背景
Android开发过程中,开发的小伙伴对动态加载代码肯定不陌生。使用各个开源框架的中都应该有接触,其主要原理离不开ClassLoader等相关的类。这里我们会从Android中ClassLoader等相关类的源码入手,更好的理解和学习动态加载类的原理。
详细分析ClassLoader加载原理
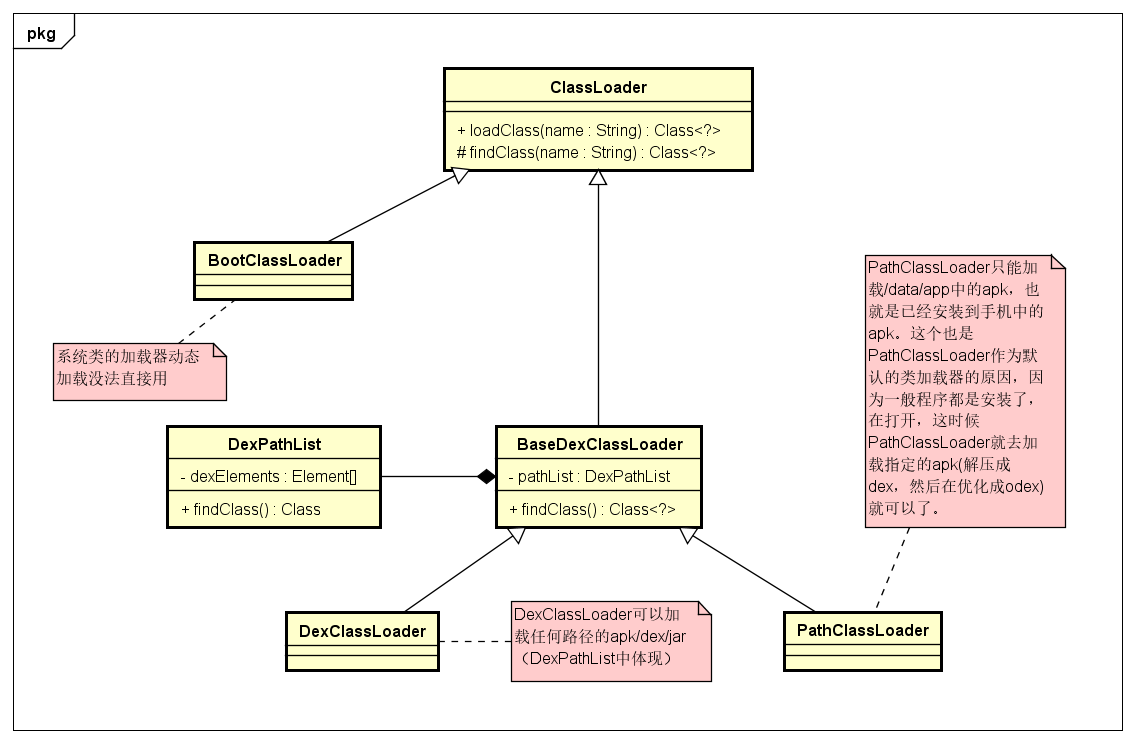
ClassLoader 的继承关系如下:
![]()
这里我们主要分析一下 BaseDexClassLoader.findClass()和 ClassLoader.loadClass()两个函数在系统中是怎么进行查找class的过程。
我们看一下系统加载类ClassLoader.loadClass()函数实现代码,在ClassLoader.java中:
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// 首先 检测是否已经加载过
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
if (parent != null) {
//去调用父类的loadClass
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
//未找到的情况下,使用findClass在当前dex查找
c = findClass(name);
}
}
return c;
}
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
- 1,
loadClass()先调用findLoadedClass()来判断当前类是否已加载;
- 2, 未查找到递归去父类中查找是否加载到缓存;
- 3, 均未缓存,去
BootClassLoader中查找;
- 4, 以上未发现,自顶级父类依次向下查找,调用
findClass()查找当前dex。
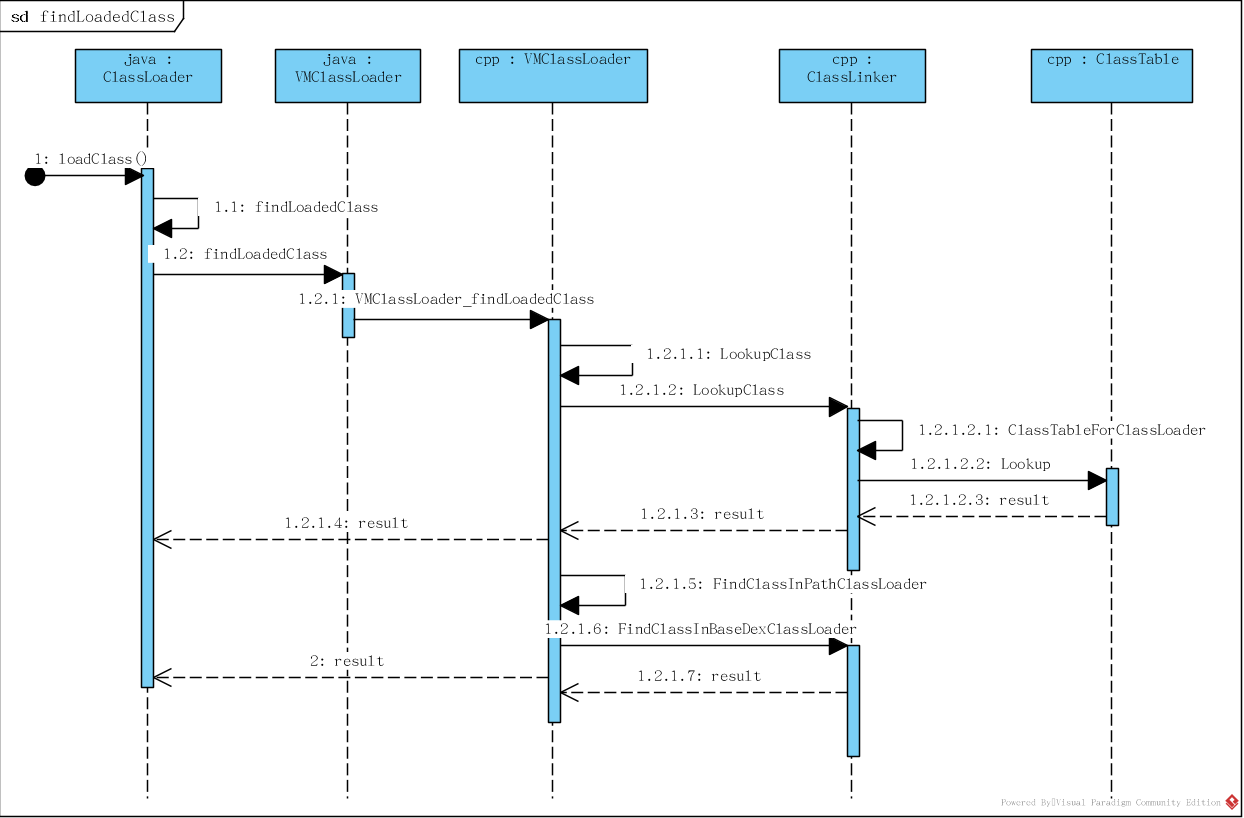
findLoadedClass函数分析
下图为findLoadedClass()的调用流程;根据调用流程图配合源代码进行详细的分析原理。
![]()
下面介绍对应的源代码实现部分:
protected final Class<?> findLoadedClass(String name) {
ClassLoader loader;
if (this == BootClassLoader.getInstance())
loader = null;
else
loader = this;
return VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass(loader, name);
}
函数最终统一调用VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass()进行查找类。
native static Class findLoadedClass(ClassLoader cl, String name);
实现在java_lang_VMClassLoader.cc文件中。
static jclass VMClassLoader_findLoadedClass(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jobject javaLoader,jstring javaName) {
....
ObjPtr<mirror::ClassLoader> loader = soa.Decode<mirror::ClassLoader>(javaLoader);
ClassLinker* cl = Runtime::Current()->GetClassLinker();
ObjPtr<mirror::Class> c = VMClassLoader::LookupClass(cl,
soa.Self(),
descriptor.c_str(),
descriptor_hash,
loader);
if (c != nullptr && c->IsResolved()) {
return soa.AddLocalReference<jclass>(c);
}
...
if (loader != nullptr) {
// Try the common case.
