版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请标明出处。 https://blog.csdn.net/chaoyu168/article/details/72026841
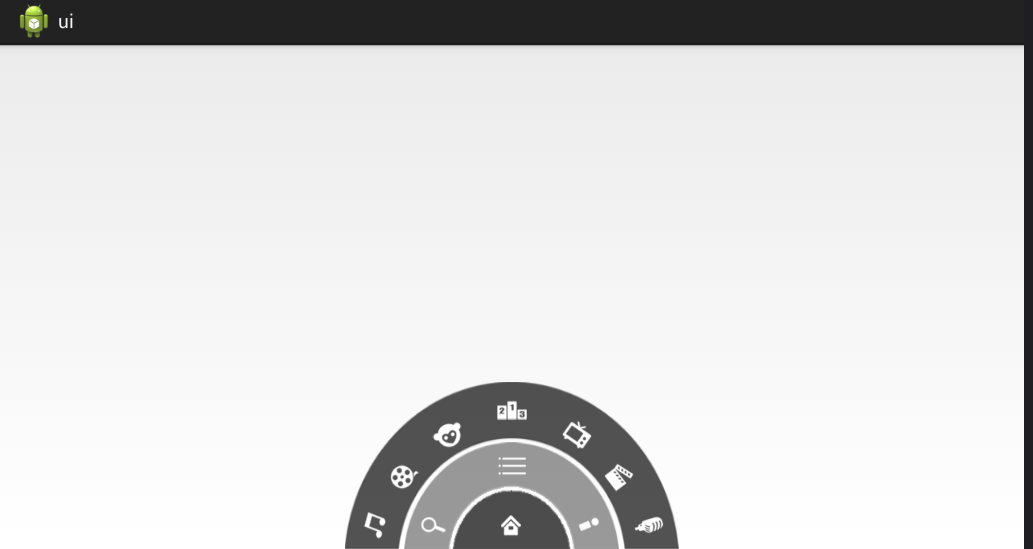
通过对系统提供的控件进行组合,不用写新的类不用继承系统的控件也能实现自定义控件的效果。下面是一个简单的例子:
效果图:
![]()
主函数:
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private String tag = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private ImageView iv_home,iv_menu;
private RelativeLayout level1,level2,level3;
private boolean isShowLevel2 = true;//是否显示2级菜单
private boolean isShowLevel3 = true;//是否显示3级菜单
private boolean isShowMenu = true;//是否显示整个菜单,包括1级,2级,3级的菜单
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
initView();
initListener();
}
private void initView() {
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
iv_home = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv_home);
iv_menu = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv_menu);
level1 = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.level1);
level2 = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.level2);
level3 = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.level3);
}
private void initListener() {
iv_home.setOnClickListener(this);
iv_menu.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if(keyCode==KeyEvent.KEYCODE_MENU){
if(isShowMenu){
//需要关闭所有菜单
int startOffset = 0;
if(isShowLevel3){
AnimUtil.closeMenu(level3, startOffset);
isShowLevel3 = false;
startOffset += 200;
}
if(isShowLevel2){
AnimUtil.closeMenu(level2, startOffset);
isShowLevel2 = false;
startOffset += 200;
}
AnimUtil.closeMenu(level1, startOffset);
}else {
//需要显示所有菜单
AnimUtil.showMenu(level1,0);
AnimUtil.showMenu(level2,200);
isShowLevel2 = true;
AnimUtil.showMenu(level3,400);
isShowLevel3 = true;
}
isShowMenu = !isShowMenu;
return true;
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.iv_home:
if(AnimUtil.animCount!=0){
//说明有动画在执行
return;
}
if(isShowLevel2){
//需要隐藏
int startOffset = 0;
if(isShowLevel3){
AnimUtil.closeMenu(level3,startOffset);
startOffset += 200;
isShowLevel3 = false;
}
AnimUtil.closeMenu(level2,startOffset);
}else{
//需要显示
// Log.e(tag, "执行显示操作");
AnimUtil.showMenu(level2,0);
}
isShowLevel2 = !isShowLevel2;
break;
case R.id.iv_menu:
if(AnimUtil.animCount!=0){
//说明有动画在执行
return;
}
if(isShowLevel3){
//隐藏3级菜单
AnimUtil.closeMenu(level3,0);
}else {
//显示3级菜单
AnimUtil.showMenu(level3,0);
}
isShowLevel3 = !isShowLevel3;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.Animation.AnimationListener;
import android.view.animation.RotateAnimation;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
public class AnimUtil {
public static int animCount = 0;//记录当前执行的动画数量
public static void closeMenu(RelativeLayout rl,int startOffset){
for (int i = 0; i < rl.getChildCount(); i++) {
rl.getChildAt(i).setEnabled(false);
}
//pivotXValue: 0-1
RotateAnimation animation = new RotateAnimation(0, -180,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 1);
animation.setDuration(500);
animation.setFillAfter(true);//动画结束后保持当时的状态
animation.setStartOffset(startOffset);
animation.setAnimationListener(new MyAnimationListener());
rl.startAnimation(animation);
}
public static void showMenu(RelativeLayout rl,int startOffset){
for (int i = 0; i < rl.getChildCount(); i++) {
rl.getChildAt(i).setEnabled(true);
}
RotateAnimation animation = new RotateAnimation(-180, 0,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f,
RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 1);
animation.setDuration(500);
animation.setFillAfter(true);//动画结束后保持当时的状态
animation.setStartOffset(startOffset);
animation.setAnimationListener(new MyAnimationListener());
rl.startAnimation(animation);
}
static class MyAnimationListener implements AnimationListener{
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {
animCount++;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
animCount--;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {
}
}
}
布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<!-- 一级菜单 -->
<RelativeLayout android:layout_width="100dp"
android:background="@drawable/level1"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:id="@+id/level1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_height="50dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:id="@+id/iv_home"
android:background="@drawable/icon_home"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<!-- 二级菜单 -->
<RelativeLayout android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="90dp"
android:id="@+id/level2"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:background="@drawable/level2">
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:background="@drawable/icon_search"/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:background="@drawable/icon_myyouku"/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:id="@+id/iv_menu"
android:background="@drawable/icon_menu"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<RelativeLayout android:layout_width="280dp"
android:layout_height="142dp"
android:id="@+id/level3"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:background="@drawable/level3">
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="15dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="12dp"
android:background="@drawable/channel1"
/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="15dp"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_marginRight="12dp"
android:background="@drawable/channel5"
/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="55dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="32dp"
android:background="@drawable/channel2"
/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="55dp"
android:layout_marginRight="32dp"
android:background="@drawable/channel6"
/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="85dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="62dp"
android:background="@drawable/channel3"
/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="85dp"
android:background="@drawable/channel7"
android:layout_marginRight="62dp"
/>
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:background="@drawable/channel4"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>