Spark HadoopRDD读取HDFS文件
Spark HadoopRDD读取HDFS文件
更多资源
- SPARK 源码分析技术分享(bilibilid视频汇总套装视频): https://www.bilibili.com/video/av37442139/
- github: https://github.com/opensourceteams/spark-scala-maven
- csdn(汇总视频在线看): https://blog.csdn.net/thinktothings/article/details/84726769
bilibili 视频说明
- Spark HadoopRDD读取HDFS文件(bilibili视频) : https://www.bilibili.com/video/av37442139/?p=28
<iframe width="800" height="500" src="//player.bilibili.com/player.html?aid=37442139&cid=66303785&page=28" scrolling="no" border="0" frameborder="no" framespacing="0" allowfullscreen="true"> </iframe>
前置条件
- Hadoop版本: Hadoop 2.6.0-cdh5.15.0
- Spark版本: SPARK 1.6.0-cdh5.15.0
概述
- 源码分析Spark HadoopRDD是如何读取HDFS上的文件
- 分析HadoopRDD预分区的计算方式,非首个分区的开始位置计算
- 来三种情况分析,不同情部下HadoopRDD的分区计算方式
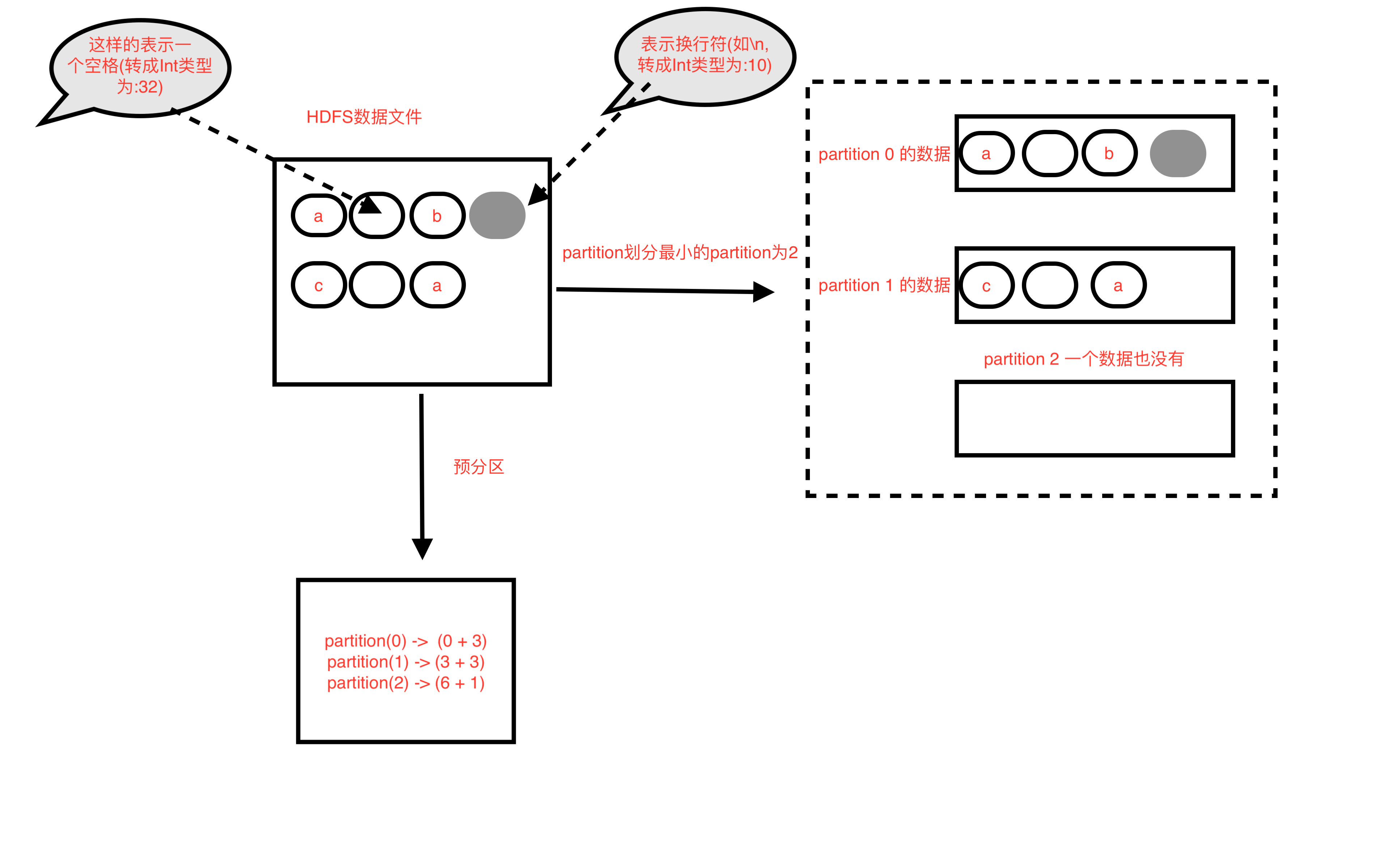
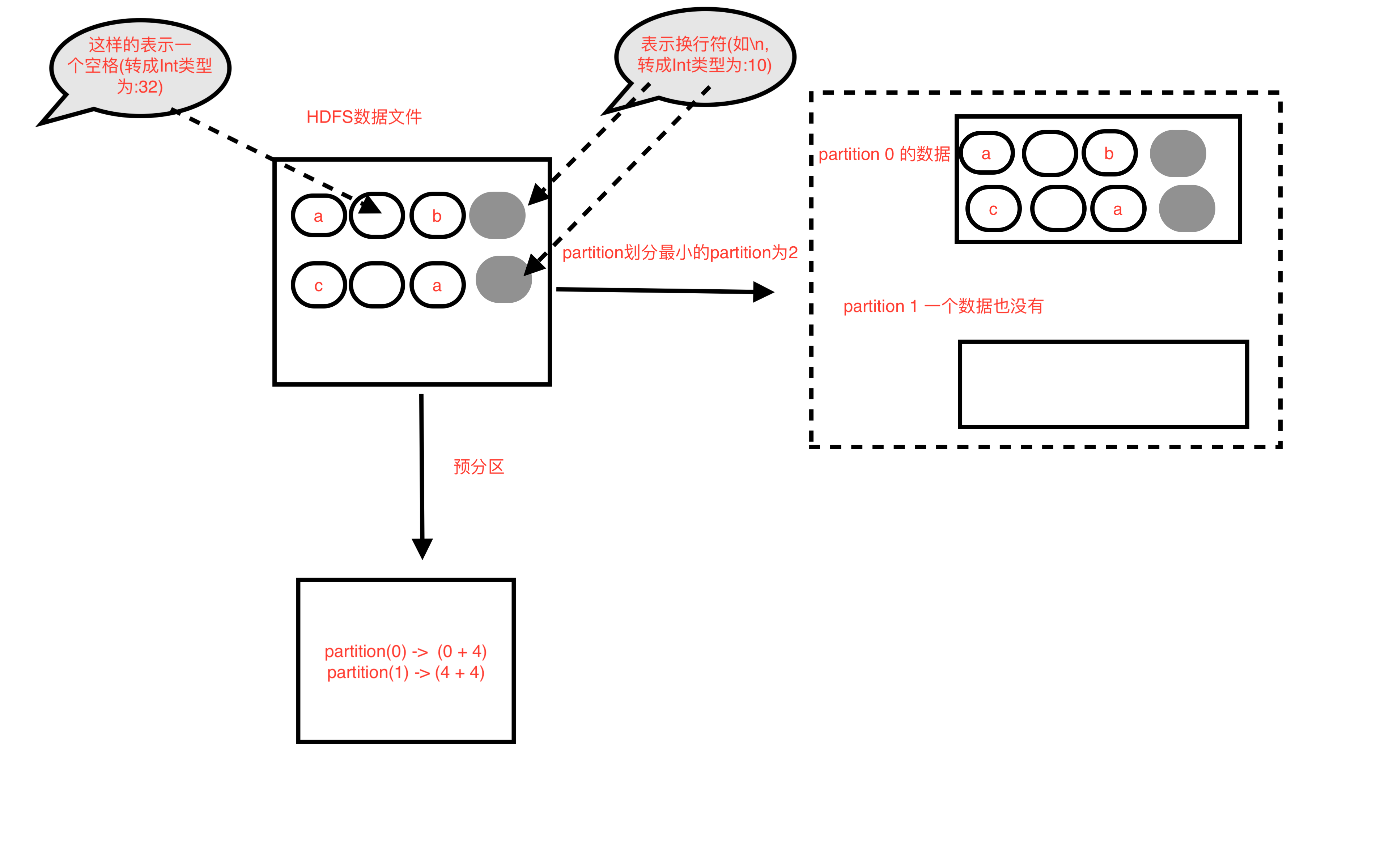
HDFS数据文件
a b k l j c a n m o HDFS 数据文件图解
HDFS 数据文件图解(对比)
图一
图二
断点位置
- org.apache.hadoop.mapred.LineRecordReader 241行, 246行, 248行,136行
HadoopRDD partition预划分方式(实际会有小的调整)
- 每个partition的长度= 文件的总长度 / 最小的分区数(默认分区数为2) //注意,是除,结果会取整, 即 goalSize = totalSize / numSplits
- 示例中每个partition的长度 = 20 / 2 =10 // 即为10个byte
- 然后依次从0开始划分10个byte长度为一个partition,最后一个小于等于10个byte的为最后一个partition
- 所以 parition(0) = hdfs文件(0 + 10) //即从文件偏移量为0开始,共10byte,0 <= 值 < 10
- 所以 parition(1) = hdfs文件(10 + 10) //即从文件偏移量为10开始,共10byte,10 <= 值 < 20
- 即 partition(i) = hdfs文件( i * goalSize + 10 )
HadoopRDD partition划分原理
- 由于需要考虑,每个partition谁先执行是不确定的,所以每个partition执行时,都需要可明确计算当前partition的数据范围
- 由于直接按partition预划分方式,会把有的一行数据拆分,有些场景不适合(如钱金额,词组一般都不希望被拆分,所以一般按行拆分)
- 所以需要按行做为最小的数据划分单元,来进行partition的数据范围划分
- HadoopRDD是这样划分的partition,还是按partition预划分方式进行预先划分,不过在计算时会进行调整
- 对于首个partition,也就是partition(0),分区数据范围的开始位置就是从0开始(0 + goalSize )
- 对于非首个partition,的开始位置需要从新计算,从预划分的当前partition的开始位置开始找第一个换行符位置(indexNewLine),当前partition的开始位置为= indexNewLine + 1,长度还是goalSize
- 对于首个partition一定能分到数据(只要HDFS文件有数据)
- 非首个partition,有可能分不到数据的情况,分不到数据的情况,就是数据被上一个partition划分完了
partition分不到数据(以下情况同时满足)
- 是非首个partition,也就是不是partition为索引为0
- partition从预分区开始位置往后读到的第一个换行符大于等于预分区的结束位置 (或者该partition就没有一个换行符)
源码分析
- HadoopRdd partition的开始位置计算(文档详情) : https://github.com/opensourceteams/spark-scala-maven/blob/master/md/HadoopRddPartitionDivide.md
- HadoopRDD
override def compute(theSplit: Partition, context: TaskContext): InterruptibleIterator[(K, V)] = { val iter = new NextIterator[(K, V)] { val split = theSplit.asInstanceOf[HadoopPartition] logInfo("Input split: " + split.inputSplit) val jobConf = getJobConf() val inputMetrics = context.taskMetrics.getInputMetricsForReadMethod(DataReadMethod.Hadoop) // Sets the thread local variable for the file's name split.inputSplit.value match { case fs: FileSplit => SqlNewHadoopRDDState.setInputFileName(fs.getPath.toString) case _ => SqlNewHadoopRDDState.unsetInputFileName() } // Find a function that will return the FileSystem bytes read by this thread. Do this before // creating RecordReader, because RecordReader's constructor might read some bytes val bytesReadCallback = inputMetrics.bytesReadCallback.orElse { split.inputSplit.value match { case _: FileSplit | _: CombineFileSplit => SparkHadoopUtil.get.getFSBytesReadOnThreadCallback() case _ => None } } inputMetrics.setBytesReadCallback(bytesReadCallback) var reader: RecordReader[K, V] = null //返回TextInputFormat对象 val inputFormat = getInputFormat(jobConf) HadoopRDD.addLocalConfiguration(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmm").format(createTime), context.stageId, theSplit.index, context.attemptNumber, jobConf) //实例化对象 org.apache.hadoop.mapred.LineRecordReader //new LineRecordReader()实例方法中, 并且会重新计算当前partition的开始位置(与预分区的会有出入) reader = inputFormat.getRecordReader(split.inputSplit.value, jobConf, Reporter.NULL) // Register an on-task-completion callback to close the input stream. context.addTaskCompletionListener{ context => closeIfNeeded() } val key: K = reader.createKey() val value: V = reader.createValue() override def getNext(): (K, V) = { try { //调用 org.apache.hadoop.mapred.LineRecordReader.next()方法 finished = !reader.next(key, value) } catch { case _: EOFException if ignoreCorruptFiles => finished = true } if (!finished) { inputMetrics.incRecordsRead(1) } //返回当前一对(key,value)对应的值 (key, value) } override def close() { if (reader != null) { SqlNewHadoopRDDState.unsetInputFileName() // Close the reader and release it. Note: it's very important that we don't close the // reader more than once, since that exposes us to MAPREDUCE-5918 when running against // Hadoop 1.x and older Hadoop 2.x releases. That bug can lead to non-deterministic // corruption issues when reading compressed input. try { reader.close() } catch { case e: Exception => if (!ShutdownHookManager.inShutdown()) { logWarning("Exception in RecordReader.close()", e) } } finally { reader = null } if (bytesReadCallback.isDefined) { inputMetrics.updateBytesRead() } else if (split.inputSplit.value.isInstanceOf[FileSplit] || split.inputSplit.value.isInstanceOf[CombineFileSplit]) { // If we can't get the bytes read from the FS stats, fall back to the split size, // which may be inaccurate. try { inputMetrics.incBytesRead(split.inputSplit.value.getLength) } catch { case e: java.io.IOException => logWarning("Unable to get input size to set InputMetrics for task", e) } } } } } new InterruptibleIterator[(K, V)](context, iter) } - TextInputFormat
- 返回LineRecordReader
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> getRecordReader( InputSplit genericSplit, JobConf job, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { reporter.setStatus(genericSplit.toString()); String delimiter = job.get("textinputformat.record.delimiter"); byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null; if (null != delimiter) { recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8); } return new LineRecordReader(job, (FileSplit) genericSplit, recordDelimiterBytes); } - LineRecordReader
- 实例方法中,重新定位当前partition的开始位置
- 如果是partition(0),开始位置是0
- 如果不是partition(0),开始位置重新计算
- 调用 in.readLine()方法,等于调用 UncompressedSplitLineReader.readLine(),注意此时传的maxLineLength参数为0
public LineRecordReader(Configuration job, FileSplit split, byte[] recordDelimiter) throws IOException { this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input. LineRecordReader.MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE); start = split.getStart(); end = start + split.getLength(); final Path file = split.getPath(); compressionCodecs = new CompressionCodecFactory(job); codec = compressionCodecs.getCodec(file); // open the file and seek to the start of the split final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job); fileIn = fs.open(file); if (isCompressedInput()) { decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec); if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) { final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn = ((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream( fileIn, decompressor, start, end, SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK); in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job, recordDelimiter); start = cIn.getAdjustedStart(); end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd(); filePosition = cIn; // take pos from compressed stream } else { in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn, decompressor), job, recordDelimiter); filePosition = fileIn; } } else { fileIn.seek(start); //读取文件,定位的文件偏移量为,当前partition预分区的开始位置 in = new UncompressedSplitLineReader( fileIn, job, recordDelimiter, split.getLength()); filePosition = fileIn; } // If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record // because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in // next() method. if (start != 0) { //调用 in.readLine()方法,等于调用 UncompressedSplitLineReader.readLine(), //注意此时传的maxLineLength参数为0 //定位当前分区的开始位置,等于预分区的位置 + 读到的第一个换行符的长度 //也就是从当前partition开始位置计算,到读到的第一次换行符,属于上一个partition,在向后位置偏移位置+1,就是当前分区的实时开始位置 start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start)); } this.pos = start; } - HadoopRDD.compute() 重写迭代器getNext()方法
- 计算下一个(key,value)的值
- 具体reader.next()方法为 LineRecordReader.next() 方法
override def getNext(): (K, V) = { try { finished = !reader.next(key, value) } catch { case _: EOFException if ignoreCorruptFiles => finished = true } if (!finished) { inputMetrics.incRecordsRead(1) } (key, value) } - LineRecordReader.next()
- 遍历当前分区的(key,value)值,就是去计算每个key,对应的值,每计算完一个(key,value)的值后,会把下一个key的索引位置进行更新
/** Read a line. */ public synchronized boolean next(LongWritable key, Text value) throws IOException { // We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper // split limit i.e. (end - 1) // getFilePosition() 等于 pos位置 while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) { key.set(pos);//调置本次的偏移位置 int newSize = 0; if (pos == 0) { //第一个partition(0) newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark(value); } else { newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos)); pos += newSize; } if (newSize == 0) { return false; } if (newSize < maxLineLength) { return true; } // line too long. try again LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " + (pos - newSize)); } return false; } - UncompressedSplitLineReader.readLine()
- 调用LineReader.readLine()方法
@Override public int readLine(Text str, int maxLineLength, int maxBytesToConsume) throws IOException { int bytesRead = 0; if (!finished) { // only allow at most one more record to be read after the stream // reports the split ended if (totalBytesRead > splitLength) { finished = true; } bytesRead = super.readLine(str, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume); } return bytesRead; } - LineReader.readLine()方法
- 调用 LineReader.readDefaultLine()方法
/** * Read one line from the InputStream into the given Text. * * @param str the object to store the given line (without newline) * @param maxLineLength the maximum number of bytes to store into str; * the rest of the line is silently discarded. * @param maxBytesToConsume the maximum number of bytes to consume * in this call. This is only a hint, because if the line cross * this threshold, we allow it to happen. It can overshoot * potentially by as much as one buffer length. * * @return the number of bytes read including the (longest) newline * found. * * @throws IOException if the underlying stream throws */ public int readLine(Text str, int maxLineLength, int maxBytesToConsume) throws IOException { if (this.recordDelimiterBytes != null) { return readCustomLine(str, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume); } else { return readDefaultLine(str, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume); } } - LineReader.readDefaultLine()方法
- 具体计算partition的开始位置的方法
- 注意,此时传过来的maxLineLength参数值为0,也就是先不实际读取数据放到(key,value)的value中
- 调用 UncompressedSplitLineReader.fillBuffer()方法,实际读取HDFS上的文件
/** * Read a line terminated by one of CR, LF, or CRLF. * 当maxLineLength=0时,也就是partition不为0时,定位开始位置的时候,该方法会读取到 */ private int readDefaultLine(Text str, int maxLineLength, int maxBytesToConsume) throws IOException { /* We're reading data from in, but the head of the stream may be * already buffered in buffer, so we have several cases: * 1. No newline characters are in the buffer, so we need to copy * everything and read another buffer from the stream. * 2. An unambiguously terminated line is in buffer, so we just * copy to str. * 3. Ambiguously terminated line is in buffer, i.e. buffer ends * in CR. In this case we copy everything up to CR to str, but * we also need to see what follows CR: if it's LF, then we * need consume LF as well, so next call to readLine will read * from after that. * We use a flag prevCharCR to signal if previous character was CR * and, if it happens to be at the end of the buffer, delay * consuming it until we have a chance to look at the char that * follows. */ str.clear(); int txtLength = 0; //tracks str.getLength(), as an optimization int newlineLength = 0; //length of terminating newline boolean prevCharCR = false; //true of prev char was CR long bytesConsumed = 0; do { int startPosn = bufferPosn; //starting from where we left off the last time if (bufferPosn >= bufferLength) { startPosn = bufferPosn = 0; if (prevCharCR) { //bytesConsumed:总计读取的数据长度(包括换行符) ++bytesConsumed; //account for CR from previous read } /** * 实际读取HDFS文件的方法 * buffer:缓冲区 * bufferLength : 这一次读到的数据长度 */ bufferLength = fillBuffer(in, buffer, prevCharCR); if (bufferLength <= 0) { break; // EOF } } //对读到的buffer数组数据进行遍历,找找第一个换行符 // bufferPosn: 读到换行符时的位置(索引),同一个分区中这个值是会保存的 for (; bufferPosn < bufferLength; ++bufferPosn) { //search for newline if (buffer[bufferPosn] == LF) { //调试时prevCharCR = false, 当找到换行符\n时,newlineLength=1 newlineLength = (prevCharCR) ? 2 : 1; ++bufferPosn; // at next invocation proceed from following byte break; } if (prevCharCR) { //CR + notLF, we are at notLF newlineLength = 1; break; } //在linux平台测试数据中没看到等于\r的,也就是调试prevCharCR一直等于false prevCharCR = (buffer[bufferPosn] == CR); } int readLength = bufferPosn - startPosn;//这一次读取的数据长度(包括换行符) if (prevCharCR && newlineLength == 0) { --readLength; //CR at the end of the buffer } //总计读取的数据长度(包括换行符) bytesConsumed += readLength; //这一次读取的数据长度(不包括换行符) int appendLength = readLength - newlineLength; if (appendLength > maxLineLength - txtLength) { //如果读到的数据长度,大于最大长度限制,做个控制 //如果maxLineLength=0, txtLength =0 时,此时是不需要读数据的,就给appendLength赋值为0 appendLength = maxLineLength - txtLength; } if (appendLength > 0) { //如果计算appendLength >0 时,把值赋值给str,也就是我们读到的值 str.append(buffer, startPosn, appendLength); //txtLength变量累加每次实际读到的长度(不包括换行符) txtLength += appendLength; } //循环条件,是没有读到换行符,并且 } while (newlineLength == 0 && bytesConsumed < maxBytesToConsume); if (bytesConsumed > Integer.MAX_VALUE) { throw new IOException("Too many bytes before newline: " + bytesConsumed); } return (int)bytesConsumed; } - UncompressedSplitLineReader.fillBuffer()方法
protected int fillBuffer(InputStream in, byte[] buffer, boolean inDelimiter) throws IOException { int maxBytesToRead = buffer.length; //缓冲的大小,默认为64KB //splitLength 当前partition的预分区大小(长度) // totalBytesRead 当前partitition总共读取了的数据长度 if (totalBytesRead < splitLength) { //说明当前partition预分区长度还没有读完,还需要继续读取剩下的长度 long leftBytesForSplit = splitLength - totalBytesRead; // check if leftBytesForSplit exceed Integer.MAX_VALUE if (leftBytesForSplit <= Integer.MAX_VALUE) { //做个比较,当前分区剩余的长度小于等于Integer.MAX_VALUE),取64KB默认长度和实际长度的一个小的值 maxBytesToRead = Math.min(maxBytesToRead, (int)leftBytesForSplit); } } //实际读取的数据长度 