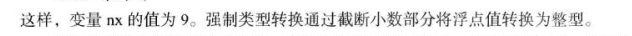拜读《核心技术卷》,笔记之。
提纲
1.编译运行第一个程序
2.使用floorMod求模
3.关于Math
4.1数据类型 4.2 变量注意事项
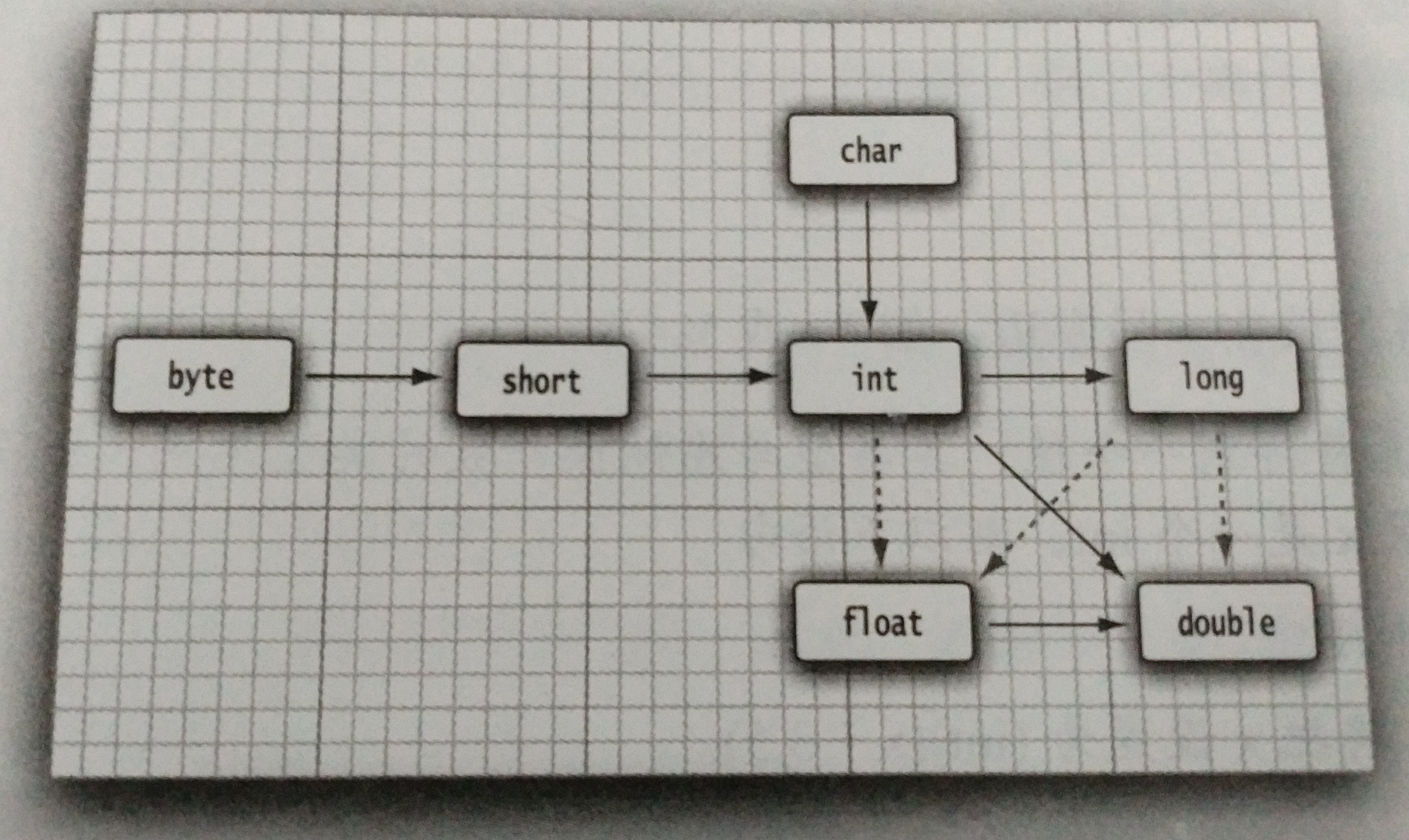
5.数值类型之间的转换(主要注意精度损失):
6.位运算
7.字符串
8.StringBuilder
9.读取输入(控制平台)
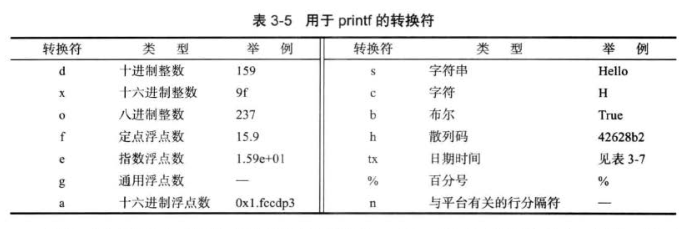
10.格式化输出
11.文件输入与输出
12.块作用域的注意事项
13.一个while语句的Demo
14.switch语句的case标签注意:
15.大数值:BigInteger、BigDecimal
1.编译运行第一个程序
结构目录:
使用cmd编译:
D:\>cd OK/corejava
D:\OK\corejava>cd v1ch02/Welcome
D:\OK\corejava\v1ch02\Welcome>javac Welcome.java
D:\OK\corejava\v1ch02\Welcome>java Welcome
Welcome to Core Java!
=====================
D:\OK\corejava\v1ch02\Welcome>
Welcome.java文件内容:
/**
* This program displays a greeting for the reader.
* @version 1.30 2014-02-27
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Welcome
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String greeting = "Welcome to Core Java!";
System.out.println(greeting);
for (int i = 0; i < greeting.length(); i++)
System.out.print("=");
