0x1 摘要
WindowOperator可以说是Flink窗口功能非常核心核心的类,是窗口功能源码的一条主线,延着这条主线去慢慢看源码会轻松很多。注:此文基于Flink 1.4.2 版本源码。
0x2 WindowOperator 类结构分析
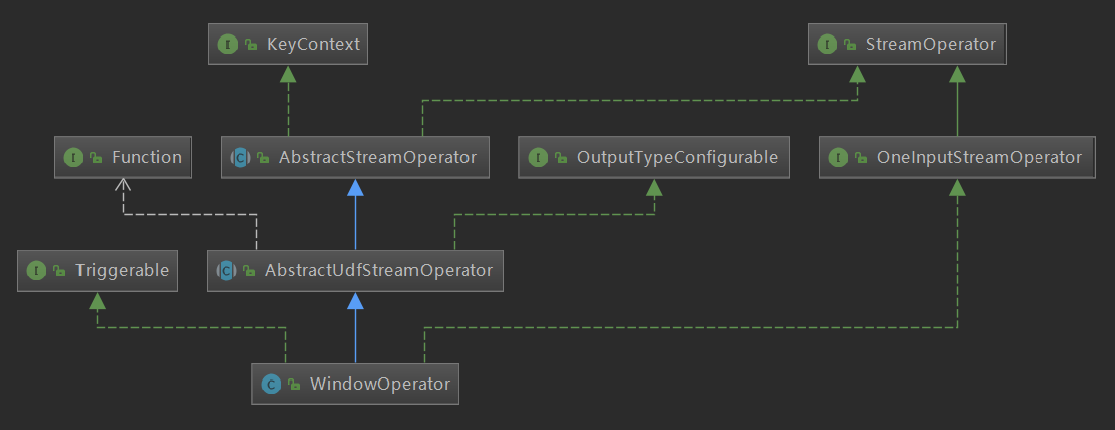
先来看一下类结构图,可以使用idea来生成类图,下图经过稍微加工,去掉一些不重要类的结构图:
![ca2a6732_bc3a_444f_b6d0_7aa927d16def ca2a6732_bc3a_444f_b6d0_7aa927d16def]()
我们核心重点关注以下一个接口:
public interface OneInputStreamOperator<IN, OUT> extends StreamOperator<OUT> {
/**
* Processes one element that arrived at this operator.
* This method is guaranteed to not be called concurrently with other methods of the operator.
*/
void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception;
/**
* Processes a {@link Watermark}.
* This method is guaranteed to not be called concurrently with other methods of the operator.
*
* @see org.apache.flink.streaming.api.watermark.Watermark
*/
void processWatermark(Watermark mark) throws Exception;
void processLatencyMarker(LatencyMarker latencyMarker) throws Exception;
}
0x3 OneInputStreamOperator 具体实现分析
此接口三个方法WindowOperator类只实现了processElement方法,其余两个方法实现全部在AbstractStreamOperator抽象类中,此文不去讲解,此文重点介绍processElement方法,这个方法也是最重要的方法。
从方法注释可以看出,每一条消息过来都会调用此方法,此方法主体很清晰,看下面条件判断语句:
final Collection<W> elementWindows = windowAssigner.assignWindows(
element.getValue(), element.getTimestamp(), windowAssignerContext);
//if element is handled by none of assigned elementWindows
boolean isSkippedElement = true;
final K key = this.<K>getKeyedStateBackend().getCurrentKey();
if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) {
...
} else {
...
}
// side output input event if
// element not handled by any window
// late arriving tag has been set
// windowAssigner is event time and current timestamp + allowed lateness no less than element timestamp
if (isSkippedElement && isElementLate(element)) {
if (lateDataOutputTag != null){
sideOutput(element);
} else {
this.numLateRecordsDropped.inc();
}
}
分为合并窗口分配器和非合并窗口分配器,我们平时使用的TumblingProcessingTimeWindows都属于非合并窗口,今天就介绍非合并窗口,即代码中else逻辑。
原代码如下:
for (W window: elementWindows) {
// drop if the window is already late
if (isWindowLate(window)) {
continue;
}
isSkippedElement = false;
windowState.setCurrentNamespace(window);
windowState.add(element.getValue());
triggerContext.key = key;
triggerContext.window = window;
TriggerResult triggerResult = triggerContext.onElement(element);
if (triggerResult.isFire()) {
ACC contents = windowState.get();
if (contents == null) {
continue;
}
emitWindowContents(window, contents);
}
if (triggerResult.isPurge()) {
windowState.clear();
}
registerCleanupTimer(window);
}
第一步:判断窗口是否延迟,如果延迟直接踩过,判断延迟的逻辑相对简单可自行查看源码
第二步:设置isSkippedElement标志位,此标志位等于false说明,当前元素可以匹配到窗口,true说明匹配不到窗口,后面会有处理逻辑
第三步:下面四行代码是一些状态设置
第四步:根据当前元素返回一个触发器结果
第五步:判断触发器结果是否需要执行,如果需要执行,则调用emitWindowContents方法执行
第六步:判断是否需要清理窗口状态信息
第七步:注册清除定时器
protected void registerCleanupTimer(W window) {
long cleanupTime = cleanupTime(window);
if (cleanupTime == Long.MAX_VALUE) {
// don't set a GC timer for "end of time"
return;
}
if (windowAssigner.isEventTime()) {
triggerContext.registerEventTimeTimer(cleanupTime);
} else {
triggerContext.registerProcessingTimeTimer(cleanupTime);
}
}
首先计算清除时间:
private long cleanupTime(W window) {
if (windowAssigner.isEventTime()) {
long cleanupTime = window.maxTimestamp() + allowedLateness;
return cleanupTime >= window.maxTimestamp() ? cleanupTime : Long.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
return window.maxTimestamp();
}
}
如果是事件时间则需要算上允许延迟时间,调用triggerContext注册Time
注:processElement方法开头代码
final Collection<W> elementWindows = windowAssigner.assignWindows(
element.getValue(), element.getTimestamp(), windowAssignerContext);
这段代码是窗口的分配,后面单独文章来分析窗口分配实现原理。
0x4 结束语
整个WindowOperator核心流程代码不多,但代码量还是比较大,里面涉及到窗口分配、时间触发器,每个点都涉及比较多的源码,不能一次性去讲完,需要慢慢去挖。