StackHandleScope<1> hs(soa.Self());
c = VMClassLoader::FindClassInPathClassLoader(cl,
soa,
soa.Self(),
descriptor.c_str(),
descriptor_hash,
hs.NewHandle(loader));
if (c != nullptr) {
return soa.AddLocalReference<jclass>(c);
}
}
return nullptr;
}
static mirror::Class* LookupClass(ClassLinker* cl,
Thread* self,
const char* descriptor,
size_t hash,
ObjPtr<mirror::ClassLoader> class_loader)
REQUIRES(!Locks::classlinker_classes_lock_)
REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {
return cl->LookupClass(self, descriptor, hash, class_loader);
}
static ObjPtr<mirror::Class> FindClassInPathClassLoader(ClassLinker* cl,
ScopedObjectAccessAlreadyRunnable& soa,
Thread* self,
const char* descriptor,
size_t hash,
Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> class_loader)
REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {
ObjPtr<mirror::Class> result;
if (cl->FindClassInBaseDexClassLoader(soa, self, descriptor, hash, class_loader, &result)) {
return result;
}
return nullptr;
}
上述代码findLoadedClass()分为两步;
- 1,通过
class_linker_->Lookupclass()进行查找加载类;
- 2,如果没找到在通过
class_linker_->FindClassInPathClassLoader()进行查找。
class_linker_在虚拟机的启动startVM()函数的时候进行的初始化。<br> Runtime::class_linker_在Runtime::Init()函数的时候做的初始化。
if (UNLIKELY(IsAotCompiler())) {
class_linker_ = new AotClassLinker(intern_table_);
} else {
class_linker_ = new ClassLinker(intern_table_);
}
继续来分析ClassLinker::LookupClass()函数的具体实现;
mirror::Class* ClassLinker::LookupClass(Thread* self,
const char* descriptor,
size_t hash,
ObjPtr<mirror::ClassLoader> class_loader) {
ReaderMutexLock mu(self, *Locks::classlinker_classes_lock_);
ClassTable* const class_table = ClassTableForClassLoader(class_loader);
if (class_table != nullptr) {
ObjPtr<mirror::Class> result = class_table->Lookup(descriptor, hash);
if (result != nullptr) {
return result.Ptr();
}
}
return nullptr;
}
LookupClass()函数通过class_loader是否为nullptr,nullptr使用boot_class_table_来获取class_table, 否则获取当前ClassLoader的ClassTable。 class_table存放当前已经加载过的class,其实可以理解为class cache。如何进行dex 解析和aot等加载系统类和解析映射到内存中的不在此处展开分析。可以了解art虚拟机启动进行详细分析。
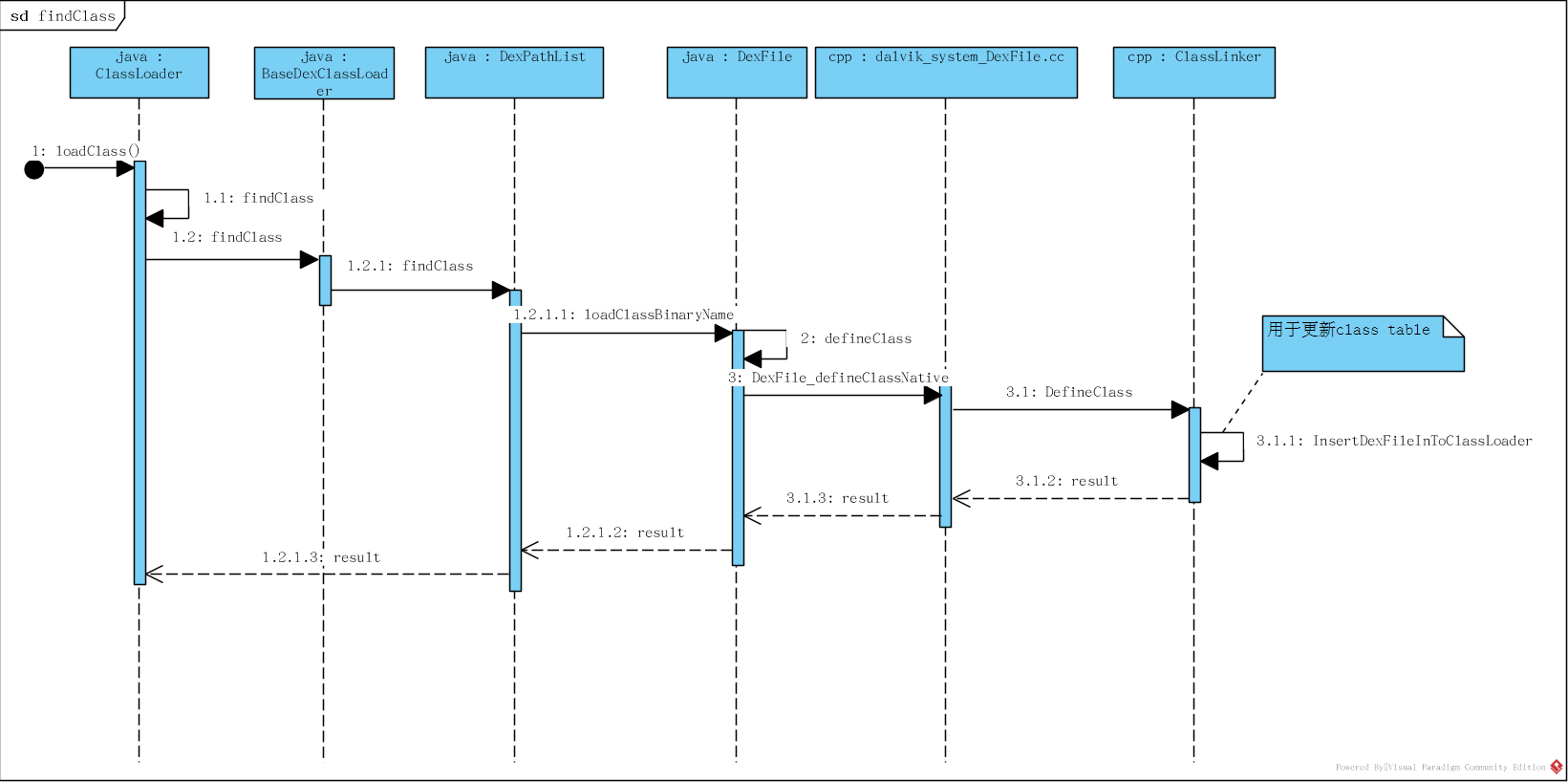
findClass()函数分析
下图是findClass的调用流程;根据调用流程图配合下面的代码进行详细的分析了解;
![]()
下面我们介绍对应的源代码实现部分。
findClass()函数在BaseDexClassLoader.java实现, 该函数主要做的事情就是在当前dex中查找类。如果类在当前dex中即返回。
代码如下:
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
if (c == null) {
...
throw cnfe;
}
return c;
}
pathList类型为DexPathList用来保存dexfile文件的句柄等dex的操作。pathList.findClass()实现在当前dex中查找类, pathList在new DexClassLoader()构造时初始化。
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) {
...
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, librarySearchPath, null);
...
}
DexPathList.java
public DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, String dexPath,
String librarySearchPath, File optimizedDirectory) {
...
this.definingContext = definingContext;
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<IOException>();
// save dexPath for BaseDexClassLoader
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory,
suppressedExceptions, definingContext);
this.nativeLibraryDirectories = splitPaths(librarySearchPath, false);
this.systemNativeLibraryDirectories =
splitPaths(System.getProperty("java.library.path"), true);
List<File> allNativeLibraryDirectories = new ArrayList<>(nativeLibraryDirectories);
allNativeLibraryDirectories.addAll(systemNativeLibraryDirectories);
this.nativeLibraryPathElements = makePathElements(allNativeLibraryDirectories);
if (suppressedExceptions.size() > 0) {
this.dexElementsSuppressedExceptions =
suppressedExceptions.toArray(new IOException[suppressedExceptions.size()]);
} else {
dexElementsSuppressedExceptions = null;
}
}
dexElements数组保存dexfile文件句柄。具体实现在makeDexElements()函数中调用loadDexFile()函数加载dex。该函数实现:
DexFile.java
private static DexFile loadDexFile(File file, File optimizedDirectory, ClassLoader loader, Element[] elements) throws IOException {
if (optimizedDirectory == null) {
return new DexFile(file, loader, elements);
} else {
String optimizedPath = optimizedPathFor(file, optimizedDirectory);
return DexFile.loadDex(file.getPath(), optimizedPath, 0, loader, elements);
}
}
DexFile.loadDex()进行解析加载dex文件。关键代码如下:
private DexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags, ClassLoader loader, DexPathList.Element[] elements) throws IOException {
...
mCookie = openDexFile(sourceName, outputName, flags, loader, elements);
mInternalCookie = mCookie;
mFileName = sourceName;
...
}
private static Object openDexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags, ClassLoader loader, DexPathList.Element[] elements) throws IOException {
// Use absolute paths to enable the use of relative paths when testing on host.
return openDexFileNative(new File(sourceName).getAbsolutePath(),
(outputName == null)
? null
: new File(outputName).getAbsolutePath(),
flags,loader,elements);
}
private static native Object openDexFileNative(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags, ClassLoader loader, DexPathList.Element[] elements);
最终打开dexfile是通过native方法实现,并且返回mCookie, mCookie类型是int用来标识dex的唯一性。 openDexFileNative()实现代码:
//`dalvik_system_DexFile.cc`
static jobject DexFile_openDexFileNative(JNIEnv* env,
jclass,
jstring javaSourceName,
jstring javaOutputName,
jint flags ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED,
jobject class_loader,
jobjectArray dex_elements)
{
...
Runtime* const runtime = Runtime::Current();
ClassLinker* linker = runtime->GetClassLinker();
...
dex_files = runtime->GetOatFileManager().OpenDexFilesFromOat(sourceName.c_str(), class_loader, dex_elements, /*out*/ &oat_file, /*out*/ &error_msgs);
....
}
上述代码通过aotManager打开并返回mCookie,进一步的打开实现不在此处展开。即上述已经已经填充elements[],下面开始展开pathList.findClass()函数的查找方式。
//BaseDexClassLoader.java
public Class<?> findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
Class<?> clazz = element.findClass(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
findClass()会遍历elements[], 每个element保存了dex的DexFile句柄,然后调用loadClassBinaryName()函数进行当前dex查找类。
//DexPathList.java
public Class<?> findClass(String name, ClassLoader definingContext,
List<Throwable> suppressed) {
return dexFile != null ? dexFile.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed): null;
}
public Class loadClassBinaryName(String name, ClassLoader loader, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
return defineClass(name, loader, mCookie, this, suppressed);
}
private static Class defineClass(String name, ClassLoader loader, Object cookie, DexFile dexFile, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
Class result = null;
try {
result = defineClassNative(name, loader, cookie, dexFile);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
}
return result;
}
真正去dex或者内存中查找类的函数在native中defineClassNative()实现, 我们来分析一下真正的实现过程:
private static native Class defineClassNative(String name, ClassLoader loader, Object cookie, DexFile dexFile)
//dalvik_system_DexFile.cc
static jclass DexFile_defineClassNative(JNIEnv* env,
jclass,
jstring javaName,
jobject javaLoader,
jobject cookie,
jobject dexFile) {
std::vector<const DexFile*> dex_files;
const OatFile* oat_file;
if (!ConvertJavaArrayToDexFiles(env, cookie, /*out*/ dex_files, /*out*/ oat_file)) {
...
return nullptr;
}
ScopedUtfChars class_name(env, javaName);
...
const std::string descriptor(DotToDescriptor(class_name.c_str()));
const size_t hash(ComputeModifiedUtf8Hash(descriptor.c_str()));
for (auto& dex_file : dex_files) {
...
ClassLinker* class_linker = Runtime::Current()->GetClassLinker();
ObjPtr<mirror::Class> result = class_linker->DefineClass(soa.Self(),
descriptor.c_str(),
hash,
class_loader,
*dex_file,
*dex_class_def);
// Add the used dex file. This only required for the DexFile.loadClass API since normal
// class loaders already keep their dex files live.
class_linker->InsertDexFileInToClassLoader(soa.Decode<mirror::Object>(dexFile),
class_loader.Get());
....
return soa.AddLocalReference<jclass>(result);
}
}
...
return nullptr;
}
通过Runtime拿到当前的ClassLinker对象,然后通过class_linker->DefineClass()在当前dex中进行查找类。然后把找到的类通过class_linker->InsertDexFileInToClassLoader()插入到class_table中进行缓存,返回查找到的类。这里不进一步展开分析。
Android ClassLoader加载过程的源代码分析到此已经分析的差不多了,如果想深入的了解具体原理,可以自己看源代码的实现。 这里就介绍到这里。初次写技术分享的文章,如有错误请指正,感谢!
<br>
(360技术原创内容,转载请务必保留文末二维码,谢谢~)
![]()
关于360技术
360技术是360技术团队打造的技术分享公众号,每天推送技术干货内容
更多技术信息欢迎关注“360技术”微信公众号