System.out.println();
}
}
上面的cmd中,javac程序是一个Java编译器,它将文件Welcome.java编译成Welcome.class.java程序启动Java虚拟机。虚拟机执行编译器放在class文件中的字节码。
2.使用floorMod求模
语法:
floorMod(position + adjustment, modulus);
package Test;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Havaatry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
int hehe = Math.floorMod(2+15,12);
System.out.println(hehe);
}
}
3.关于Math
三角函数
Math.sin
Math.cos
Math.tan
Math.atan
Math.atan2
对数
Math.exp
Math.log
Math.log10
两个常量
Math.PI
Math.E
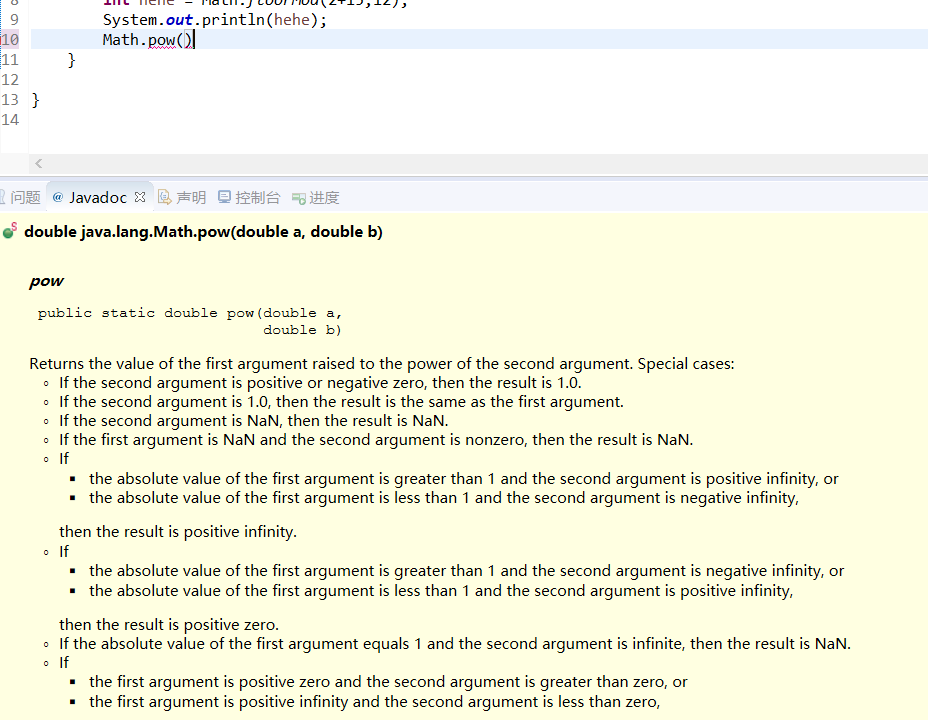
通过Javadoc进行具体查看:
double y = Math.pow(x, a);
//将y的值设置为x的a次幂。
4.1数据类型
- 长整型值后缀一个L或者l(如400000000000L)。
- 十六进制前缀0x或0X。
- 八进制前缀0,例如010对应八进制的8.显然八进制表示法容易混淆,建议最好不使用八进制常数。
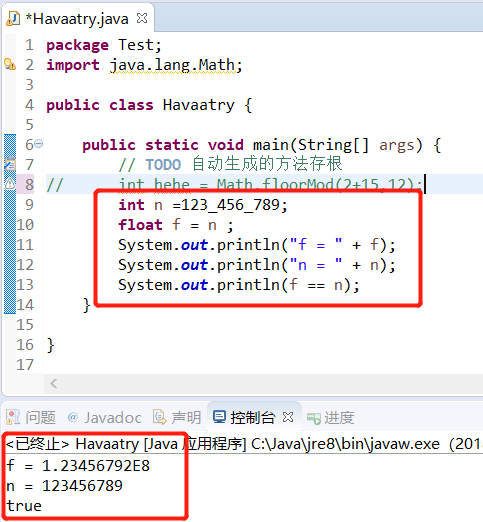
- Java 7 开始,可以用0b或0B写二进制数,如0B1001就是9.另外,同样是从Java 7 开始,还可以为数字字面量加下划线。如用1_000_000(或0b1111_0100_0010_0100_0000)表示一百万。这些下划线只为易读,Java编译器会去除这些下划线。
- 绝大部分应用程序都采用double类型,float类型的精度很难满足需求。float类型需要后缀F或f,否则默认浮点数值为double。
- Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY、Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY、Double.NaN三个常量分别表示正无穷大、负无穷大、NaN(不是一个数字,计算0/0或者负数的平方根结果为NaN)。
- boolean类型只有false和true两个值,用来判定逻辑条件。整型值和布尔值之间不能进行相互转换。在C++中,数值甚至指针可以代替boolean值,值0相当于布尔值false,非0值相当于布尔值true,在Java中不可以!
- final表示的变量只能被赋值一次,一旦被赋值就不能再更改。
4.2 变量注意事项
5.数值类型之间的转换(主要注意精度损失):
double x = 9.997;
int nx = (int) x;
舍入运算:
double x = 9.997;
int nx = (int) Math.round(x);
6.位运算
&(“and”) | (“or”) ^(“xor”) ~(“not”)
这些运算符按位模式处理。例如,如果n是一个整数变量,而且用二进制表示的n从右边数第4位为1,则
int fourthBItFromRight = (n & 0b1000) / 0b1000;
会返回1(结果递等为0b1000 / 0b1000),否则返回0(递等为 0b 0000 / 0b1000)。
7.字符串 (参考)
没有内置的字符串类型,标准库中提供了一个预定义类,String,例如:
String greeting = "Hello";
每个用双引号括起来的字符串都是 String 类的一个实例
<1>子串(substring方法)
String greeting = "Hello";
String s = greeting.substring(0,3); //Hel,不包含3,从0开始计数
<2>拼接(+)
System.out.println("The answer is"+answer);
使用定界分隔符(join):
String all = String.join("/","S","M","L","XL"); //"S/M/L/XL"
<3>不可变字符串(例:将Hello改为Help!)
