本文由庄汇晔同学编写~
在 Angular 项目中,经常会使用到 observable subscribe,但是 subscribe 读取了数据之后,真的就是万事大吉了吗?这个问题的答案或许是,或许不是。有些 observable 需要 unsubscribe,而有些并不用。在接下来的文章里,我会介绍:
- observable 的种类:何种 observable 需要 unsubscribe,以及没有 unsubscribe 会造成什么样的问题。
- 在 angular 项目中,可能会遇到的observable 的场景,以及他们是否需要 unsubscribe,为什么需要/不需要?
- unsubscribe 的方法。
一、observable 的种类:何种 observable 需要 unsubscribe,以及没有unsubscribe 会造成什么样的问题。
从 observable 能否结束(complete)的角度来看,observable 分为两类:finite observable(有限事件流)和 infinite observable(无限事件流)。区分他们的方法很简单:即 finite observable 只能 emit 一个值(或是一个错误),随即结束。而 infinite observable 会 emit 多个值,而不会结束。
finite Observable 的例子有:http client request,infinite Observable 的例子有:DOM eventListener。如果不取消订阅,将会出现内存泄漏,执行意料之外回调函数的问题。所以,一定需要 unsubscribe 的是 infinite observable(无限事件流),而 finite observable(有限事件流)一般不需要 unsubscribe。
二、在 angular 项目中,可能会遇到的 subscribe 的场景,他们需要 unsubscribe 吗?为什么需要/不需要?
1、Http Client 请求(this.httpClient.get(...).subscribe)
fetchFromBackend() {
let subscription$ = this.http.get(`http://example.com`).subscribe(...)
}
是否需要 unsubscribe:视情况而定。
原因:http client 为有限事件流,当 Observable complete 后,angular 会自动关闭 Observable。由于 unsubscribe http client request 并不意味着取消请求,而是取消了返回数据后的回调函数,所以需要根据场合来取消 subscription。如果在回调函数中,如果有会造成内存泄漏的代码,则严格意义上来说,应该需要 unsubscribe
更多详情请移步阅读:https://medium.com/angular-in-depth/why-you-have-to-unsubscribe-from-observable-92502d5639d0
2、Component 之间传递信息使用的 Behavior subject
// in service file
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'any',
})
export class MyComponentService {
public dataSource = new BehaviorSubject < any > (null);
....
}
// in component data boardcaster
this.myComponentService.dataSource.next(...)
// in component data subscriber
this.myComponentService.dataSource.subscribe(...)
是否需要 unsubscribe:需要。
原因:这种为无限事件流,无法预期它的回调函数会造成什么样的问题,所以需要 unsubscribe
3、Form control,响应式表单的变化监听(例如:this.form.valueChanges.subscribe)
initForm() {
this.form = new FormGroup({ ...});
this.valueChanges = this.form.valueChanges.subscribe(...);
}
是否需要 unsubscribe:需要。
原因:这种为无限事件流,虽然 component unmount 后,form 也不存在,但是这样会造成内存泄漏,导致性能下降等问题。
4、Dom 中的 fromEvent 事件监听(例如:Observable.fromEvent(this.element.nativeElement, 'click').subscribe)
@ViewChild('myElement', { static: false })
myElement: ElementRef;
constructor(private element : ElementRef) { }
click: Subscription;
ngOnInit() {
this.click = Observable.fromEvent(this.myElement.nativeElement, 'click').subscribe(...);
}
是否需要 unsubscribe:需要。
原因:这种为无限事件流,虽然 component unmount 后,dom element 不存在,但是这样会造成内存泄漏,导致性能下降等问题。
5、router 变化事件(例如:this.route.queryParams.subscribe)
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute, private router: Router) {
this.route.params.subscribe(console.log);
this.route.queryParams.subscribe(console.log);
this.route.fragment.subscribe(console.log);
this.route.data.subscribe(console.log);
this.route.url.subscribe(console.log);
this.router.events.subscribe(console.log);
}
是否需要 unsubscribe:需要。
原因:这种为无限事件流,如果不 unsubscribe,会运行错误的回调函数,造成不可控的问题
三、unsubscribe 的方法
1,使用 rxjs takeUntil,takeWhile,take(n),first operator:
简介:rxjs take 系列的 operator 可以限定取得 Observable emit 的次数或者时机,当次数或时机不符合时,Observable 就会走向完成状态。所以,在 angular 项目中,可以灵活利用组件的生命周期函数,使得组件需要 unsubscribe 的 Observable 在组件销毁时,自动完成。first operator 则和 take(1)类似,是只取得第一个 emit 值,随后完成。
takeUntil(notifier: ObservableInput)会一直监听他的数据源,直到 notifier Observable emit 一个值
import { Subject, takeUntil } from 'rxjs';
export class Foo implements OnInit {
private destroy$ = new Subject();
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.auth.fireAuthUser$
.pipe(takeUntil(this.destroy$))
.subscribe({
next: (data) => console.log(data),
complete: () => this.uponComplete(),
});
}
uponComplete() {
console.log('Finally completed');
}
ngOnDestroy() {
this.destroy$.next(true);
this.destroy$.complete();
}
}
与 takeUnitl 类似,只是 takeUnitl 的参数是一个判断函数,而 takeWhile 的参数是一个 Observable export class ViewRouteComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy { alive: boolean = true
constructor(private titleService: TitleService) {
ngOnInit() {
this.titleService.emitter1$
.pipe(takeWhile(() => this.alive))
.subscribe((data: any) => { /_ ... do something 1 _/ })
}
ngOnDestroy() {
this.alive = false
}
}
在取得 n 次 emit 之后,Observable 会自动完成
@Component({
...
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
subscription$
ngOnInit() {
let observable$ = Rx.Observable.interval(1000);
this.subscription$ = observable$.pipe(take(1)).
subscribe(x => console.log(x))
}
}
在取得第一次 emit 后,Observable 自动完成
@Component({
...
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
subscription$
ngOnInit() {
let observable$ = Rx.Observable.interval(1000);
this.subscription$ = observable$.pipe(first()).
subscribe(x => console.log(x))
}
}
2,使用 unsubscribe 方法
使用 unsubscribe 方法是非常直观的一种方式,只需在 angular 组件的 ngOnDesrtoy 中调用即可。
这里的例子使用了一个 subscription array,在 ngOnDestroy 中 unsubscribe
export class AppComponent implements OnInit, OnDestroy {
subscription1$: Subscription
subscription2$: Subscription
subscriptions: Subscription[] = []
ngOnInit() {
var observable1$ = Rx.Observable.interval(1000);
var observable2$ = Rx.Observable.interval(400);
this.subscription1$ = observable1$.subscribe(x =>
console.log("From interval 1000", x)
);
this.subscription2$ = observable2$.subscribe(x =>
console.log("From interval 400", x)
);
this.subscriptions.push(this.subscription1$);
this.subscriptions.push(this.subscription2$);
}
ngOnDestroy() {
this.subscriptions.forEach((subscription) =>
subscription.unsubscribe()
);
}
}
3,使用 async pipe
官方文档:https://angular.io/api/common/AsyncPipe
使用这种方式可以无需手动 unsubscribe,也不用担心内存泄漏的问题。但是它的局限性也在于,它只能被使用在模版(template)中。请考虑如下场景:在用户点击按钮后,需要提交一个表单。此时,使用 async pipe 则变得不怎么合适了。
@Component({
selector: 'async-observable-pipe',
template: '<div><code>observable|async</code>: Time: {{ time | async }}</div>'
})
export class AsyncObservablePipeComponent {
time = new Observable < string > ((observer: Observer<string>) => {
setInterval(() => observer.next(new Date().toString()), 1000);
});
}
补充:如何查看组件销毁后,是否存在 unsubscribe 的 subscription?
方法 1:从静态代码检查中规避
使用 eslint 工具,配置 rxjs-no-ignored-subscription 规则:https://github.com/cartant/eslint-plugin-rxjs/blob/main/docs/rules/no-ignored-subscription.md
方法 2:使用堆快照查看内存泄漏
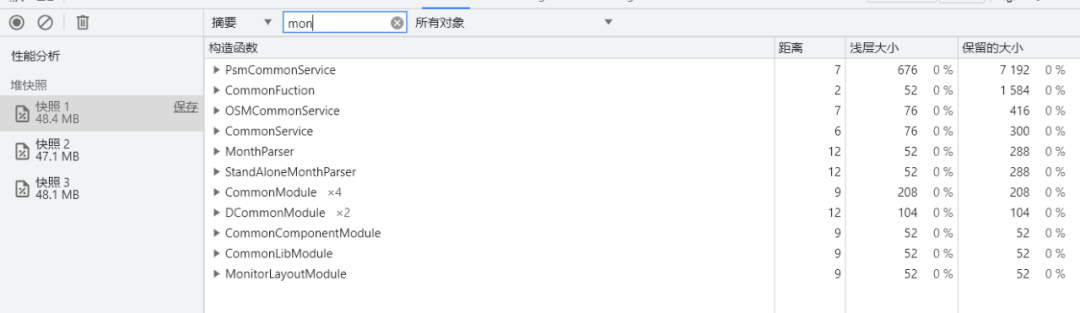
例子中想要查看内存泄漏的组件是 MonthlyReportComponent,此时使用开发者工具,在加载组件前使用快照功能,并搜索组件名称,是看不到内存泄漏的
![]()
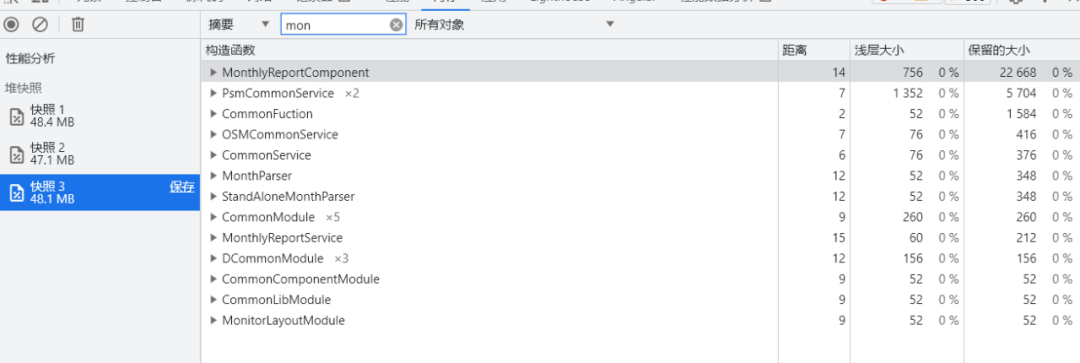
在组件加载后,unmount,再次捕捉快照,再次搜索组件名称,查看堆快照:
![]()
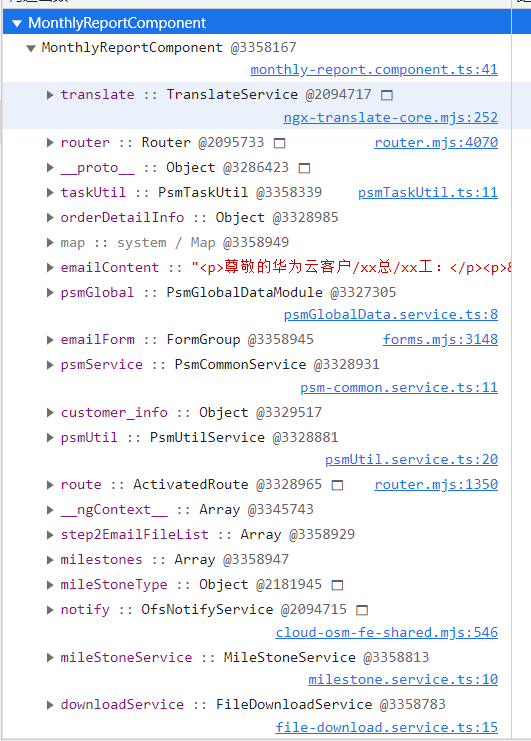
查看里面是否有 BehaviorSubject,Observable 等未取消订阅的对象
![]()
参考文档:
http client:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35042929/is-it-necessary-to-unsubscribe-from-observables-created-by-http-methods
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38008334/angular-rxjs-when-should-i-unsubscribe-from-subscription
https://medium.com/angular-in-depth/why-you-have-to-unsubscribe-from-observable-92502d5639d0
如何 unsubscribe:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41364078/angular-2-does-subscribing-to-formcontrols-valuechanges-need-an-unsubscribe
https://blog.bitsrc.io/6-ways-to-unsubscribe-from-observables-in-angular-ab912819a78f
https://benlesh.medium.com/rxjs-dont-unsubscribe-6753ed4fda87
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/69333761/angular-12-rxjs-safe-to-use-takewhile-without-ondestroy
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38008334/angular-rxjs-when-should-i-unsubscribe-from-subscription
如何查看存在 unsubscribe:
https://itnext.io/angular-rxjs-detecting-memory-leaks-bdd312a070a0
关于 OpenTiny
![]()
OpenTiny 是一套企业级 Web 前端开发解决方案,提供跨端、跨框架、跨版本的 TinyVue 组件库,包含基于 Angular+TypeScript 的 TinyNG 组件库,拥有灵活扩展的低代码引擎 TinyEngine,具备主题配置系统TinyTheme / 中后台模板 TinyPro/ TinyCLI 命令行等丰富的效率提升工具,可帮助开发者高效开发 Web 应用。
欢迎加入 OpenTiny 开源社区。添加微信小助手:opentiny-official 一起参与交流前端技术~更多视频内容也可关注B站、抖音、小红书、视频号
OpenTiny 也在持续招募贡献者,欢迎一起共建
OpenTiny 官网:https://opentiny.design/
OpenTiny 代码仓库:https://github.com/opentiny/
TinyVue 源码:https://github.com/opentiny/tiny-vue
TinyEngine 源码: https://github.com/opentiny/tiny-engine
欢迎进入代码仓库 Star🌟TinyEngine、TinyVue、TinyNG、TinyCLI~ 如果你也想要共建,可以进入代码仓库,找到 good first issue标签,一起参与开源贡献~