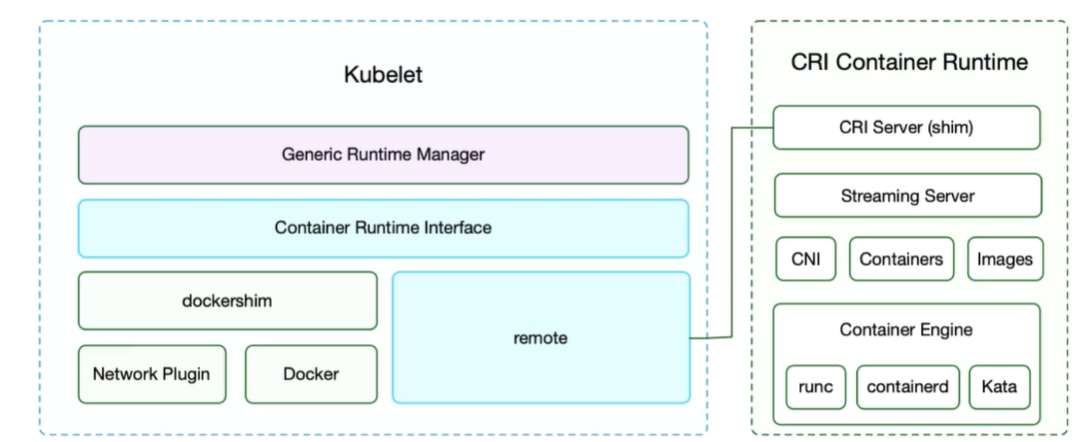
CRI 为 kubelet 提供一套抽象的容器调度的接口,CRI 主要承接 kubelet 对容器的操作。CRI 得通信协议是 gRPC,当时主要考虑到性能问题。加入 CRI 后 kubelet 得架构如下图所示。
![kubelet-architecture.png kubelet-architecture.png]()
Kubelet 现在主要包含两个运行时的模块,一个是 dockershim, 一个是 remote。dockershim 是原来的提供Docker的运行时接口(PS: docker果然还是一等公民??:)。remote包对应的就是 CRI 接口,采用gRPC,通过 RemoteRuntime 和 CRI RuntimeService相连:
...
// createAndStartFakeRemoteRuntime creates and starts fakeremote.RemoteRuntime.
// It returns the RemoteRuntime, endpoint on success.
// Users should call fakeRuntime.Stop() to cleanup the server.
func createAndStartFakeRemoteRuntime(t *testing.T) (*fakeremote.RemoteRuntime, string) {
endpoint, err := fakeremote.GenerateEndpoint()
require.NoError(t, err)
fakeRuntime := fakeremote.NewFakeRemoteRuntime()
fakeRuntime.Start(endpoint)
return fakeRuntime, endpoint
}
func createRemoteRuntimeService(endpoint string, t *testing.T) internalapi.RuntimeService {
runtimeService, err := NewRemoteRuntimeService(endpoint, defaultConnectionTimeout)
require.NoError(t, err)
return runtimeService
}
func TestVersion(t *testing.T) {
fakeRuntime, endpoint := createAndStartFakeRemoteRuntime(t)
defer fakeRuntime.Stop()
r := createRemoteRuntimeService(endpoint, t)
version, err := r.Version(apitest.FakeVersion)
assert.NoError(t, err)
assert.Equal(t, apitest.FakeVersion, version.Version)
assert.Equal(t, apitest.FakeRuntimeName, version.RuntimeName)
}
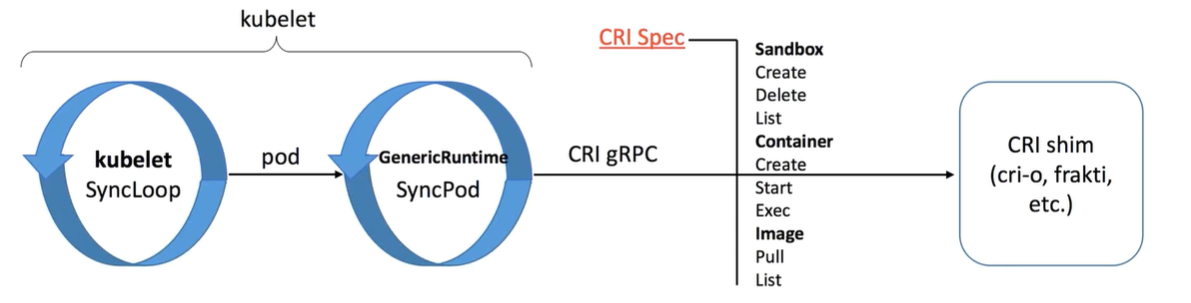
CRI 容器运行时的三类行为
CRI 容器运行时主要描述了三种服务的行为 Sandbox、Container、Image:
![kubelet-process.png kubelet-process.png]()
Sandbox:
// PodSandboxManager contains methods for operating on PodSandboxes. The methods
// are thread-safe.
type PodSandboxManager interface {
// RunPodSandbox creates and starts a pod-level sandbox. Runtimes should ensure
// the sandbox is in ready state.