String greeting = "Hello";
greeting = greeting.substring(0,3)+"p!";
将来自文件或键盘的单个字符或短的字符串汇集成字符串
<4>检测字符串是否相等:(equals 方法)
s.equals(t) //比较字符串s和t,返回true或false
检测字符串是否相等,不区分大小写(equalsIgnoreCase 方法)
"Hello".equals("hello") //返回false
"Hello".equalsIgnoreCase("hello") //返回true
双等号(==)只能确定两个字符串是否放置在线程池中的同一个位置上
<5>空串与null串
检测空串(""):
if (str.length() == 0) 或 if (str.equals(""))
null表示目前没有任何对象与该变量关联。检测方法:
if (str == null)
检测一个字符串既不是null,也不为空:
if (str != null && str.length() != 0)
先检测str不为null,如果在一个null值上调用方法,会出现错误
String类关键方法:
8.StringBuilder
使用:
1.构建一个空的字符串构建器 :
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
2.加入字符或字符串
builder.append(ch) ; //appends a single character
builder.append(str) ; // appends a string
3.在需要构建字符串时就凋用 toString 方法,得到String对象:
String completedString = builder.toString();
StringBuilder类关键方法:
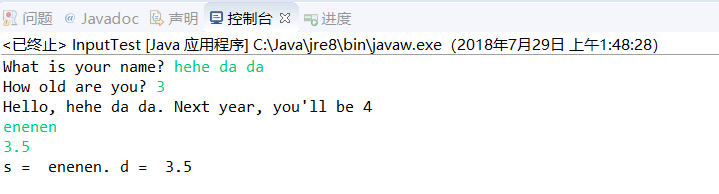
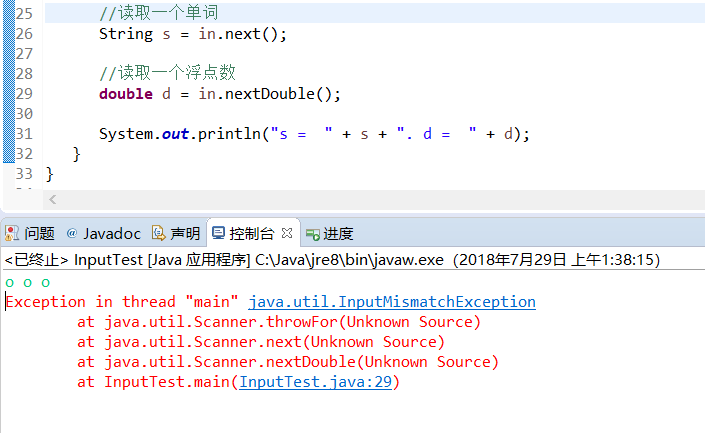
9.读取输入
Demo 代码中的方法均以Enter作为结束:
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates console input.
* @version 1.10 2004-02-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class InputTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// get first input
System.out.print("What is your name? ");
String name = in.nextLine();//读取一行,可以读入空格
// get second input
System.out.print("How old are you? ");
int age = in.nextInt();//读取一个整数
// display output on console
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + ". Next year, you'll be " + (age + 1));
//读取一个单词
String s = in.next();
//读取一个浮点数
double d = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("s = " + s + ". d = " + d);