int bytesRead = in.read(buffer, 0, maxBytesToRead); // If the split ended in the middle of a record delimiter then we need // to read one additional record, as the consumer of the next split will // not recognize the partial delimiter as a record. // However if using the default delimiter and the next character is a // linefeed then next split will treat it as a delimiter all by itself // and the additional record read should not be performed. if (totalBytesRead == splitLength && inDelimiter && bytesRead > 0) { if (usingCRLF) { needAdditionalRecord = (buffer[0] != '\n'); } else { needAdditionalRecord = true; } } if (bytesRead > 0) { //读到了数据,当前partitition读到的总数据长度做个累加 totalBytesRead += bytesRead; } return bytesRead; }  关注公众号
关注公众号 低调大师中文资讯倾力打造互联网数据资讯、行业资源、电子商务、移动互联网、网络营销平台。
持续更新报道IT业界、互联网、市场资讯、驱动更新,是最及时权威的产业资讯及硬件资讯报道平台。
转载内容版权归作者及来源网站所有,本站原创内容转载请注明来源。
- 上一篇

SpringCloud源码:Ribbon负载均衡分析
本文主要分析 SpringCloud 中 Ribbon 负载均衡流程和原理。 SpringCloud版本为:Edgware.RELEASE。 一.时序图 和以前一样,先把图贴出来,直观一点: 二.源码分析 我们先从 contoller 里面看如何使用 Ribbon 来负载均衡的: @GetMapping("/user/{id}") public User findById(@PathVariable Long id) { //return this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://192.168.2.110:8001/" + id, User.class); return this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://microservice-provider-user/" + id, User.class); } 可以看到,在整合 Ribbon 之前,请求Rest是通过IP端口直接请求。整合 Ribbon 之后,请求的地址改成了 http://applicationName ,官方取名为虚拟主机...
- 下一篇

这次,彻底弄懂接口及抽象类
本文出自伯特的《楼兰计划》,转载务必注明作者及出处。 下文旨在讨论抽象类和接口的作用、实例及使用场景,都是我的理解和总结。更多关于接口和抽象类的概念知识,可自行查阅相关文档。 1. 抽象类及其作用 抽象类,顾名思义,即类的抽象。 在介绍面向对象概念时,我们知道类是客观事物的抽象,而抽象类又是类的进一步抽象,该怎么理解呢? 举个例子,我们定义若干个类 class BMW、class Benz、class Audi,分别对客观事物“宝马”、“奔驰”、“奥迪”三种汽车进行抽象,包含相关属性和行为(即方法)。但是我们知道,汽车都有通用的属性和行为,比如品牌、发动机、方向盘、轮胎等属性,前进、后退、转弯等行为,所以我们可以在宝马、奔驰等汽车之上,进一步抽象出“汽车”类 abstract class Car,包含通用的特性(属性和方法)。让 BMW、Benz、Audi 等继承抽象类 extends Car,便拥有了汽车的通用特性,然后在抽象类基础上定义各自的特殊属性及方法。 这里的 abstract class Car 即抽象类,可以看出,抽象类是用来捕捉子类的通用特性的,包括属性及行为。 2. ...
相关文章
文章评论
共有0条评论来说两句吧...
文章二维码
点击排行
推荐阅读
最新文章
- CentOS7编译安装Gcc9.2.0,解决mysql等软件编译问题
- CentOS6,7,8上安装Nginx,支持https2.0的开启
- Docker快速安装Oracle11G,搭建oracle11g学习环境
- CentOS8编译安装MySQL8.0.19
- Docker使用Oracle官方镜像安装(12C,18C,19C)
- CentOS关闭SELinux安全模块
- SpringBoot2更换Tomcat为Jetty,小型站点的福音
- SpringBoot2配置默认Tomcat设置,开启更多高级功能
- CentOS8,CentOS7,CentOS6编译安装Redis5.0.7
- Linux系统CentOS6、CentOS7手动修改IP地址










 微信收款码
微信收款码 支付宝收款码
支付宝收款码