RunPodSandbox(config *runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig, runtimeHandler string) (string, error)
// StopPodSandbox stops the sandbox. If there are any running containers in the
// sandbox, they should be force terminated.
StopPodSandbox(podSandboxID string) error
// RemovePodSandbox removes the sandbox. If there are running containers in the
// sandbox, they should be forcibly removed.
RemovePodSandbox(podSandboxID string) error
// PodSandboxStatus returns the Status of the PodSandbox.
PodSandboxStatus(podSandboxID string) (*runtimeapi.PodSandboxStatus, error)
// ListPodSandbox returns a list of Sandbox.
ListPodSandbox(filter *runtimeapi.PodSandboxFilter) ([]*runtimeapi.PodSandbox, error)
// PortForward prepares a streaming endpoint to forward ports from a PodSandbox, and returns the address.
PortForward(*runtimeapi.PortForwardRequest) (*runtimeapi.PortForwardResponse, error)
}
Container:
// ContainerManager contains methods to manipulate containers managed by a
// container runtime. The methods are thread-safe.
type ContainerManager interface {
// CreateContainer creates a new container in specified PodSandbox.
CreateContainer(podSandboxID string, config *runtimeapi.ContainerConfig, sandboxConfig *runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig) (string, error)
// StartContainer starts the container.
StartContainer(containerID string) error
// StopContainer stops a running container with a grace period (i.e., timeout).
StopContainer(containerID string, timeout int64) error
// RemoveContainer removes the container.
RemoveContainer(containerID string) error
// ListContainers lists all containers by filters.
ListContainers(filter *runtimeapi.ContainerFilter) ([]*runtimeapi.Container, error)
// ContainerStatus returns the status of the container.
ContainerStatus(containerID string) (*runtimeapi.ContainerStatus, error)
// UpdateContainerResources updates the cgroup resources for the container.
UpdateContainerResources(containerID string, resources *runtimeapi.LinuxContainerResources) error
// ExecSync executes a command in the container, and returns the stdout output.
// If command exits with a non-zero exit code, an error is returned.
ExecSync(containerID string, cmd []string, timeout time.Duration) (stdout []byte, stderr []byte, err error)
// Exec prepares a streaming endpoint to execute a command in the container, and returns the address.
Exec(*runtimeapi.ExecRequest) (*runtimeapi.ExecResponse, error)
// Attach prepares a streaming endpoint to attach to a running container, and returns the address.
Attach(req *runtimeapi.AttachRequest) (*runtimeapi.AttachResponse, error)
// ReopenContainerLog asks runtime to reopen the stdout/stderr log file
// for the container. If it returns error, new container log file MUST NOT
// be created.
ReopenContainerLog(ContainerID string) error
}
Image:
// ImageManagerService interface should be implemented by a container image
// manager.
// The methods should be thread-safe.
type ImageManagerService interface {
// ListImages lists the existing images.
ListImages(filter *runtimeapi.ImageFilter) ([]*runtimeapi.Image, error)
// ImageStatus returns the status of the image.
ImageStatus(image *runtimeapi.ImageSpec) (*runtimeapi.Image, error)
// PullImage pulls an image with the authentication config.
PullImage(image *runtimeapi.ImageSpec, auth *runtimeapi.AuthConfig, podSandboxConfig *runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig) (string, error)
// RemoveImage removes the image.
RemoveImage(image *runtimeapi.ImageSpec) error
// ImageFsInfo returns information of the filesystem that is used to store images.