}
}
要想读取一个整数,就调用nextInt()方法
如:int age = in.nextInt();
next()输入不能隔着空格,不然会报错:
Scanner关键API:
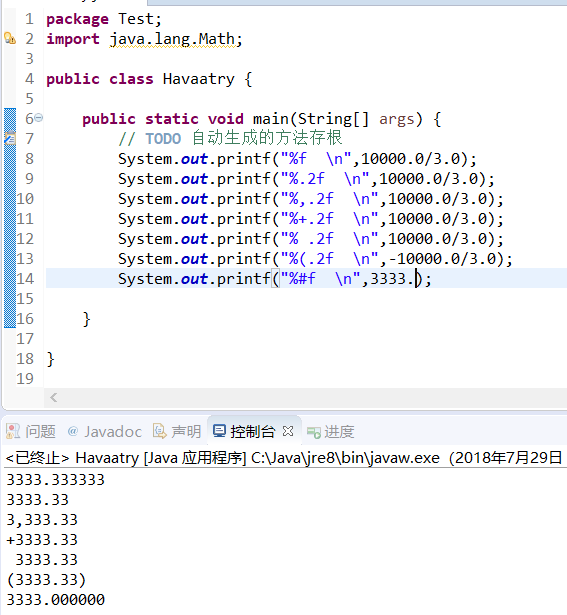
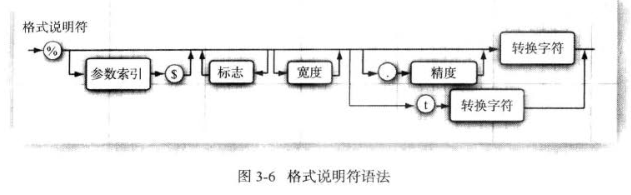
10.格式化输出
package Test;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Havaatry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
System.out.printf("%f \n",10000.0/3.0);
System.out.printf("%.2f \n",10000.0/3.0);
System.out.printf("%,.2f \n",10000.0/3.0);
System.out.printf("%+.2f \n",10000.0/3.0);
System.out.printf("% .2f \n",10000.0/3.0);
System.out.printf("%(.2f \n",-10000.0/3.0);
System.out.printf("%#f \n",3333.);
}
}
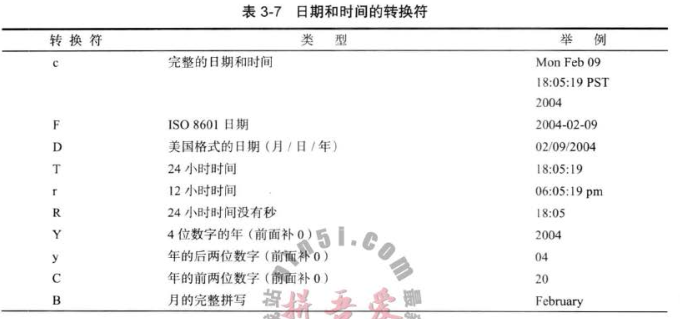
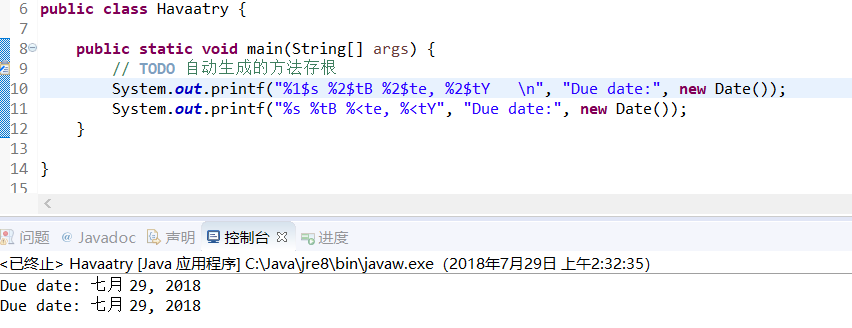
Date类和相关的格式化选项;格式包括两个字母,以t开始,以表3-7中的任意字母结束:
Demo:
System.out.printf("%1$s %2$tB %2$te, %2$tY \n", "Due date:", new Date());
System.out.printf("%s %tB %<te, %<tY", "Due date:", new Date());
11.文件输入与输出
要想对文件进行读取,就需要一个用File对象构造一个Scanner对象,如下所示:
Scanner in = new Scanner(Paths.get("myfile.txt"),"UTF-8");
!!!!!!!在这之后,就可以利用前面介绍的任何一个Scanner方法对文件进行读取
!!!!!!!"UTF-8"乃字符编码,如果省略了这个参数,则会使用运行这个Java程序的机器的“默认编码”。这不是一个好主意,
如果在不同的机器上运行这个程序,可能会有不同的表现。
注意:
要想写入文件就需要构建一个PrintWriter对象,在构造器中,只需要提供文件名:
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("myfile.txt","UTF-8");
如果文件不存在,创建该文件。可以像输出到System.out一样使用print、println以及printf命令。
本节相关API
12.块作用域的注意事项
13.一个while语句的Demo:
首先计算退休账户中的余额,然后再询问是否打算退休,只要用户回答“N”,循环就重复执行。这是一个需要至少执行一次循环的很好示例,因为用户必须先看到余额才能知道是否满足退休所用。
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates a <code>do/while</code> loop.