ImageFsInfo() ([]*runtimeapi.FilesystemUsage, error)
}
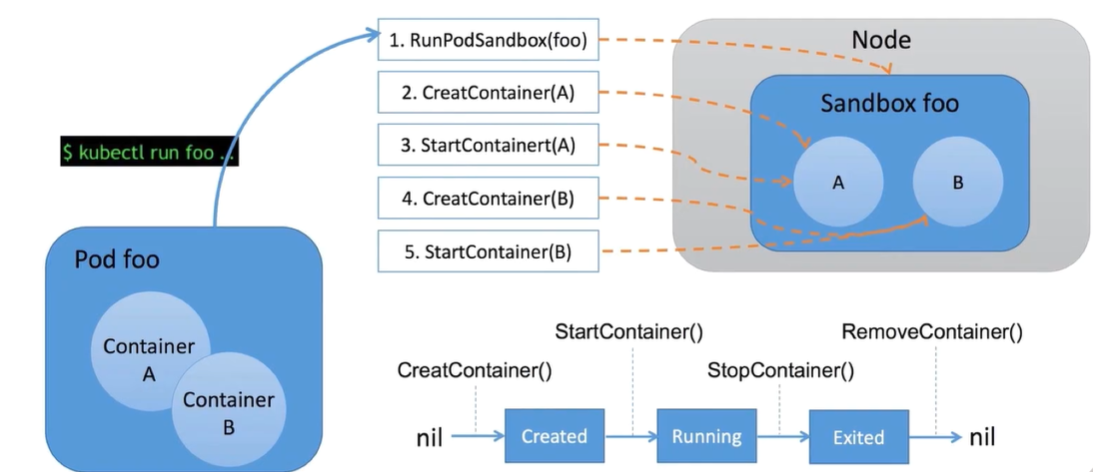
CRI 容器生命周期操作流程
kubelet创建一个Pod主要可以拆解成:
- 调用
RunPodSandox创建一个pod沙盒
- 调用
CreateContainer创建一个容器
- 调用
StartContainer启动一个容器
![cri-container-lifecycle.png cri-container-lifecycle.png]()
CRI Streaming接口
streaming接口主要是用于执行 exec 命令,exec 命令主要用于 attach 容器进行交互,通过流式接口的可以节省资源,提高连接的可靠性。
kubelet 调用 Exec() 接口发给 RuntimeService ,RuntimeService 返回一个 url 给到 apiserver, 让 apiserver 跟 Stream Server 直接建立连接,获取流式数据。 由于绕过了kubelet,因此Stream Server 也提高连接的可靠性
CRI 中 Exec() 接口:
// ContainerManager contains methods to manipulate containers managed by a
// container runtime. The methods are thread-safe.
type ContainerManager interface {
...
// Exec prepares a streaming endpoint to execute a command in the container, and returns the address.
Exec(*runtimeapi.ExecRequest) (*runtimeapi.ExecResponse, error)
// Attach prepares a streaming endpoint to attach to a running container, and returns the address.
Attach(req *runtimeapi.AttachRequest) (*runtimeapi.AttachResponse, error)
...
}
![cri-streaming.png cri-streaming.png]()
CRI proto接口定义
CRI 是一个为kubelet提供的一个广泛的容器运行时的无需编译的接口插件。 CRI 包含了一个 protocol buffers 和 gRPC API。kubernetes1.18的 CRI 代码路径:kubernetes/staging/src/k8s.io/cri-api/。
CRI中定义了容器和镜像的服务的接口,因为容器运行时与镜像的生命周期是彼此隔离的,因此需要定义两个服务 RuntimeService 和 ImageService。
RuntimeService的proto接口定义文件
// Runtime service defines the public APIs for remote container runtimes
service RuntimeService {
// Version returns the runtime name, runtime version, and runtime API version.
rpc Version(VersionRequest) returns (VersionResponse) {}
// RunPodSandbox creates and starts a pod-level sandbox. Runtimes must ensure
// the sandbox is in the ready state on success.
rpc RunPodSandbox(RunPodSandboxRequest) returns (RunPodSandboxResponse) {}
// StopPodSandbox stops any running process that is part of the sandbox and
// reclaims network resources (e.g., IP addresses) allocated to the sandbox.
// If there are any running containers in the sandbox, they must be forcibly
// terminated.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if all relevant
// resources have already been reclaimed. kubelet will call StopPodSandbox
// at least once before calling RemovePodSandbox. It will also attempt to
// reclaim resources eagerly, as soon as a sandbox is not needed. Hence,
// multiple StopPodSandbox calls are expected.
rpc StopPodSandbox(StopPodSandboxRequest) returns (StopPodSandboxResponse) {}
// RemovePodSandbox removes the sandbox. If there are any running containers
// in the sandbox, they must be forcibly terminated and removed.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the sandbox has
// already been removed.
rpc RemovePodSandbox(RemovePodSandboxRequest) returns (RemovePodSandboxResponse) {}
// PodSandboxStatus returns the status of the PodSandbox. If the PodSandbox is not
// present, returns an error.
rpc PodSandboxStatus(PodSandboxStatusRequest) returns (PodSandboxStatusResponse) {}
// ListPodSandbox returns a list of PodSandboxes.
rpc ListPodSandbox(ListPodSandboxRequest) returns (ListPodSandboxResponse) {}
// CreateContainer creates a new container in specified PodSandbox
rpc CreateContainer(CreateContainerRequest) returns (CreateContainerResponse) {}
// StartContainer starts the container.
rpc StartContainer(StartContainerRequest) returns (StartContainerResponse) {}
// StopContainer stops a running container with a grace period (i.e., timeout).
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has
// already been stopped.
// TODO: what must the runtime do after the grace period is reached?
rpc StopContainer(StopContainerRequest) returns (StopContainerResponse) {}
// RemoveContainer removes the container. If the container is running, the
// container must be forcibly removed.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has
// already been removed.
rpc RemoveContainer(RemoveContainerRequest) returns (RemoveContainerResponse) {}
// ListContainers lists all containers by filters.
rpc ListContainers(ListContainersRequest) returns (ListContainersResponse) {}
// ContainerStatus returns status of the container. If the container is not
// present, returns an error.
rpc ContainerStatus(ContainerStatusRequest) returns (ContainerStatusResponse) {}
// UpdateContainerResources updates ContainerConfig of the container.
rpc UpdateContainerResources(UpdateContainerResourcesRequest) returns (UpdateContainerResourcesResponse) {}
// ReopenContainerLog asks runtime to reopen the stdout/stderr log file
// for the container. This is often called after the log file has been
// rotated. If the container is not running, container runtime can choose
// to either create a new log file and return nil, or return an error.
// Once it returns error, new container log file MUST NOT be created.
rpc ReopenContainerLog(ReopenContainerLogRequest) returns (ReopenContainerLogResponse) {}
// ExecSync runs a command in a container synchronously.
rpc ExecSync(ExecSyncRequest) returns (ExecSyncResponse) {}
// Exec prepares a streaming endpoint to execute a command in the container.
rpc Exec(ExecRequest) returns (ExecResponse) {}
// Attach prepares a streaming endpoint to attach to a running container.
rpc Attach(AttachRequest) returns (AttachResponse) {}
// PortForward prepares a streaming endpoint to forward ports from a PodSandbox.
rpc PortForward(PortForwardRequest) returns (PortForwardResponse) {}
// ContainerStats returns stats of the container. If the container does not
// exist, the call returns an error.
rpc ContainerStats(ContainerStatsRequest) returns (ContainerStatsResponse) {}
// ListContainerStats returns stats of all running containers.
rpc ListContainerStats(ListContainerStatsRequest) returns (ListContainerStatsResponse) {}
// UpdateRuntimeConfig updates the runtime configuration based on the given request.
rpc UpdateRuntimeConfig(UpdateRuntimeConfigRequest) returns (UpdateRuntimeConfigResponse) {}
// Status returns the status of the runtime.
rpc Status(StatusRequest) returns (StatusResponse) {}
}
ImageService 的 proto 接口定义文件:
// ImageService defines the public APIs for managing images.
service ImageService {
// ListImages lists existing images.
rpc ListImages(ListImagesRequest) returns (ListImagesResponse) {}
// ImageStatus returns the status of the image. If the image is not
// present, returns a response with ImageStatusResponse.Image set to
// nil.
rpc ImageStatus(ImageStatusRequest) returns (ImageStatusResponse) {}
// PullImage pulls an image with authentication config.
rpc PullImage(PullImageRequest) returns (PullImageResponse) {}
// RemoveImage removes the image.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the image has
// already been removed.
rpc RemoveImage(RemoveImageRequest) returns (RemoveImageResponse) {}
// ImageFSInfo returns information of the filesystem that is used to store images.
rpc ImageFsInfo(ImageFsInfoRequest) returns (ImageFsInfoResponse) {}
}
CRI工具介绍
- CRI命令工具:crictl,帮助用户和开发者调试容器问题
- CRI测试工具:critest,用于验证CRI接口的测试工具,验证是否满足Kubelet要求。
crictl 安装:
VERSION="v1.17.0"
wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cri-tools/releases/download/$VERSION/crictl-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo tar zxvf crictl-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin
rm -f crictl-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
critest 安装:
VERSION="v1.17.0"
wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cri-tools/releases/download/$VERSION/critest-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo tar zxvf critest-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin
rm -f critest-$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
参考文献