* @version 1.20 2004-02-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Retirement2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("How much money will you contribute every year? ");
double payment = in.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Interest rate in %: ");
double interestRate = in.nextDouble();
double balance = 0;
int year = 0;
String input;
// update account balance while user isn't ready to retire
do
{
// add this year's payment and interest
balance += payment;
double interest = balance * interestRate / 100;
balance += interest;
year++;
// print current balance
System.out.printf("After year %d, your balance is %,.2f%n", year, balance);
// ask if ready to retire and get input
System.out.print("Ready to retire? (Y/N) ");
input = in.next();
}
while (input.equals("N"));
}
}
执行结果:
How much money will you contribute every year? 30
Interest rate in %: 0.3
After year 1, your balance is 30.09
Ready to retire? (Y/N) N
After year 2, your balance is 60.27
Ready to retire? (Y/N) N
After year 3, your balance is 90.54
Ready to retire? (Y/N) N
After year 4, your balance is 120.90
Ready to retire? (Y/N) N
After year 5, your balance is 151.36
Ready to retire? (Y/N) N
After year 6, your balance is 181.90
Ready to retire? (Y/N) N
After year 7, your balance is 212.54
Ready to retire? (Y/N) N
After year 8, your balance is 243.26
Ready to retire? (Y/N) Y
14.switch语句的case标签注意:
15.大数值:BigInteger、BigDecimal
如果基本的整数和浮点数精度不能够满足需求,那么可以使用java.math包中的两个很有用的类:BigInteger和BigDecimal。这两个类可以处理包含任意长度数字序列的数值。BigInteger类实现了任意精度的整数运算,BigDecimal实现了任意精度的浮点数运算。
使用静态的valueOf方法可以将普通的数值转换为大数值:
BigInteger a = BigInteger.valueOf(100);
遗憾的是,不能使用人们熟悉的算术运算符(如:+和 * )处理大数值。而需要使用大数值类中的add和multiply方法。
BigInteger c = a.add(b); / / c = a + b
BigInteger d = c.multiply(b.add(BigInteger.valueOf(2))); / / d = c * ( b + 2 )
下面上一个例子,先用普通数据类型写一个(排列组合的)组合算法,其中变量k为欲取数,n为总数:
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates a <code>for</code> loop.
* @version 1.20 2004-02-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class LotteryOdds
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("How many numbers do you need to draw? ");
int k = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("What is the highest number you can draw? ");
int n = in.nextInt();
/*
* compute binomial coefficient n*(n-1)*(n-2)*...*(n-k+1)/(1*2*3*...*k)
*/
int lotteryOdds = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
lotteryOdds = lotteryOdds * (n - i + 1) / i;
System.out.println("Your odds are 1 in " + lotteryOdds + ". Good luck!");
}
}
测试——组合10中取2,结果为45:
下面用大数值进行计算:
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program uses big numbers to compute the odds of winning the grand prize in a lottery.
* @version 1.20 2004-02-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class BigIntegerTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("How many numbers do you need to draw? ");
int k = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("What is the highest number you can draw? ");
int n = in.nextInt();
/*
* compute binomial coefficient n*(n-1)*(n-2)*...*(n-k+1)/(1*2*3*...*k)
*/
BigInteger lotteryOdds = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
lotteryOdds = lotteryOdds.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(n - i + 1)).divide(
BigInteger.valueOf(i));
System.out.println("Your odds are 1 in " + lotteryOdds + ". Good luck!");
}
}
比较:
lotteryOdds = lotteryOdds * (n - i + 1) / i;
跟
lotteryOdds = lotteryOdds.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(n - i + 1)).divide(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
关键API: